使用Spring注解@EventListener实现监听原理
目录
- @EventListener使用方式
- @EventListener实现原理
- 1.引入时机-获取bean定义
- 2.实例化时机-new对象
- 3.作用时机->将加了EventListener注解的方法识别出来
- 总结
@EventListener使用方式
package com.cyl.listener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.PayloadApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CylOrderSecListener {
@EventListener
public void listen(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.outrdHKzl.println(event);
}
}
@EventListener实现原理
主要通过EventListenerMethodProcessor和DefaultEventListenerFactory这两个类实现。
- EventListenerMethodProcessor的作用是识别所有使用eventListener注解的方法
- DefaultEventListenerFactory将EventListenerMethodProcessor识别出的方法封装成为监听器类
以代码new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext为入口调试代码去讲解EventListenerMethodProcessor和DefaultEventListenerFactory如何去生效的
package com.cyl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AppConfig.class);
context.refresh();
}
}
1.引入时机-获取bean定义
EventListenerMethodProcessor和DefaultEventListenerFactory的bean定义信息在容器初始化最开始阶段,DefaultListableBeanFactory实例化后,被注册到DefaultListableBeanFactory的beanDefinitionMap中。
执行new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,会优先执行父类 GenericApplicationContex构造方法,实例化一个bean工厂
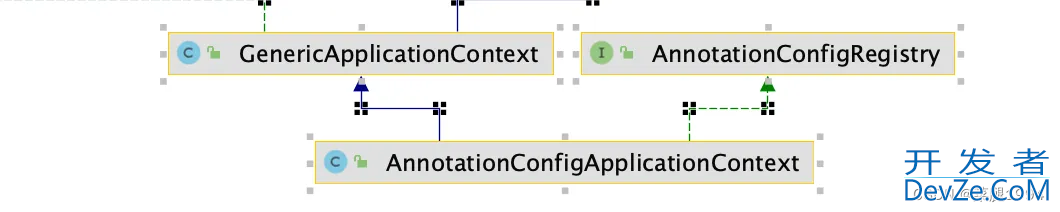

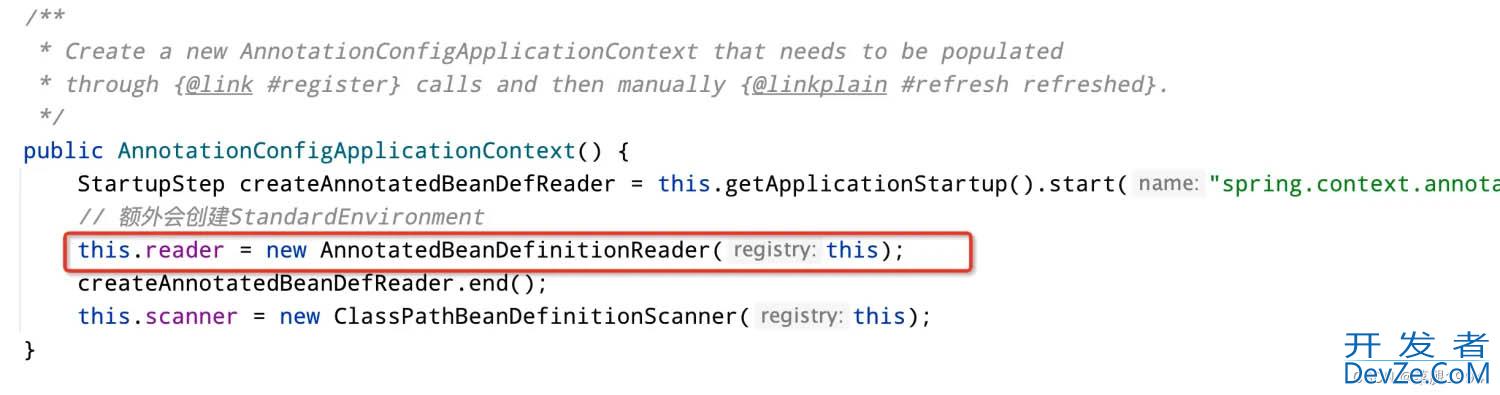
GenericApplicationContext执行完后,会实例化AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,可以理解为容器内一个bean定义阅读器,负责将bean定义注册到bean工厂中。
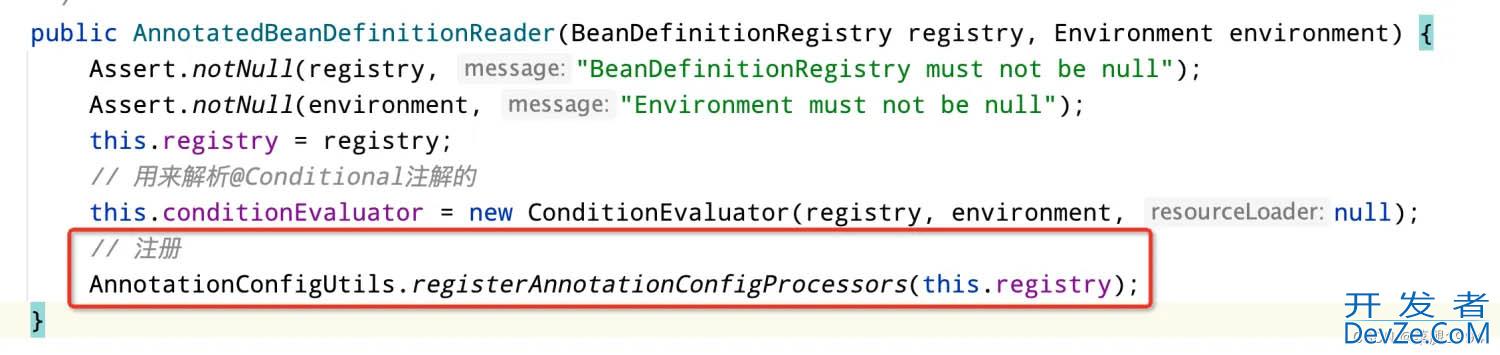
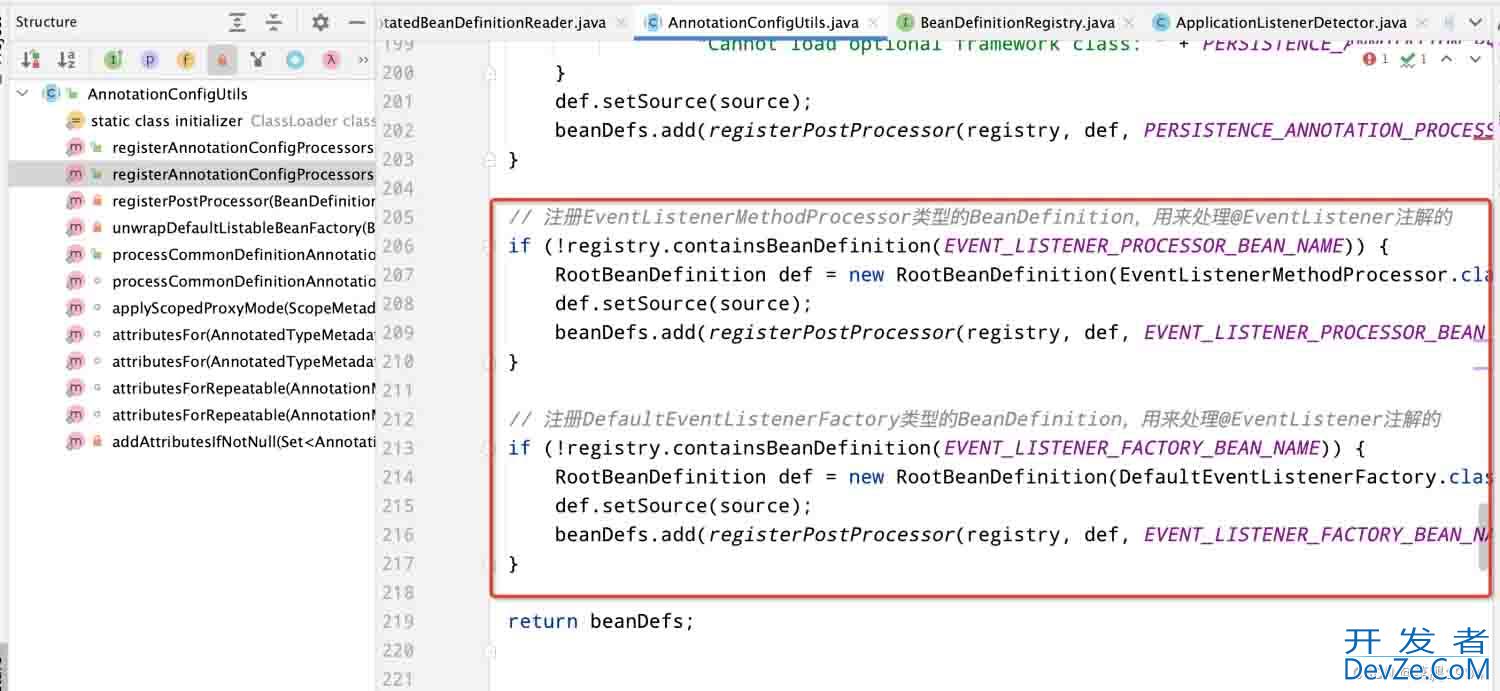
实例化AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader会注册一些bean定义到bean工厂中,其中就包括了EventListenerMethodProcessor和DefaultEventListenerFactory。
2.实例化时机-new对象
只引入了bean定义,还未真正对bean进行实例化,实例化步骤是在spring执行refresh时
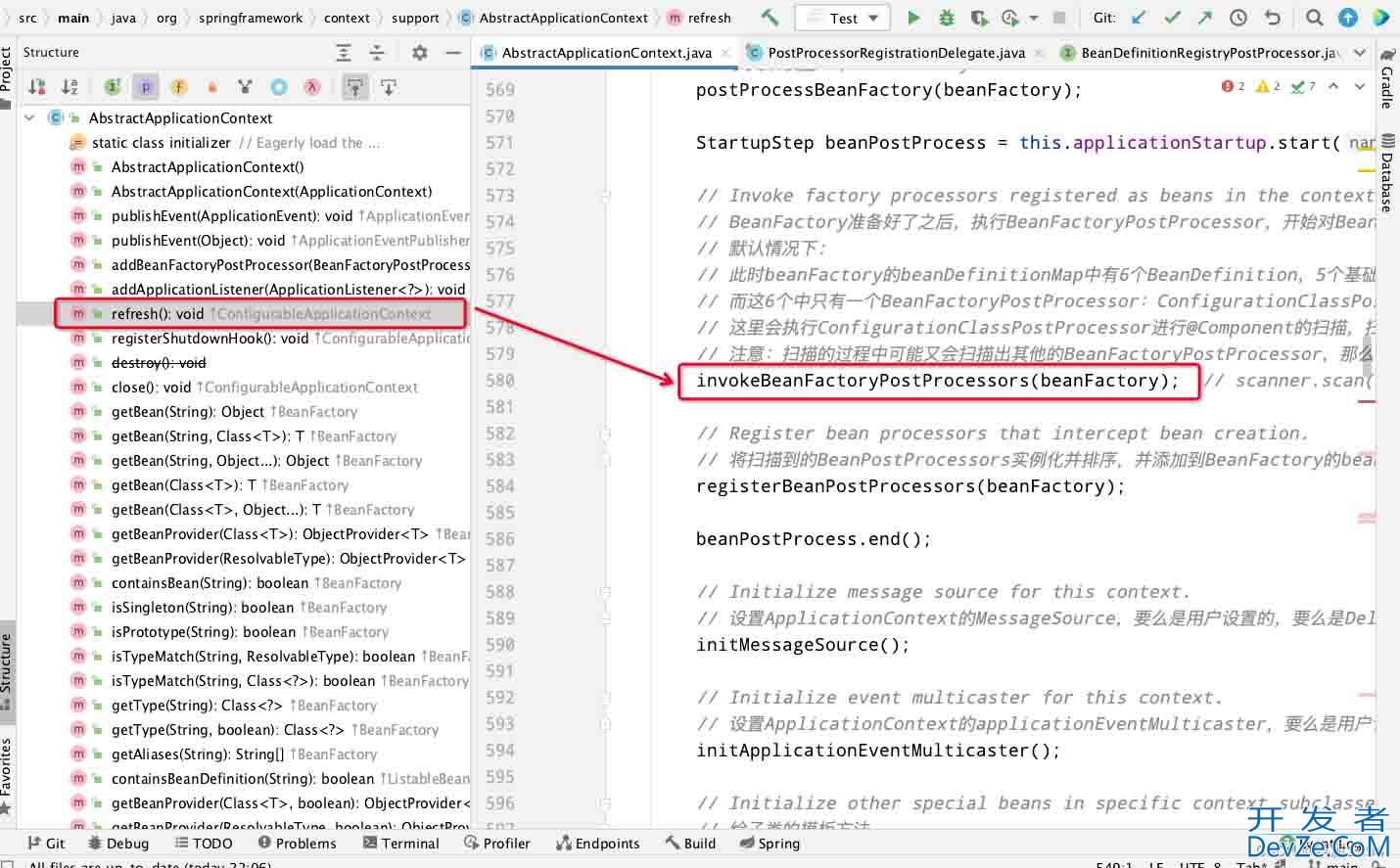
走到方法内,会调用
org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, Java.util.List<org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor>)
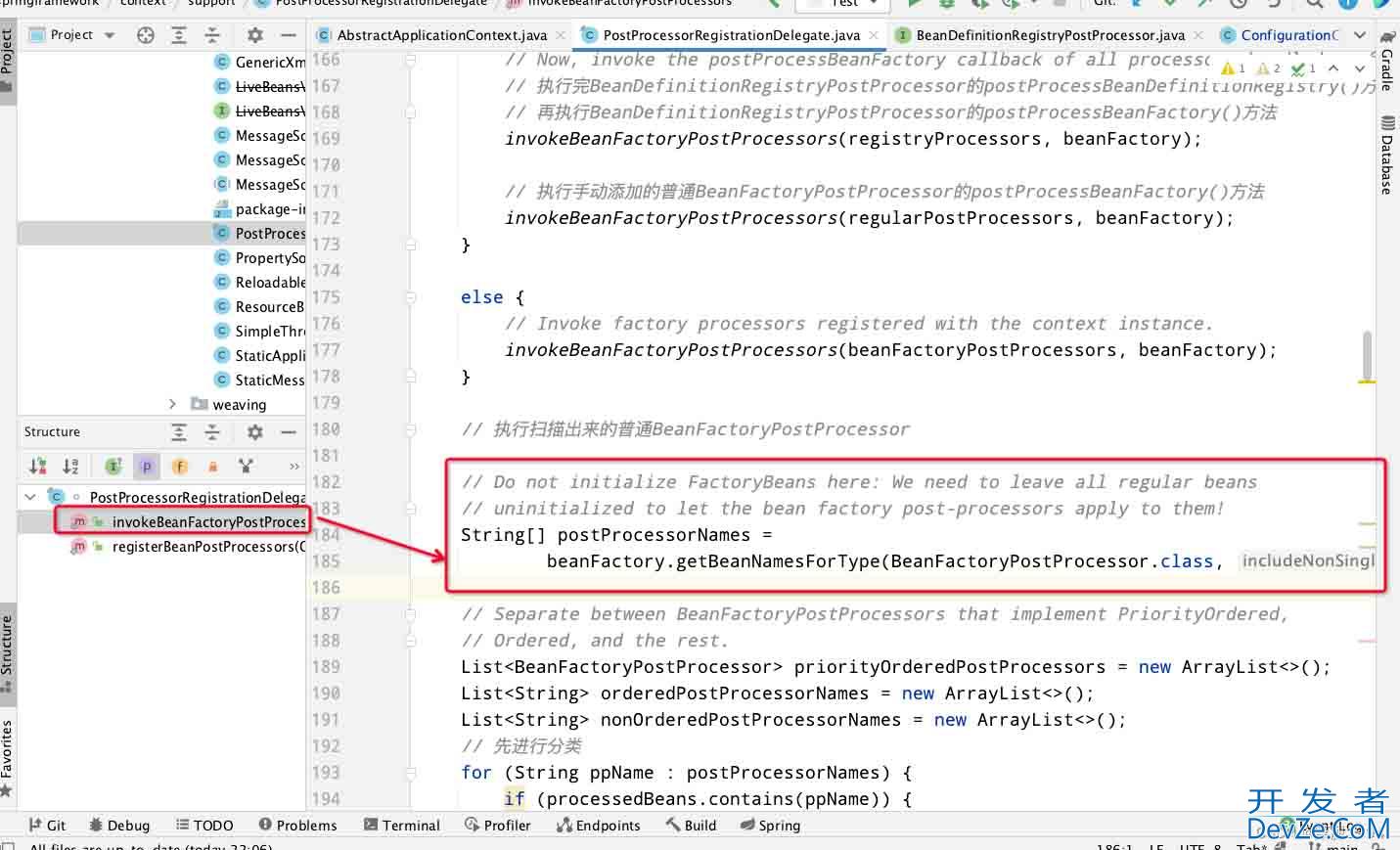
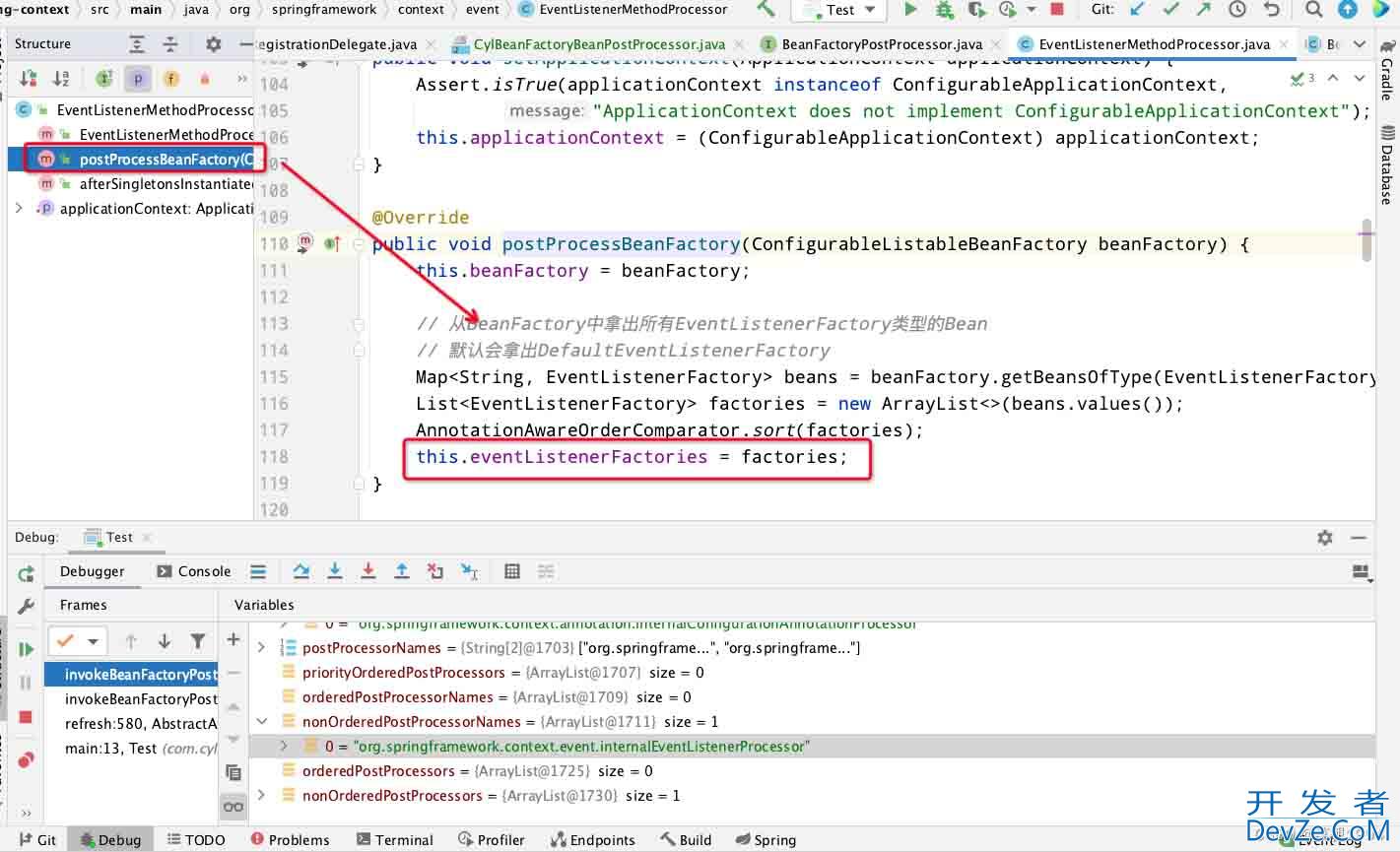
关注代码184行,获取普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor类,而EventListenerMethodProcessor实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,此处打断点也会获取该类名
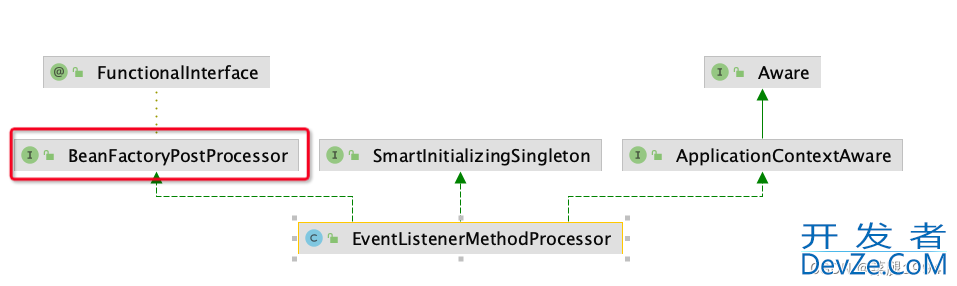
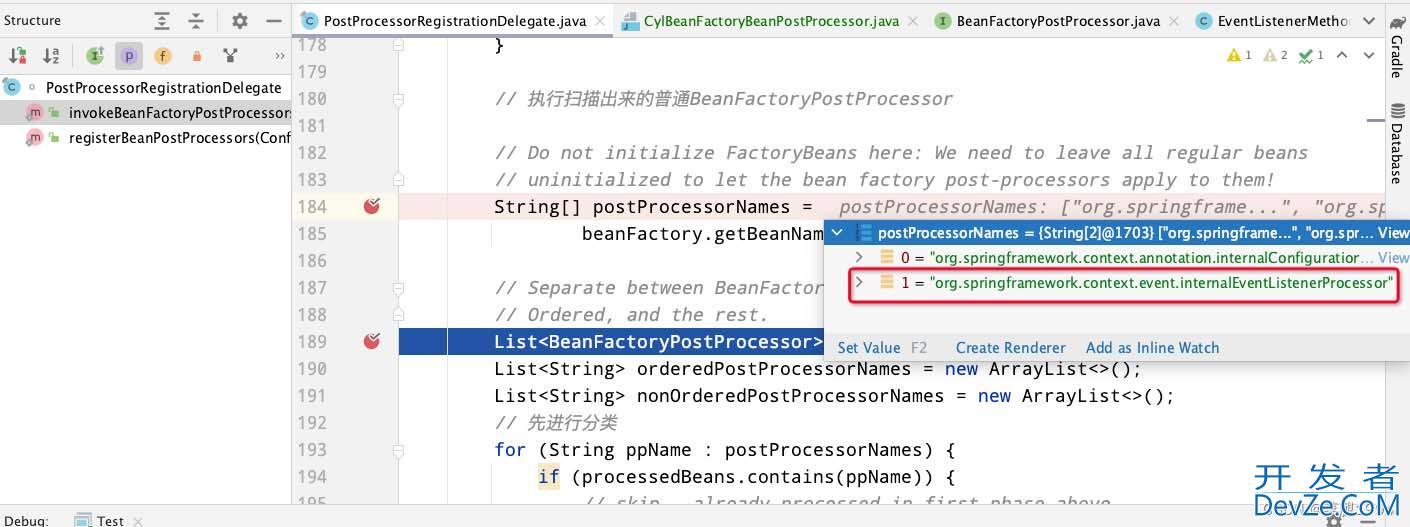
由于EventListenerMethodProcessor没有实现PriorityOrdered或者Ordered接口,所以就被放入了nonOrderedPostProcessorNames中最后被执行
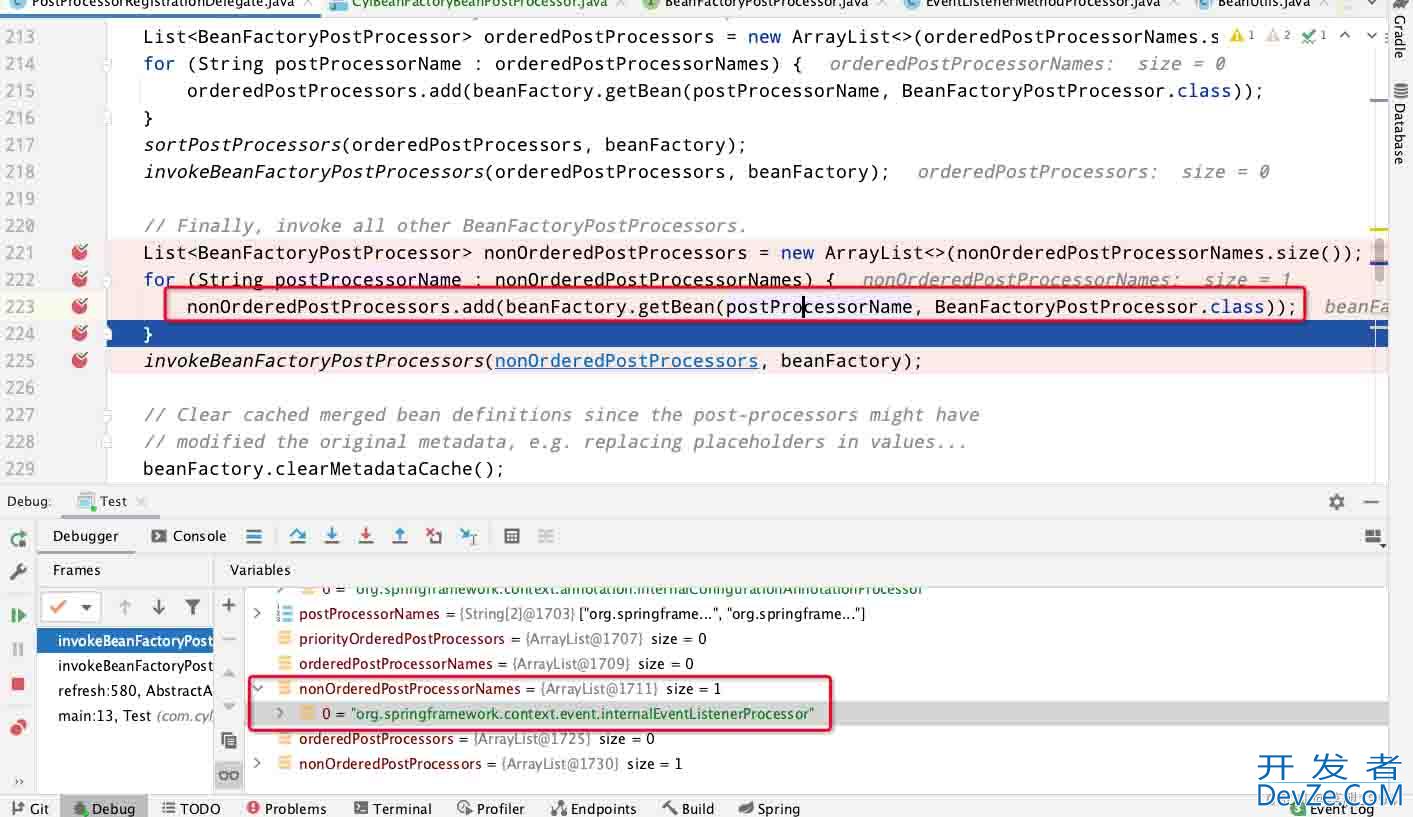
当执行beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)会进行实例化走到EventListenerMethodProcessor的构造函数中
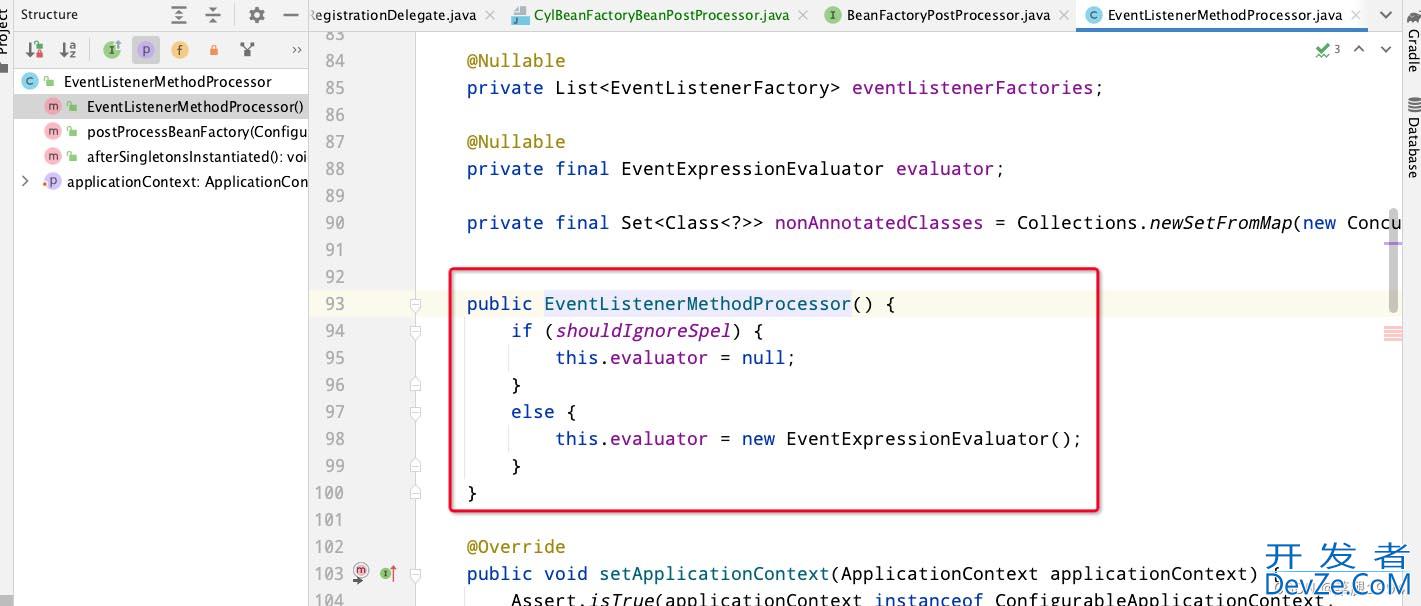
到此EventListenerMethodProcessor实例化好了,代码继续执行
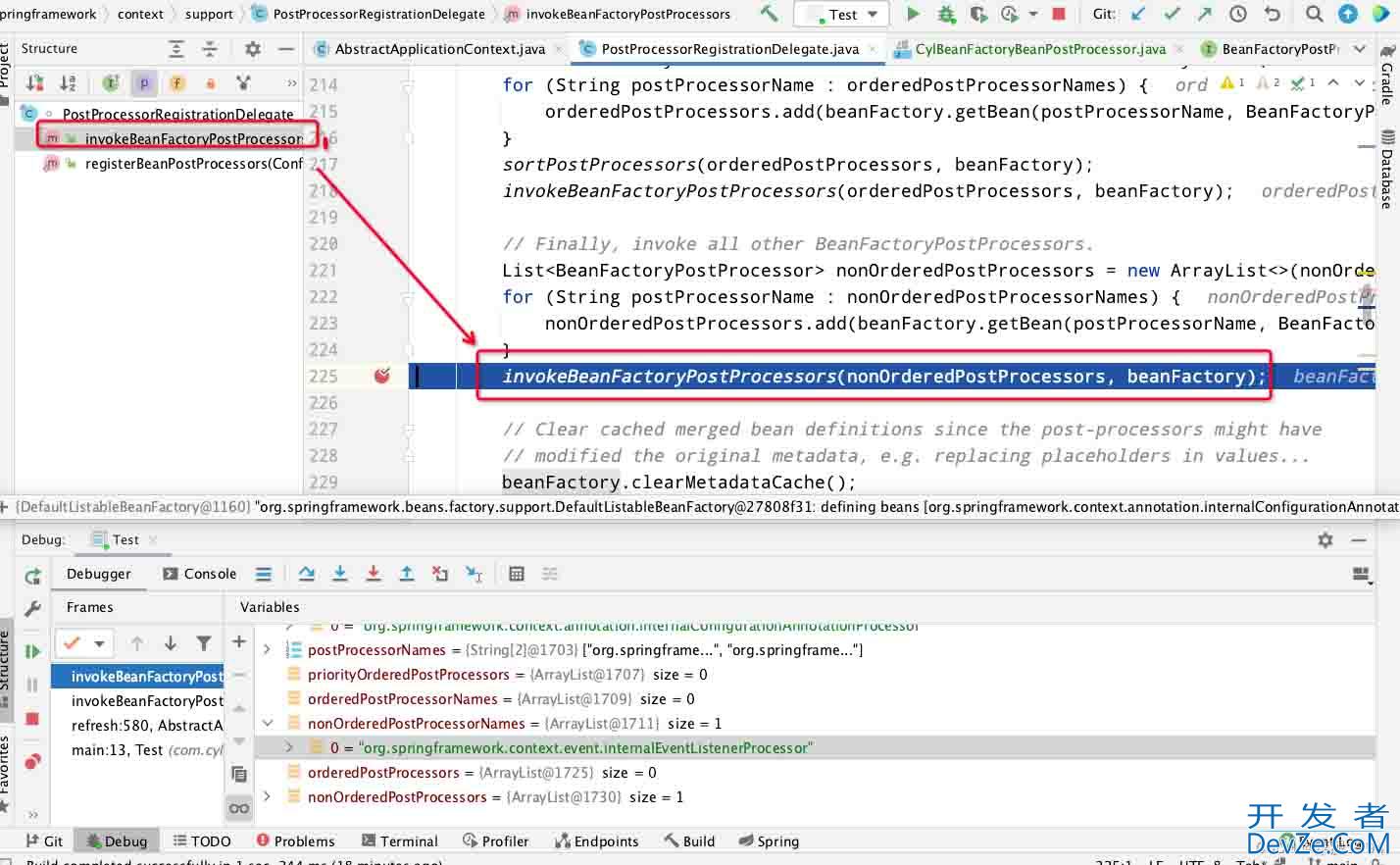
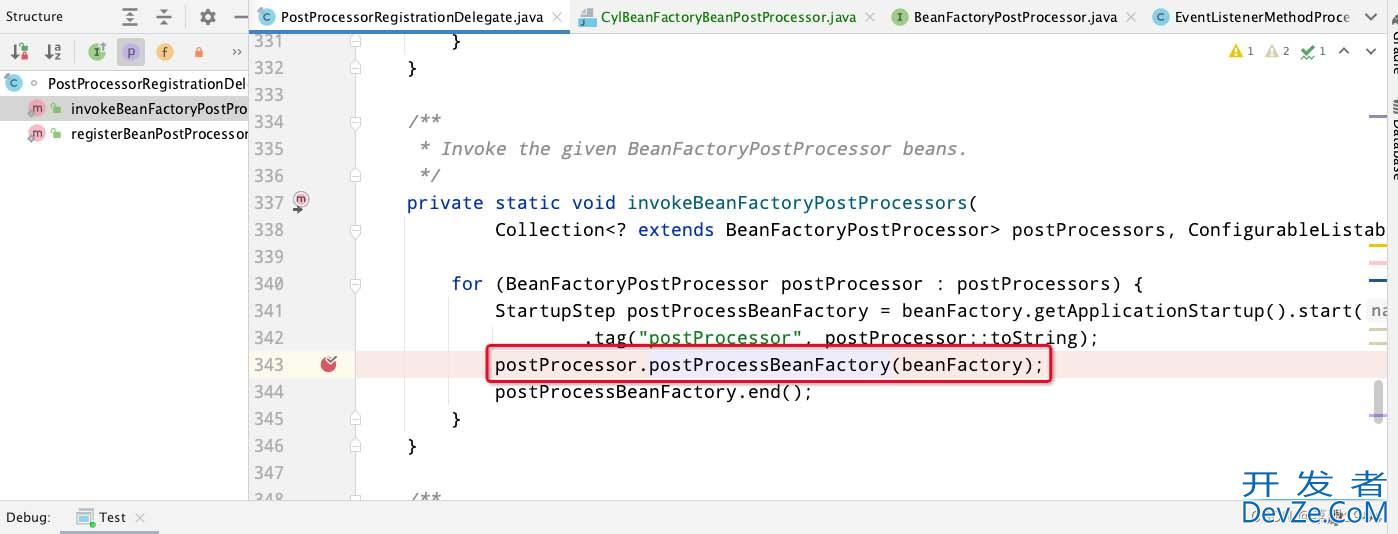
会执行到EventListenerMethodProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(),在这里实例化DefaultEventListenerFactory
3.作用时机->将加了EventListener注解的方法识别出来
并封装为监听器,加载spring容器中
当执行
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
初始化后,
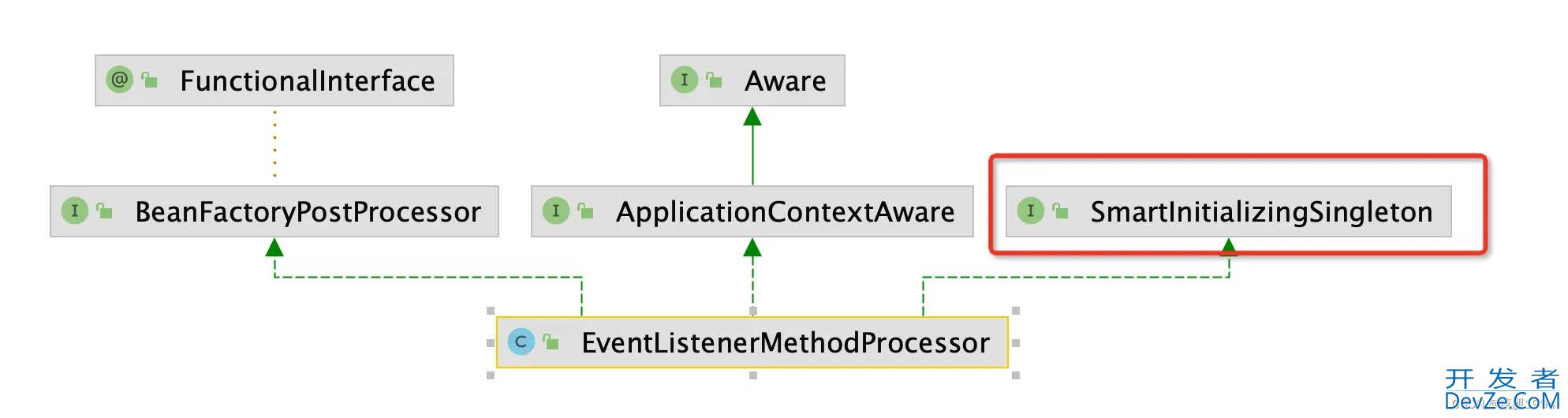
因EventListenerMethodProcessor实现了SmartInitializingSingleton,
而所有实现SmartInitializingSingleton类对象都需要在所有对象初始化后再执行afterSingletonsInstantiated
即:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterjavascriptate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 获取合并后的BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 获取FactoryBean对象
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
// 创建真正的Bean对象(getObject()返回的对象)
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 创建Bean对象
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// 所有的非懒加载单例Bean都创建完了后
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
smartInitialize.end();
}
}
}
当执行smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();就会调到
org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor#afterSingletonsInstantiated
EventListenerMethodProcessor真正的处理逻辑来了,主要看第38行关键方法
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory;
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No ConfigurableListableBeanFactory set");
String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(beanName)) {
// 拿到当前Bean对象的类型
Class<?> type = null;
try {
type = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(beanFactory, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (type != null) {
if (ScopedObject.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
try {
Class<?> targetClass = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(
beanFactory, ScopedProxyUtils.getTargetBeanName(beanName));
if (targetClass != null) {
type = targetClass;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An invalid scoped proxy arrangement - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target bean for scoped proxy '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
try {
python //关键方法
processBean(beanName, type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor#processBean,关注下面代码的注释,主要逻辑就是会遍历所有单例池中的对象,找到对象中加@EventListener注解的方法,然后通过EventListenerFactory将方法设置成监听器,注册到spring容器中
private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&
!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) {
// 找到所有加了@EventListener注解的方法
Map<php;Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;
Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories;
Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
// 利用EventListenerFactory来对加了@EventListener注解的方法生成ApplicationListener对象
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaLuator);
}
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
rdHKzl logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
}
发布事件,生效
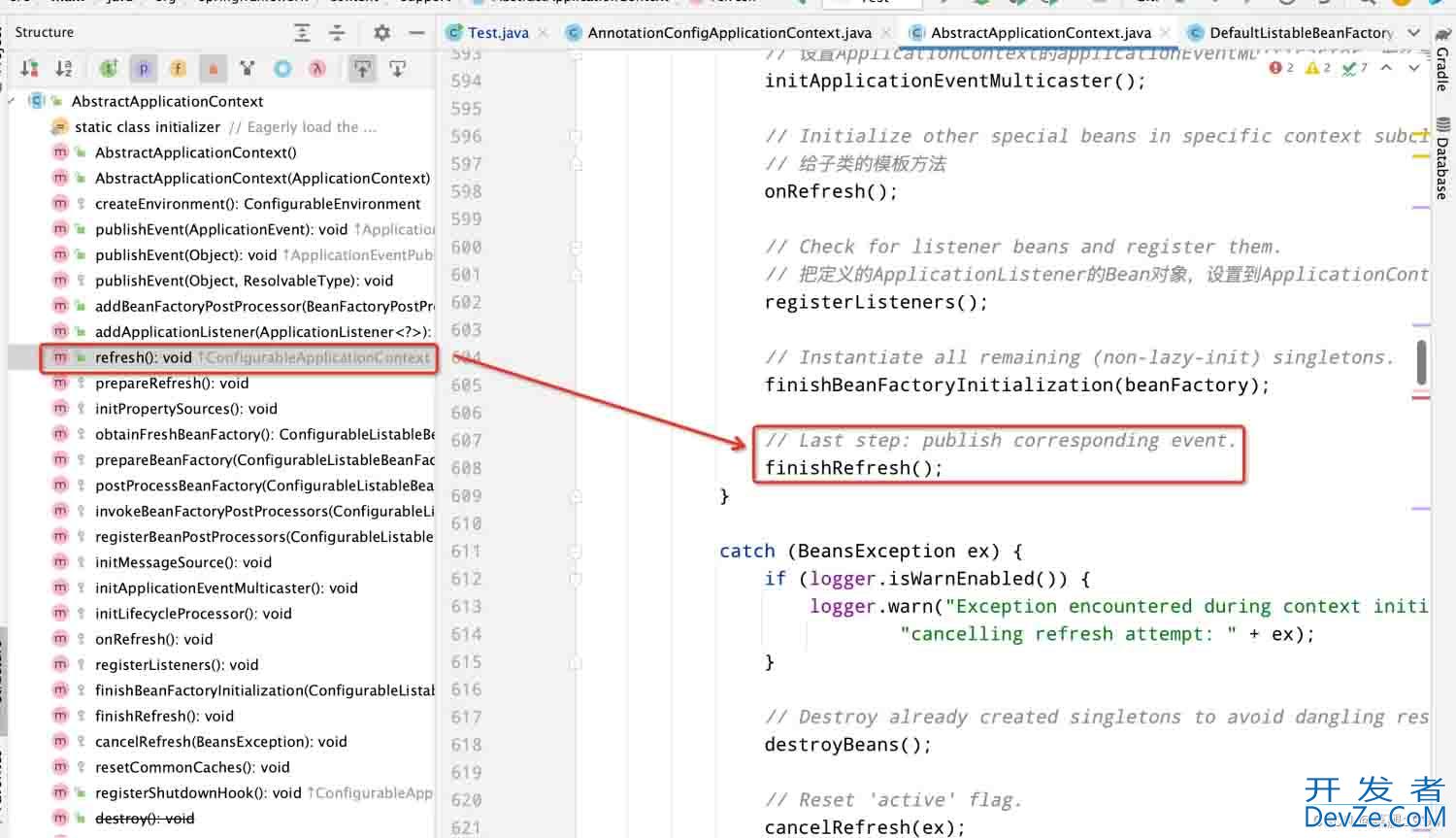
容器初始化后,设置的监听器会收到容器初始化完成的事件,然后执行自定义的监听事件
容器初始化最后阶段,即执行org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishRefresh
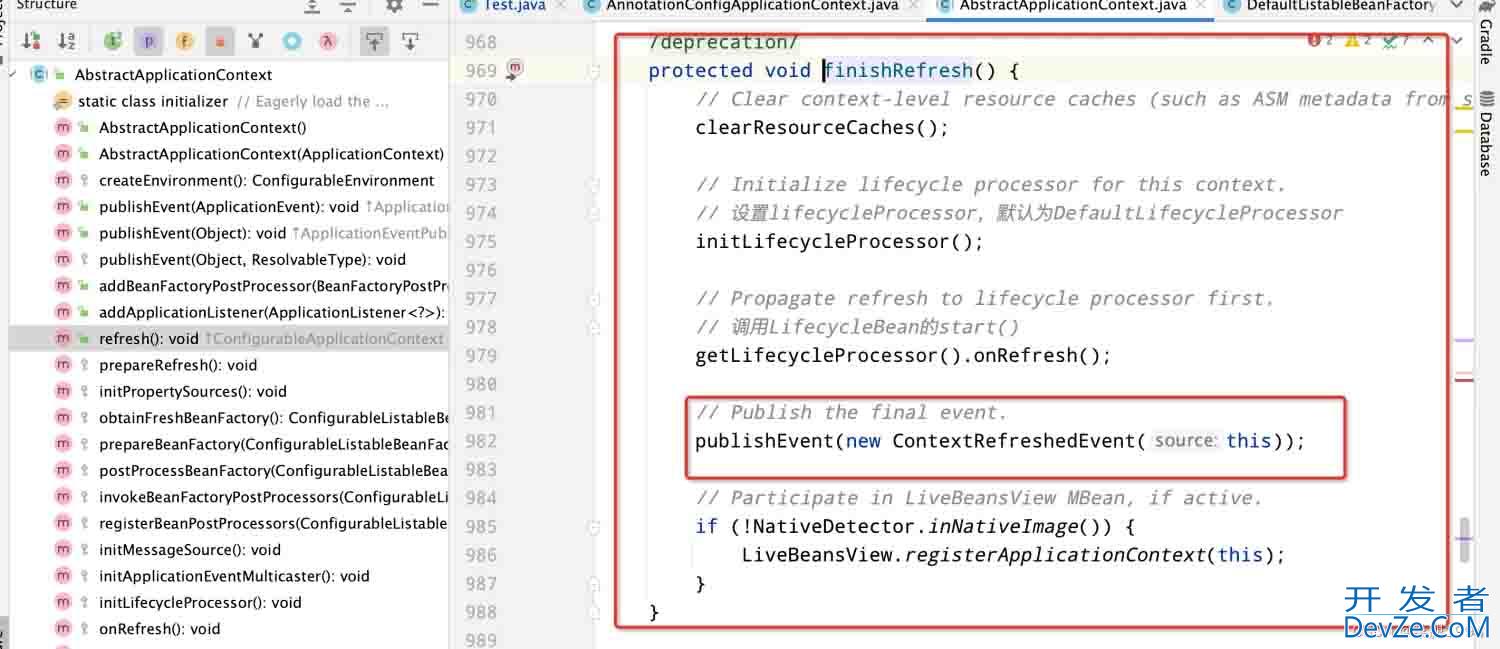
最终效果图为:
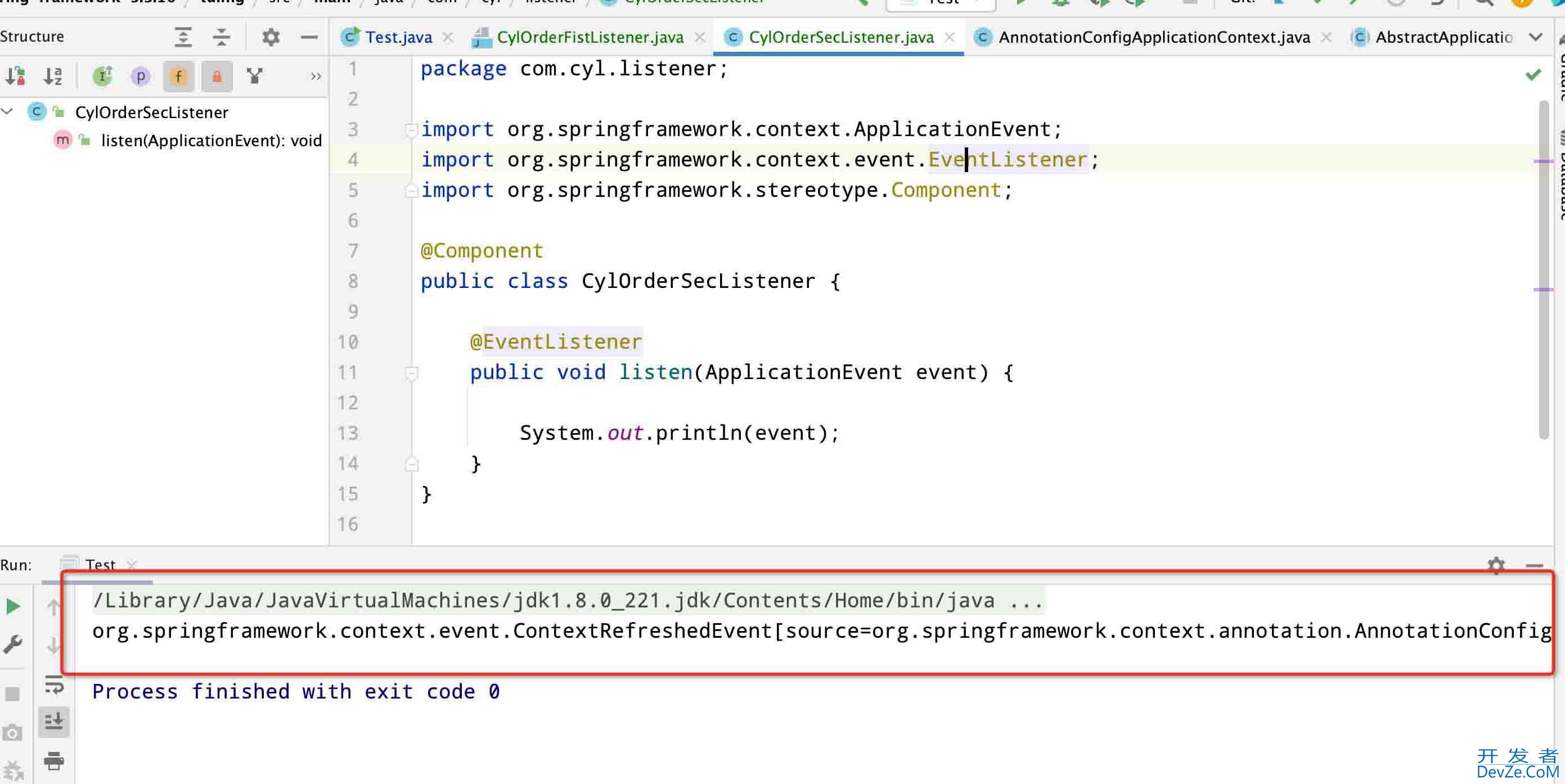
总结
EventListenerMethodProcessor和DefaultEventListenerFactory两个类是注解EventListener的逻辑处理类,先在spring容器初始化阶段先显示引入这两个类的bean定义,然后spring容器在执行beanFactory的后置处理器逻辑时,对这两个类进行实例化;
最后待所有非懒加载单例bean都初始化完后,执行EventListenerMethodProcessor的afterSingletonsInstantiated即初始化后方法,识别出所有加了注解EventListener的方法,将这些方法用DefaultEventListenerFactory封装成监听器类,注册到spring容器中。
待发布事件时,再从spring容器中获取所有监听器类,回调监听方法。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论