Spring JPA学习之delete方法示例详解
目录
- 一、deleteById 和 delete
- deleteById(Id id)(通过id进行删除)
- deletandroide(T entity)(通过实体对象进行删除)
- 实例
- service 层
- control层
- 二、deleteAllById 和 deleteAll
- 1、deleteAllById(Iterable<? extends ID> ids)(通过id进行批量删除)
- 2、deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities)(通过实体对象进行批量删除)
- 实例
- service 层
- control层
- 三、deleteAllInBATch 和 deleteAllByIdInBatch
- 1、deleteAllInBatch(Iterable<T> entities)(通过实体对象进行批量删除)
- 2、deleteAllByIdInBatch(Iterable<ID> ids)源码(通过ids批量删除)
- 结论:
一、deleteById 和 delete
为什么要把这两个方法放在一起呢?我们先看源码再说
deleteById(Id id)(通过id进行删编程客栈除)
@Transactional
@Override
public void deleteById(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
delete(findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new EmptyResultDataAccessException(
String.format("No %s entity with id %s exists!", entityInformation.getJavaType(), id), 1)));
}
delete(T entity)(通过实体对象进行删除)
@Override
@Transactional
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void delete(T entity) {
Assert.notNull(entity, "Entity must not be null!");
if (entityInformation.isNew(entity)) {
return;
}
Class<?> type = ProxyUtils.getUserClass(entity);
T existing = (T) em.find(type, entityInformation.getId(entity));
// if the entity to be deleted doesn't exist, delete is a NOOP
if (existing == null) {
return;
}
em.remove(em.contains(entity) ? entity : em.merge(entity));
}
一目了然了吧!deleteById 先在方法体内通过 id 求出 entity 对象,然后调用了 delete 的方法。也就是说,这两个方法同根同源,使用起来差距不大,结果呢?也是一样的,就是单条删除。实际使用中呢,也是使用 deleteById 的情况比较多,废话少说,try it。
实例
service 层
添加deleteById方法(deleteById 是 JPA 自带接口不需要在dao层中添加)
@Transactional
public void deleteById(Integer id){
userDao.deleteById(id);
}
control层
/**
* 通过id进行删除数据
* @param id
*/
@GetMapping("/deleteById")
public void deleteById(Integer id){
userService.deleteById(id);
}
执行请求 /deleteById?id=2,控制台打印如下:
Hibernate: select user0_.id as id1_0_0_, user0_.age as age2_0_0_, user0_.name as name3_0_0_ from user user0_ where user0_.id=? Hibernate: delete from user where id=?
结论
先通过 select 查询实体对象是否存在,然后再通过 id 进行删除。
二、deleteAllById 和 deleteAll
1、deleteAllById(Iterable<? extends ID> ids)(通过id进行批量删除)
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteAllById(Iterable<? extends ID> ids) {
Assert.notNull(ids, "Ids must not be null!");
for (ID id : ids) {
deleteById(id);
}
}
结论
通过源码可以看出,就是遍历 ids 然后循环调用上面的 deleteById(Id id) 方法。
2、deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities)(通过实体对象进行批量删除)
@Override
@Transacti编程onal
public void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities) {
Assert.notNull(entities, "Entities must not be null!");
for (T entity : entities) {
delete(entity);
}
}
结论
这个呢?也就是遍历 entities 然后循环调用上面的 delete(T entity) 方法
还有一个不传参数的deleteAll()方法来删除所有数据(慎用)
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteAll() {
for (T element : findAll()) {
android delete(element);
}
}
就是通过findAll求出所有实体对象然后循环调用delete方法
综上所述,我们发现以上所有的删除事件都是调用了delete(T entity)方法,也就是差距不是很大,就是单条 和多条删除的区别。
实例
service 层
添加 deleteAllById 方法(deleteAllById 是三方件自带接口不需要在dao层中添加)
@Transactional
public void deleteAllById(Iterable ids){
userDao.deleteAllById(ids);
}
control层
/**
* 通过id进行批量删除
* @param ids
*/
@GetMapping("/deleteAllById")
public void deleteAllById(Integer[] ids){
userService.deleteAllById(Arrays.asList(ids));
}
浏览器测试成功 /deleteAllById?id=3,4删除前:
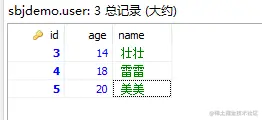
删除后:
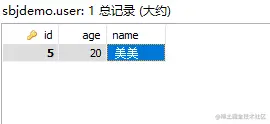
控制台打印如下:
Hibernate: select user0_.id as id1_0_0_, user0_.age as age2_0_0_, user0_.name as name3_0_0_ from user user0_ where user0_.id=?
Hibernate: select user0_.id as id1_0_0_, user0_.age as age2_0_0_, user0_.name as name3_0_0_ from user user0_ where user0_.id=?Hibernate: delete from user where id=?Hibernate: delete from user where id=?
由此可以看出,数据是一条一条的进行了删除。
三、deleteAllInBatch 和 deleteAllByIdInBatch
1、deleteAllInBatch(Iterable<T> entities)(通过实体对象进行批量删除)
public static final String DELETE_ALL_QUERY_STRING = "delete from %s x";
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteAllInBatch(Iterable<T> entities) {
Assert.notNull(entities, "Entities must not be null!");
if (!entities.iterator().hasNext()) {
return;
}
applyAndBind(getQueryString(DELETE_ALL_QUERY_STRING, entityInformation.getEntityName()), entities, em)
.executeUpdate();
}
/**
* Creates a where-clause referencing the given entities and appends it to the given query string. Binds the given
* entities to the query.
*
* @param <T> type of the entities.
* @param queryString must not be {@literal null}.
* @param entities must not be {@literal null}.
* @param entityManager must not be {@literal null}.
* @return Guaranteed to be not {@literal null}.
*/
public static <T> Query applyAndBind(String queryString, Iterable<T> entities, EntityManager entityManager) {
Assert.notNull(queryString, "Querystring must not be null!");
Assert.notNull(entities, "Iterable of entities must not be null!");
Assert.notNull(entityManager, "EntityManager must not be null!");
Iterator<T> iterator = entities.iterator();
if (!iterator.hasNext()) {
return entityManager.createQuery(query开发者_Python培训String);
}
String alias = detectAlias(queryString);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(queryString);
builder.append(" where");
int i = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
iterator.next();
builder.append(String.format(" %s = ?%d", alias, ++i));
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
builder.append(" or");
}
}
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(builder.toString());
iterator = entities.iterator();
i = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
query.setParameter(++i, iterator.next());
}
return query;
}
通过上面的源码,我们大体能猜测出deleteAllInBatch(Iterable<T> entities)的实现原理:
delete from %s where x=? or x=?实际测试一下:http://localhost:7777/deleteAllInBatch?ids=14,15,16&names=a,b,c&ages=0,0,0控制台打印如下:
Hibernate: delete from user where id=? or id=? or id=?
2、deleteAllByIdInBatch(Iterable<ID> ids)源码(通过ids批量删除)
public static final String DELETE_ALL_QUERY_BY_ID_STRING = "delete from %s x where %s in :ids";
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteAllByIdInBatch(Iterable<ID> ids) {
Assert.notNull(ids, "Ids must not be null!");
if (!ids.iterator().hasNext()) {
return;
}
if (entityInformation.hasCompositeId()) {
List<T> entities = new ArrayList<>();
// generate entity (proxies) without accessing the database.
ids.forEach(id -> entities.add(getReferenceById(id)));
deleteAllInBatch(entities);
} else {
String queryString = String.format(DELETE_ALL_QUERY_BY_ID_STRING, entityInformation.getEntityName(),
entityInformation.getIdAttribute().getName());
Query query = em.createQuery(queryString);
/**
* Some JPA providers require {@code ids} to be a {@link Collection} so we must convert if it's not already.
*/
if (Collection.class.isInstance(ids)) {
query.setParameter("ids", ids);
} else {
Collection<ID> idsCollection = StreamSupport.stream(ids.spliterator(), false)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
query.setParameter("ids", idsCollection);
}
query.executeUpdate();
}
}
通过上面源码我们大体可以猜出deleteAllByIdInBatch(Iterable ids)的实现原理:
delete from %s where id in (?,?,?)实际测试一下:http://localhost:7777/deleteAllByIdInBandroidatch?ids=17,18,19 控制台打印如下:
Hibernate: delete from user where id in (? , ? , ?)
这里同样有个不带参数的deleteAllInBatch()的方法,源码如下:
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteAllInBatch() {
em.createQuery(getDeleteAllQueryString()).executeUpdate();
}
public static final String DELETE_ALL_QUERY_STRING = "delete from %s x";
private String getDeleteAllQueryString() {
return getQueryString(DELETE_ALL_QUERY_STRING, entityInformation.getEntityName());
}
通过源码不难猜到实现原理吧,多的不说,直接给测试的控制台数据:
Hibernate: delete from user
结论:
从上面两种删除接口来看,第二种实现比起第一种更加的快捷;
第一种就是一条一条的进行删除操作,如果有万级的数据,执行起来肯定非常耗时,所以如果数据量比较大的话,还是建议大家使用第二种。
以上就是Spring JPA学习之delete方法示例详解的详细内容,更多关于Spring JPA delete方法的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论