springboot+dubbo实现时间轮算法
目录
- 前言
- 一、参数说明
- 二、具体实现
- 1、HashedwheelTimer
- 2、createWheel
- 3、newTimeout
- 4、start
- 5、run
- 6、waitForNextTick
- 7、transferTimeoutsToBuckets
- 8、expireTimeouts
- 总结
前言
时间轮(TimingWheel)是一种高效利用线程资源进行批量化调度的算法,广泛应用于各种操作系统的定时任务调度中,如linux的crontab,以及Java开发中常用的Dubbo、Netty、Kafka等框架。时间轮的核心思想是将时间划分为若干个时间间隔(bucket),每个时间间隔代表一个时间段,并通过一个循环的数据结构(类似于时钟)来管理这些时间间隔。
文章基于3.1.0版本进行分析
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
一、参数说明
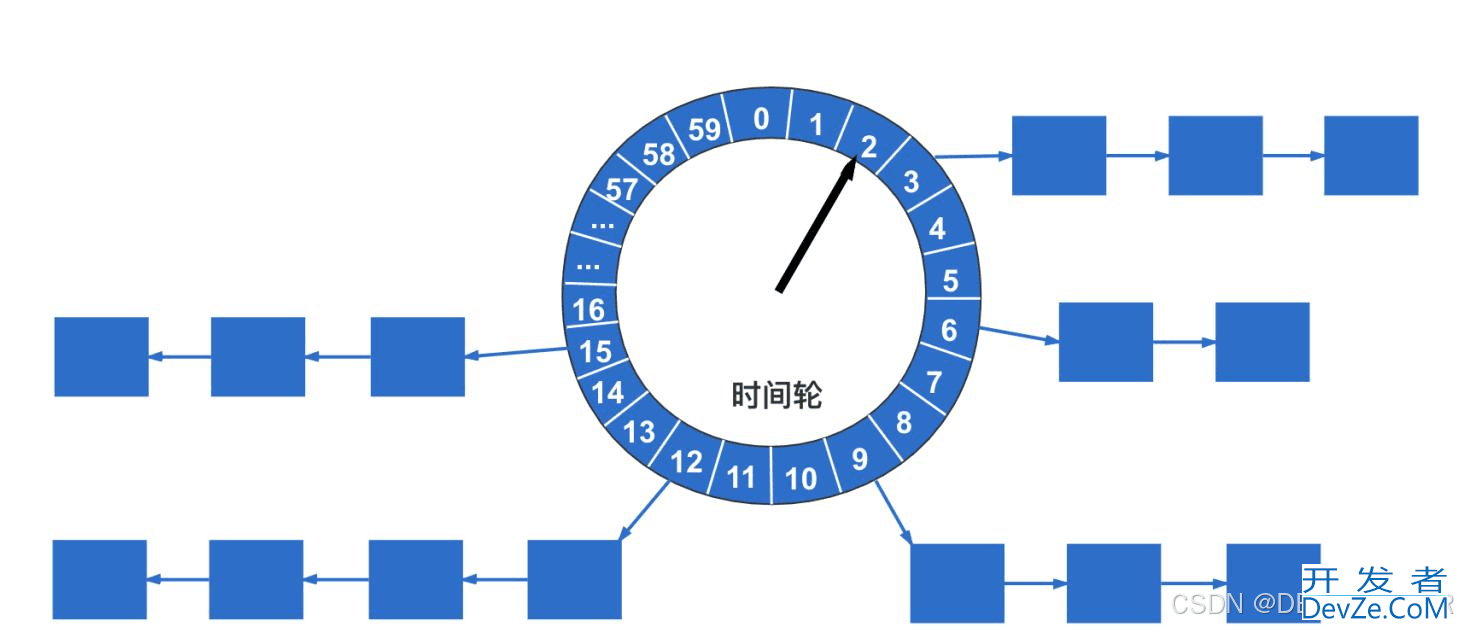
- tickDuration:表示一个槽所代表的时间范围 默认100ms
- ticksPerWheel:表示该时间轮有多少个槽 默认512
- startTime:表示该时间轮的开始时间
- interval:时间轮所能表示的时间android跨度,也就是 tickDuration * ticksPerWheel
- currentTime:表示当前时间,也就是时间轮指针指向的时间
- wheel:表示TimerTaskList的数组,即各个槽,每个bucket都是一个 HashedWheelBucket 。
- HashedWheelBucket:存储TimerTaskEntry的双向链表
- HashedWheelTimeout:延迟任务,有两个值 deadline 和 remainingRounds
- deadline:TimerTask 最后的执行时间
- remainingRounds:剩余圈数
- timeouts:用来保存新增的HashedWheelTimeout,每次执行会拿出10W个放入HashedWheelBucket
二、具体实现
1、HashedWheelTimer
时间轮实现类
public HashedWheelTimer(
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
long tickDuration, TimeUnit unit, int ticksPerWheel,
long maxPendingTimeouts) {
// 检查参数
if (threadFactory == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("threadFactory");
}
if (unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("unit");
}
if (tickDurphpation <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("tickDuration must be greater than 0: " + tickDuration);
}
if (ticksPerWheel <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ticksPerWheel must be greater than 0: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
// Normalize ticksPerWheel to power of two and initialize the wheel.
// 创建时间轮
wheel = createWheel(ticksPerWheel);
// 位运算标识
// 因为一圈的长度为2的n次方,mask = 2^n-1后低位将全部是1,然后deadline& mast == deadline % wheel.length
// deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay) - startTime; TODO
mask = wheel.length - 1;
// Convert tickDuration to nanos.
// 时间轮的基本时间跨度,转成最小时间单位Nanos
this.tickDuration = unit.toNanos(tickDuration);
// Prevent overflow.
// 时间跨度限制不能太大,计算会有问题
if (this.tickDuration >= Long.MAX_VALUE / wheel.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"tickDuration: %d (expected: 0 < tickDuration in nanos < %d",
tickDuration, Long.MAX_VALUE / wheel.length));
}
// 创建时间轮工作线程
workerThread = threadFactory.newThread(worker);
this.maxPendingTimeouts = maxPendingTimeouts;
// 延迟任务太多的时间,警告日志
if (INSTANCE_COUNTER.incrementAndGet() > INSTANCE_COUNT_LIMIT &&
WARNED_TOO_MANY_INSTANCES.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
reportTooManyInstances();
}
}
参数说明:
- threadFactory线程工厂,创建时间轮线程
- tickDuration每一tick的时间
- timeUnittickDuration的时间单位
- ticksPerWheel就是轮子一共有多个格子,即要多少个tick才能走完这个wheel一圈。
2、createWheel
创建时间轮
private static HashedWheelBucket[] createWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
if (ticksPerWheel <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ticksPerWheel must be greater than 0: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
if (ticksPerWheel > 1073741824) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ticksPerWheel may not be greater than 2^30: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
// 如果不是2^n 则调整为2^n
ticksPerWheel = normalizeTicksPerWheel(ticksPerWheel);
// 初始化时间轮槽
HashedWheelBucket[] wheel = new HashedWheelBucket[ticksPerWheel];
for (int i = 0; i < wheel.length; i++) {
wheel[i] = new HashedWheelBucket();
}
return wheel;
}
3、newTimeout
添加新任务
public Timeout newTimeout(TimerTask task, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
if (unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("unit");
}
long pendingTimeoutsCount = pendingTimeouts.incrementAndGet();
// 如果任务大于最大量,则不允许继续添加
if (maxPendingTimeouts > 0 && pendingTimeoutsCount > maxPendingTimeouts) {
pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Number of pending timeouts ("
+ pendingTimeoutsCount + ") is greater than or equal to maximum allowed pending "
+ "timeouts (" + maxPendingTimeouts + ")");
}
// 启动时间轮工作线程
start();
// Add the timeout to the timeout queue which will be processed on the next tick.
// During processing all the queued HashedWheelTimeouts will be added to the correct HashedWheelBucket.
long deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay) - startTime;
// Guard against overflow.
// 如果为负数,那么说明超过了long的最大值
if (delay > 0 && deadline < 0) {
deadline = Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = new HashedWheelTimeout(this, task, deadline);
timeouts.add(timeout);
return timeout;
}
4、start
启动时间轮
public void start() {
switch (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(this)) {
// 如果是初始化 启动实践论
case WORKER_STATE_INIT:
// 保证只启动一次,原子性
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_INIT, WORKER_STATE_STARTED)) {
workerThread.start();
}
break;
// 已经启动过了
case WORKER_STATE_STARTED:
break;
// 时间轮停止了
case WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN:
throw new IllegalStateException("cannot be started once stopped");
default:
throw new Error("Invalid WorkerState");
}
// Wait until the startTime is initialized by the worker.
// 线程启动执行任务是异步的,这里是等待workerThread.start(),线程已经启动了
while (startTime == 0) {
try {
startTimeInitialized.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
// Ignore - it will be ready very soon.
}
}
}
5、run
workerThread.start()启动后,会执行Worker的run方法
public void run() {
// Initialize the startTime.
startTime = System.nanoTime();
if (startTime == 0) {
// We use 0 as an indicator for the uninitialized value here, so make sure it's not 0 when initialized.
startTime = 1;
}
// Notify the other threads waiting for the initialization at start().
// 唤醒被阻塞的start()方法。
startTimeInitialized.countDown();
do {
// 等下一个槽的到达时间,开始执行上一个槽的任务 TODO 不明白这里的设计,哪位大佬知道可以指点一下
final long deadline = waitForNextTick();
if (deadline >编程客栈; 0) {
// 计算时间轮的槽位
int idx = (int) (tick & mask);
// 移除取消的了task
processCancelledTasks();
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[idx];
// 将newTimeout()方法中加入到待处理定时任务队列中的任务加入到指定的格子中
transferTimeoutsToBuckets();
// 运行目前指针指向的槽中的bucket链表中的任务,执行到期的延时任务
bucket.expireTimeouts(deadline);
tick++;
}
}
// 如果Worker_State一只是started状态,就一直循环
while (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_STARTED);
// Fill the unprocessedTimeouts so we can return them from stop() method.
for (HashedWheelBucket bucket : wheel) {
// 清除时间轮中超时未处理的任务
bucket.clearTimeouts(unprocessedTimeouts);
}
for (; ; ) {
// 遍历任务队列,发现如果有任务被取消,则添加到unprocessedTimeouts,也就是不需要处理的队列中。
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
break;
}
if (!timeout.isCancelled()) {
unprocessedTimeouts.add(timeout);
}
}
// 再次移除取消的了task
processCancelledTasks();
}
6、waitForNextTick
一个钟表上的间隔是代表一个单位时间的间隔,那么waitForNextTick就是根据当前时间计算出跳动到下个时间的时间间隔,然后进行sleep,结束后进入下一个时间间隔,下一个间隔到来的时候返回。
/**
* 根据startTime和当前槽位计算目标nanoTime,
* 等待时间到达
*
* @return Long.MIN_VALUE if received a shutdown request,
* current time otherwise (with Long.MIN_VALUE changed by +1)
*/
private long waitForNextTick() {
// tick槽位,tickDuration表示每个时间格的跨度,所以deadline返回的是下一次时间轮指针跳动的时间
long deadline = tickDuration * (tick + 1);
for (; ; ) {
// 计算当前时间距离启动时间的时间间隔,期间休眠
final long currentTime = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
// 计算sleepTimeMs先加999999,应该是不足1ms的,补足1ms
long sleepTimeMs = (deadline - currentTime + 999999) / 1000000;
// sleepTimeMs小于零表示走到了下一个时间槽位置
if (sleepTimeMs <= 0) {
if (currentTime == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
return -Long.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
return currentTime;
}
}
// Windows 时间换算
if (isWindows()) {
sleepTimeMs = sleepTimeMs / 10 * 10;
}
try {
// 当前时间距离下一次tick时间还有一段距离,需要sleep
Thread.sleep(sleepTimeMs);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) {
return Long.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
}
}
7、transferTimeoutsToBuckets
转移任务到时间轮的具体槽中
// 将延时任务队列中等待添加到时间轮中的延时任务转移到时间轮的指定位置
private void transferTimeoutsToBuckets() {
// transfer only max. 100000 timeouts per tick to prevent a thread to stale the workerThread when it just
// adds new timeouts in a loop.
// 循环100000次,也就是每次转移10w个任务
// 为了防止这个操作销毁太多时间,导致更多的任务时间不准,因此一次最多操作10w个
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
// 从阻塞队列中获得具体的任务
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
// all processed
break;
}
if (timeout.state() == HashedWheelTimeout.ST_CANCELLED) {
// Was cancelled in the meantime.
continue;
}
编程
// 计算tick次数,deadline表示当前任务的延迟时间,tickDuration表示时间槽的间隔,两者相除就可以计算当前任务需要tick几次才能被执行
long calculated = timeout.deadline / tickDuration;
// 计算剩余的轮数, 只有 timer 走够轮数, 并且到达了 task 所在的 slot, task 才会过期.(被执行)
timeout.remainingRounds = (calculated - tick) / wheel.length;
// Ensure we don't schedule for past.
// 如果任务在timeouts队列里面放久了, 以至于已经过了执行时间, 这个时候就使用当前tick, 也就是放到当前bucket, 此方法调用完后就会被执行
final long ticks = Math.max(calculated, tick);
// 算出任务应该插入的 wheel 的 slot, stopIndex = tick 次数 & mask, mask = wheel.length - 1
int stopIndex = (int) (ticks & mask);
// 把timeout任务插入到指定的bucket链中。
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[stopIndex];
bucket.addTimeout(timeout);
}
}
8、expireTimeouts
当指针跳动到某一个时间槽中时,会就触发这个槽中的任务的执行。该功能是通过expireTimeouts来实现
void expireTimeouts(long deadline) {
// 双向链表
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = head;
// process all timeouts
// 遍历当前时间槽中的所有任务
while (timeout != null) {
HashedWheelTimeout next = timeout.next;
// 如果当前任务要被执行,那么remainingRounds应该小于或者等于0
if (timeout.remainingRounhttp://www.devze.comds <= 0) {
// 从bucket链表中移除当前timeout,并返回链表中下一个timeout
next = remove(timeout);
// 如果timeout的时间小于当前的时间,那么就调用expire执行task
if (timeout.deadline <= deadline) {
timeout.expire();
} else {
// The timeout was placed into a wrong slot. This should never happen.
// 不可能发生的情况,就是说round已经为0了,deadline却 > 当前槽的deadline
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"timeout.deadline (%d) > deadline (%d)", timeout.deadline, deadline));
}
} else if (timeout.isCancelled()) {
next = remove(timeout);
} else {
// 因为当前的槽位已经过了,说明已经走了一圈了,把轮数减一
timeout.remainingRounds--;
}
// 把指针放置到下一个timeout
timeout = next;
}
}
总结
时间轮(TimingWheel)在计算机科学中,特别是在任务调度和时间管理方面,具有重要的意义,我们可以结合业务进行使用
- 节省cpu资源
- 易于实现和维护
- 批量化调度模型
- 高效处理大量定时任务
- 灵活适应不同应用场景
到此这篇关于springboot+dubbo实现时间轮算法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot dubbo时间轮内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论