Spring Boot集成Redisson实现延迟队列
目录
- 项目场景:
- 解决方案:
- 1.集成Redisson
- 2.配置多线程
- 3.具体业务
- 4.延迟队列(关键代码)
- 5.测试接口
- 6.测试结果
- 总结:
项目场景:
在电商、支付等领域,往往会有这样的场景,用户下单后放弃支付了,那这笔订单会在指定的时间段后进行关闭操作,细心的你一定发现了像某宝、某东都有这样的逻辑,而且时间很准确,误差在1s内;那他们是怎么实现的呢?
一般实现的方法有几种:使用 redisson、rocketmq、rabbitmq等消息队列的延时投递功能。
解决方案:
一般项目集成redis的比较多,所以我这篇文章就说下redisson延迟队列,如果使用rocketmq或rabbitmq需要额外集成中间件,比较麻烦一点。
1.集成redisson
maven依赖xHSTEh
<dependency> <groupId>org.redisson</groupId> <artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.21.1</version> </dependency>
yml配置,单节点配置可以兼容redis的配置方式
# redis配置
spring:
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
password: redis@pass
port: 6001
更详细的配置参考:Spring Boot整合Redisson的两种方式
2.配置多线程
因为延迟队列可能会多个任务同时执行,所以需要多线程处理。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import owww.devze.comrg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import Java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class ExecutorConfig {
/**
* 异步任务自定义线程池
*/
@Bean(name = "taskExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncServiceExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//配置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(50);
//配置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(500);
//配置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(300);
//允许线程空闲时间
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
//配置线程池中的线程的名称前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("taskExecutor-");
// rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务
// CALLER_RUNS:不在新线程中执行任务,而是有调用者所在的线程来执行
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//调用shutdown()方法时等待所有的任务完成后再关闭
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
//等待所有任务完成后的最大等待时间
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
return executor;
}
}
3.具体业务
比如消息通知、关闭订单等 ,这里加上了@Async注解,可以异步执行
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Async
public void executeQueue(Object value) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("执行任务:"+value);
//打印时间方便查看
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("执行任务的时间:"+sdf.format(new Date()));
//自己的业务逻辑,可以根据id发送通知消息等
//......
}
}
4.延迟队列(关键代码)
这里包括添加延迟队列,和消费延迟队列,@PostConstruct注解的意思是服务启动加载一次,参考
Spring Boot项目启动时执行指定的方法
Spring Boot中多个PostConstruct注解执行顺序控制
import org.redisson.api.RblockingQueue;
import org.redisson.api.RDelayedQueue;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springfra编程客栈mework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
private AsyncService asyncService;
@Resource
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* 添加延迟任务
*/
public void addQueue() {
//获取延迟队列
RBlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = redissonClient.getBlockingQueue("delayedQueue");
RDelayedQueue<Object> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getDelayedQueue(blockingQueue);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
long delayTime = 5+i; //延迟时间(秒)
// long delayTime = 5; //这里时间统一,可以测试并发执行
delayedQueue.offer("延迟任务"+i, delayTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
//打印时间方便查看
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("添加任务的时间:"+sdf.format(new Date()));
}
/**
* 服务启动时加载,开始消费延迟队列
*/
@PostConstruct
public void consumer() {
System.out.println("服务启动时加载>>>>>>");
//获取延迟队列
RBlockingQueue<Object> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getBlockingQueue("delayedQueue");
//启用一个线程来消费这个延迟队列
executor.execute(() ->{
while (true){
try {
// System.out.println("while中的线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
//获取延迟队列中的任务
Object value = delayedQueue.poll();
if(value == null){
//如果没有任务就休眠1秒,休眠时间根据业务自己定义
Thread.sleep(1000); //这里休眠时间越短,误差就越小
continue;
}
//异步处理延迟队列中的消息
asyncService.executeQueue(value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
5.测试接口
import com.test.service.TestService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestControlle编程客栈r {
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
/*
* 添加延迟任务
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/addQueue")
public String addQueue() {
testService.addQueue();
return "success";
}
}
6.测试结果
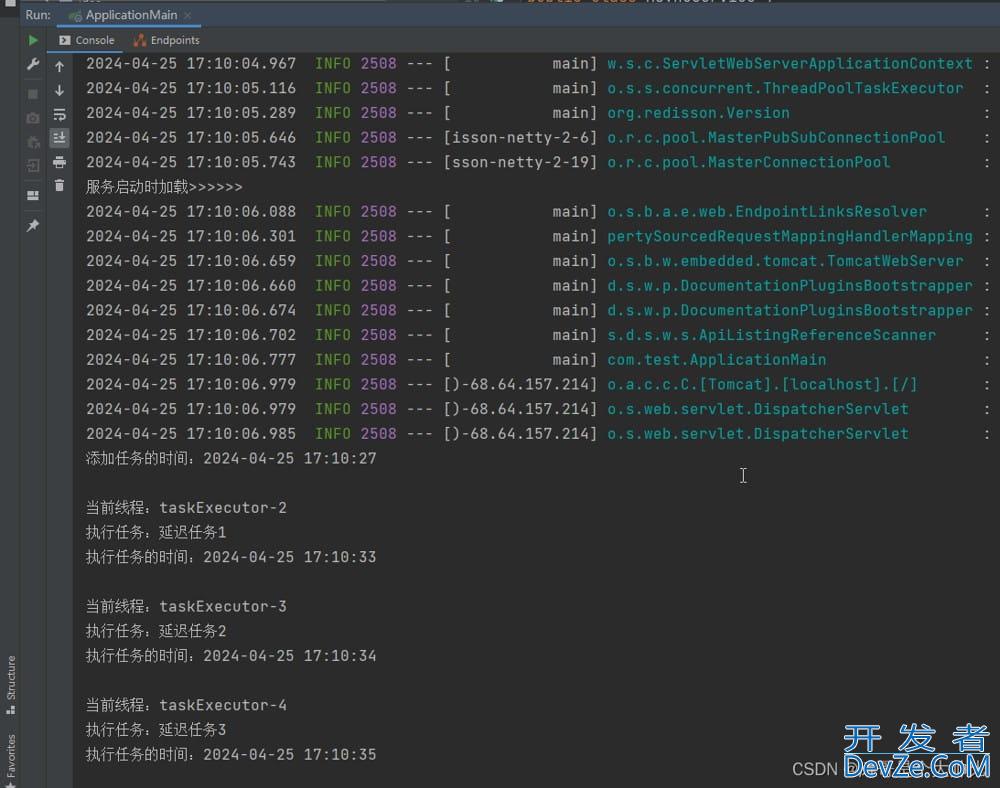
总结:
- Redisson的的RDelayedQueue是基于Redis实现的,而Redis本身并不保证数据的持久性。如果Redis服务器宕机,那么所有在RDelayedQueue中的数据都会丢失。因此,我们需要在应用层面进行持久化设计,例如定期将RDelayedQueue中的数据持久化到数据库。
- 在设计延迟任务时,我们应该根据实际需求来合理设置延迟时间,避免设置过长的延迟时间导致内存占用过高。
到此这篇关于Spring Boot集成Redisson实现延迟队列的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot Redisson延迟队列内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编编程程客栈(www.devze.com)!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论