java基础之TreeMap实现类全面详解
目录
- TreeMap详解
- 关键变量
- 构造函数
- get方法
- put方法
- remove方法
TreeMap详解
TreeMap是Map接口的一个实现类,底层基于红黑树的实现,按照key的顺序存储
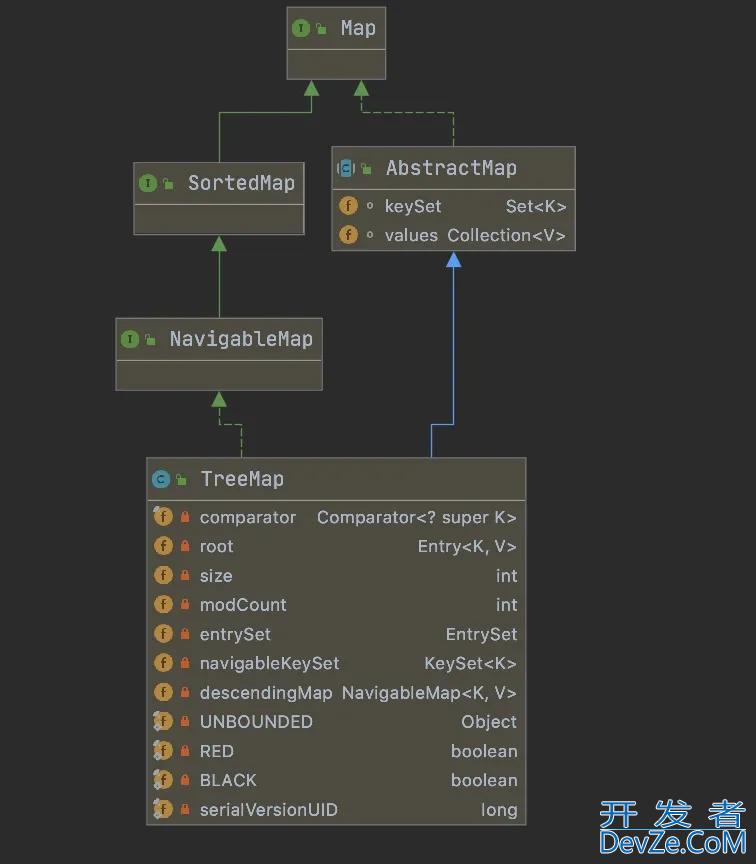
从继承结构可以看到TreeMap除了继承了AbstractMap类,还实现了NavigableMap接口,而NavigableMap接口是继承自SortedMap接口的,所以TreeMap是可以进行排序的
关键变量
// 比较器,根据比较器来决定TreeMap的排序,如果为空,按照key做自然排序(最小的在根节点)
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
// 根节点
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* The number of entries in the tree
* 树的大小
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
* 修改次数
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
// Entry为TreeMap的内部类
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
}
构造函数
// 默认空参构造器,比较器设置为空
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
// 提供比较器
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (Java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
// 从这里可以看出TreeMap的key不可以为null
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
// 获取根节点
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
// 判断是根节点的左子树还是右子树
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
// 根节点为null,表示这是第一个元素
if (t == null) {
// 主要是为了确保key是可排序的类,以及key不能为null
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
// 第三个参数为父节点的entry,根节点没有父节点,所以为null
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
// 存在比较器的情况
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 不存在比较器,进行自然排序
else {
// key不能为null
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
// do...while是为了找到该key所要存放的位置(找到父节点)
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
// 比父节点小,是左子树
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
// 插入之后还要进行平衡操作
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
x.color = RED;
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
if (parentOf(x) == leftOjavascriptf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x =php= rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentO编程f(x)));
}
} else {
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK;
}
remove方法
public V remove(Object key) {
// 获取到该key对应的节点 和get相同
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
// 存在两个子树(左子树和右子树)
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
// 找到与p数值最接近的节点(即右子树的最左叶子节点)
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
// 找到所要替代的节点
Entry<K,V> replacejsment = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
// 替换节点
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = pythonreplacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
// 删除的节点为黑色节点,需要进行平衡
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
}
// 此时replacement为null(表明 p没有左子树也没有右子树),如果p没有父节点,表明该树只有一个根节点
else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
}
// 此时replacement为null(表明 p没有左子树也没有右子树),表明该节点为叶子节点
else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
// 删除的节点为黑色节点,需要进行平衡
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
// 将p从树中移除
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
// 右节点不为null,找到后继节点(即右子树的左叶子节点)
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else { // symmetric
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
以上就是java基础之TreeMap实现类全面详解的详细内容,更多关于java TreeMap实现类的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论