Java并发编程之ConcurrentLinkedQueue解读
目录
- 一、简介
- 二、结构
- 三、入队
- 四、出列
- 五、ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用特点
一、简介
工作中有时候需要使用线程安全的队列。如果要实现一个线程安全的队列有两种方式:一种是使用阻塞算法,另一种是使用非阻塞算法。使用阻塞算法的队列可以用一个锁(入队和出队用同一把锁)或两个锁(入队和出队用不同的锁)等方式来实现。非阻塞的实现方式则可以使用循环CAS的方式来实现。而ConcurrentLinkedQueue就是juc包中自带的经典非堵塞方式实现的工具类
二、结构
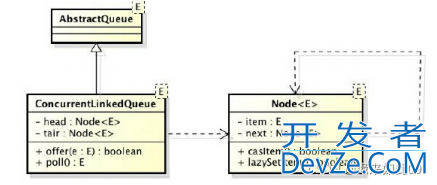
ConcurrentLinkedQueue由head节点和tail节点组成,每个节点(Node)由节点元素(item)和指向下一个节点(next)的引用组成,节点与节点之间就是通过这个next关联起来,从而组成一张链表结构的队列。默认情况下head节点存储的元素为空,tail节点等于head节点。
private transient volatile Node<E> tail = head;
三、入队
从源代码角度来看,整个入队过程主要做两件事情:第一是定位出尾节点;第二是使用CAS算法将入队节点设置成尾节点的next节点,如不成功则重试。
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
// 入队前,创建一个入队节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e)www.devze.com;
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {
// 创建一个指向tail节点的引用
Node<E> q = p.next;
if (q == null) {
// p is last node
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
// Successful CAS is the linearization point
// for e to become an element of this queue,
编程客栈 // and for newNode to become "live".
if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
return true;
}
// Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next
}
else if (p == q)
// We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it
// will also be off-list, in which case we need to
// jump to head, from which all live nodes are always
// reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet.
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
// Check for tail updates after two hops.
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
tail节点并不总是尾节点,所以每次入队都必须先通过tail节点来找到尾节点。尾节点可能是tail节点,也可能是tail节点的next节点。代码中循环体中的第一个if就是判断tail是否有next节点,有则表示next节点可能是尾节点。获取tail节点的next节点需要注意的是p节点等于p的next节点的情况,只有一种可能就是p节点和p的next节点都等于空,表示这个队列刚初始化,正准备添加节点,所以需要返回head节点。
/**
*返回 p 的后继节点,或者如果 p.next 已经链接到 self 则返回头节点,这只有在使用现在不在列表*中的陈旧指针遍历时才会为真。
**/
final Node<E> succ(Node<E> p) {
Node<E> next = p.next;
return (p == next) ? head : next;
}
四、出列
public E poll() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) {
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
//入列折腾的tail,那出列折腾的就是head
E item = p.item;
//出列判断依据是节点的item=null
qXEhEXKC //item != null, 并且能将操作编程节点的item设置null, 表示出列成功
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {
if (p != h)
//一旦出列成功需要对head进行移动
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);
return item;
编程 }
else if ((q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
}
else if (p == q)
//第一轮操作失败,下一轮继续,调回到循环前
continue restartFromHead;
else
//推动head节点移动
p = q;
}
}
}
五、ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用特点
ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用约定:
1:不允许null入列
2:在入队的最后一个元素的next为null
3:队列中所有未删除的节点的item都不能为null且都能从head节点遍历到
4:删除节点是将item设置为null, 队列迭代时跳过item为null节点
5:head节点跟tail不一定指向头节点或尾节点,可能存在滞后性
到此这篇关于Java并发编程之ConcurrentLinkedQueue解读的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java中的ConcurrentLinkedQueue内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论