Go语言数据结构之二叉树可视化详解
目录
- 题目
- 源代码
- 做题思路
- 扩展
- 左右并列展示
- 上下并列展示
- 总结回顾
题目
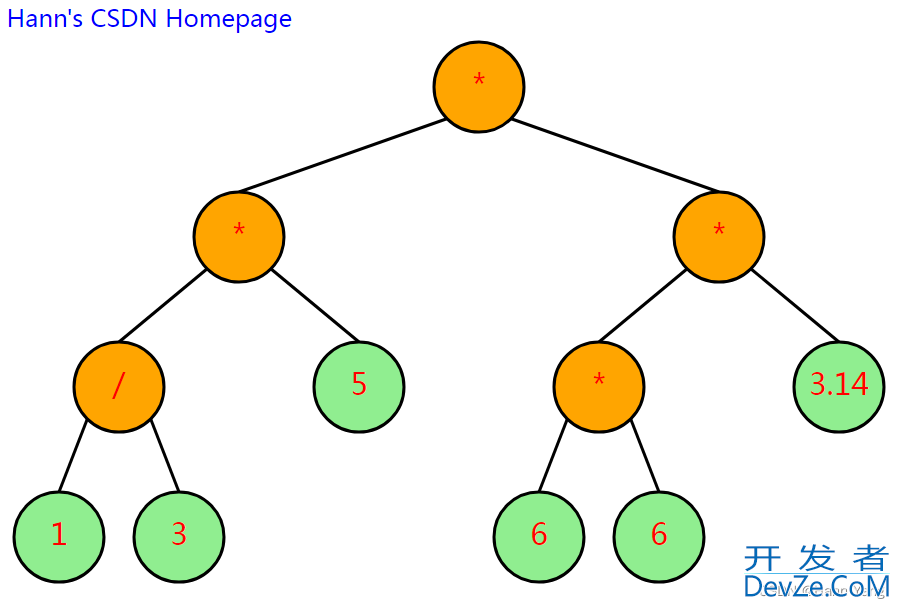
以图形展示任意二叉树,如下图,一个中缀表达式表示的二叉树:3.14*r²*h/3
源代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"os/exec"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
type any = interface{}
type btNode struct {
Data any
Lchild *btNode
Rchild *btNode
}
type biTree struct {
Root *btNode
Info *biTreeInfo
}
type biTreeInfo struct {
Data []any
DataLevel [][]any
L, R []bool
X, Y, W []int
Index, Nodes int
Width, Height int
MarginX, MarginY int
SpaceX, SpaceY int
SvgWidth, SvgHeight int
SvgXML string
}
func Build(Data ...any) *biTree {
if len(Data) == 0 || Data[0] == nil {
return &biTree{}
}
node := &btNode{Data: Data[0]}
Queue := []*btNode{node}
for lst := Data[1:]; len(lst) > 0 && len(Queue) > 0; {
cur, val := Queue[0], lst[0]
Queue, lst = Queue[1:], lst[1:]
if val != nil {
cur.Lchild = &btNode{Data: val}
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Lchild)
}
if len(lst) > 0 {
val, lst = lst[0], lst[1:]
if val != nil {
cur.Rchild = &btNode{Data: val}
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Rchild)
}
}
}
return &biTree{Root: node}
}
func BuildFromList(List []any) *biTree {
return Build(List...)
}
func AinArray(sub int, array []int) int {
for idx, arr := range array {
if sub == arr {
return idx
}
}
return -1
}
func Pow2(x int) int { //x>=0
res := 1
for i := 0; i < x; i++ {
res *= 2
}
return res
}
func Max(L, R int) int {
if L > R {
return L
} else {
return R
}
}
func (bt *btNode) MaxDepth() int {
if bt == nil {
return 0
}
Lmax := bt.Lchild.MaxDepth()
Rmax := bt.Rchild.MaxDepth()
return 1 + Max(Lmax, Rmax)
}
func (bt *btNode) Coordinate(x, y, w int) []any {
var res []any
if bt != nil {
L, R := bt.Lchild != nil, bt.Rchild != nil
res = append(res, []any{bt.Data, L, R, x, y, w})
res = append(res, bt.Lchild.Coordinate(x-w, y+1, w/2)...)
res = append(res, bt.Rchild.Coordinate(x+w, y+1, w/2)...)
}
return res
}
func (bt *biTree) NodeInfo() []any {
return bt.Root.Coordinate(0, 0, Pow2(bt.Root.MaxDepth()-2))
}
func (bt *biTree) TreeInfo() {
height := bt.Root.MaxDepth()
width := Pow2(height - 1)
lsInfo := bt.NodeInfo()
btInfo := &biTreeInfo{
Height: height,
Width: width,
Nodes: len(lsInfo),
}
for _, data := range lsInfo {
for i, info := range data.([]any) {
switch i {
case 0:
btInfo.Data = append(btInfo.Data, info.(any))
case 1:
btInfo.L = append(btInfo.L, info.(bool))
case 2:
btInfo.R = append(btInfo.R, info.(bool))
case 3:
btInfo.X = append(btInfo.X, info.(int))
case 4:
btInfo.Y = append(btInfo.Y, info.(int))
case 5:
btInfo.W = append(btInfo.W, info.(int))
}
}
}
for j, k := 0, width*2; j < height; j++ {
DLevel := []any{}
for i := k / 2; i < width*2; i += k {
index := AinArray(i-width, btInfo.X)
if index > -1 {
DLevel = append(DLevel, btInfo.Data[index])
} else {
DLevel = append(DLevel, nil)
}
DLevel = append(DLevel, []int{i, j})
if k/4 == 0 {
DLevel = append(DLevel, []int{0, 0})
DLevel = append(DLevel, []int{0, 0})
} else {
DLevel = append(DLevel, []int{i - k/4, j + 1})
DLevel = append(DLevel, []int{i + k/4, j + 1})
}
}
k /= 2
btInfo.DataLevel = append(btInfo.DataLevel, DLevel)
}
bt.Info = btInfo
}
func (bt *biTree) Info2SVG(Margin ...int) string {
var res, Line, Color string
info := bt.Info
MarginX, MarginY := 0, 10
SpaceX, SpaceY := 40, 100
switch len(Margin) {
case 0:
break
case 1:
MarginX = Margin[0]
case 2:
MarginX, MarginY = Margin[0], Margin[1]
case 3:
MarginX, MarginY, SpaceX = Margin[0], Margin[1], Margin[2]
default:
MarginX, MarginY = Margin[0], Margin[1]
SpaceX, SpaceY = Margin[2], Margin[3]
android }
info.MarginX, inf编程客栈o.MarginY = MarginX, MarginY
info.SpaceX, info.SpaceY = SpaceX, SpaceY
info.SvgWidth = Pow2(info.Height)*info.SpaceX + info.SpaceX
info.SvgHeight = info.Height * info.SpaceY
for i, Data := range info.Data {
Node := "\n\t<g id=\"INDEX,M,N\">\n\t<CIRCLE/>\n\t<TEXT/>\n\t<LEAF/>\n\t</g>"
DataStr := ""
switch Data.(type) {
case int:
DataStr = strconv.Itoa(Data.(int))
case float64:
DataStr = strconv.FormatFloat(Data.(float64), 'g', -1, 64)
case string:
DataStr = Data.(string)
default:
DataStr = "Error Type"
}
Node = strings.Replace(Node, "INDEX", strconv.Itoa(info.Index), 1)
Node = strings.Replace(Node, "M", strconv.Itoa(info.X[i]), 1)
Node = strings.Replace(Node, "N", strconv.Itoa(info.Y[i]), 1)
x0, y0 := (info.X[i]+info.Width)*SpaceX+MarginX, 50+info.Y[i]*SpaceY+MarginY
x1, y1 := x0-info.W[i]*SpaceX, y0+SpaceY-30
x2, y2 := x0+info.W[i]*SpaceX, y0+SpaceY-30
Color = "orange"
if info.L[i] && info.R[i] {
Line = XmlLine(x0-21, y0+21, x1, y1) + "\n\t" + XmlLine(x0+21, y0+21, x2, y2)
} else if info.L[i] && !info.R[编程客栈i] {
Line = XmlLine(x0-21, y0+21, x1, y1)
} else if !info.L[i] && info.R[i] {
Line = XmlLine(x0+21, y0+21, x2, y2)
} else {
Color = "lightgreen"
}
Node = strings.Replace(Node, "<CIRCLE/>",http://www.devze.com XmlCircle(x0, y0, Color), 1)
Node = strings.Replace(Node, "<TEXT/>", XmlText(x0, y0, DataStr), 1)
if info.L[i] || info.R[i] {
Node = strings.Replace(Node, "<LEAF/>", Line, 1)
}
res += Node
}
info.SvgXml = res
return res
}
func XmlCircle(X, Y int, Color string) string {
Radius := 30
Circle := "<circle cx=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X) + "\" cy=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y) +
"\" r=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Radius) + "\" stroke=\"black\" stroke-width=" +
"\"2\" fill=\"" + Color + "\" />"
return Circle
}
func XmlText(X, Y int, DATA string) string {
iFontSize, tColor := 20, "red"
Text := "<text x=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X) + "\" y=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y) +
"\" fill=\"" + tColor + "\" font-siwww.devze.comze=\"" + strconv.Itoa(iFontSize) +
"\" text-anchor=\"middle\" dominant-baseline=\"middle\">" + DATA + "</text>"
return Text
}
func XmlLine(X1, Y1, X2, Y2 int) string {
Line := "<line x1=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X1) + "\" y1=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y1) +
"\" x2=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X2) + "\" y2=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y2) +
"\" style=\"stroke:black;stroke-width:2\" />"
return Line
}
func (bt *biTree) ShowSVG(FileName ...string) {
var file *os.File
var err1 error
Head := "<svg xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/2000/svg\" xmlns:xlink" +
"=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" version=\"1.1\" width=" +
"\"Width\" height=\"Height\">\nLINKCONTENT\n</svg>"
Link := `<a xlink:href="https://blog.csdn.net/boysoft2002" target="_blank">
<text x="5" y="20" fill="blue">Hann's CSDN Homepage</text></a>`
Xml := strings.Replace(Head, "LINK", Link, 1)
Xml = strings.Replace(Xml, "Width", strconv.Itoa(bt.Info.SvgWidth), 1)
Xml = strings.Replace(Xml, "Height", strconv.Itoa(bt.Info.SvgHeight), 1)
Xml = strings.Replace(Xml, "CONTENT", bt.Info.SvgXml, 1)
svgFile := "biTree.svg"
if len(FileName) > 0 {
svgFile = FileName[0] + ".svg"
}
file, err1 = os.Create(svgFile)
if err1 != nil {
panic(err1)
}
_, err1 = io.WriteString(file, Xml)
if err1 != nil {
panic(err1)
}
file.Close()
exec.Command("cmd", "/c", "start", svgFile).Start()
//linux 代码:
//exec.Command("xdg-open", svgFile).Start()
//MAC 代码:
//exec.Command("open", svgFile).Start()
}
func main() {
list := []any{"*", "*", "*", "/", 5, "*", 3.14, 1, 3, nil, nil, 6, 6}
tree := Build(list...)
tree.TreeInfo()
tree.Info2SVG()
tree.ShowSVG()
fmt.Println(tree.Info.Data)
fmt.Println(tree.Info.DataLevel)
}
做题思路
增加一个结构biTreeInfo,在遍历二叉树时把作图要用的信息存入此结构中,方便读取信息。
type any = interface{}
type btNode struct {
Data any
Lchild *btNode
Rchild *btNode
}
type biTree struct {
Root *btNode
Info *biTreeInfo
}
type biTreeInfo struct {
Data []any
DataLevel [][]any
L, R []bool
X, Y, W []int
Index, Nodes int
Width, Height int
MarginX, MarginY int
SpaceX, SpaceY int
SvgWidth, SvgHeight int
SvgXml string
}
//数据域类型用 type any = interface{} 自定义类型,模拟成any数据类型。
遍历二叉树获取每个结点在svg图形中的坐标,使用先序递归遍历:
func (bt *btNode) Coordinate(x, y, w int) []any {
var res []any
if bt != nil {
L, R := bt.Lchild != nil, bt.Rchild != nil
res = append(res, []any{bt.Data, L, R, x, y, w})
res = append(res, bt.Lchild.Coordinate(x-w, y+1, w/2)...)
res = append(res, bt.Rchild.Coordinate(x+w, y+1, w/2)...)
}
return res
}
二叉树的每个结点,转svg时有圆、文字、左或右直线(叶结点没有真线)。
func XmlCircle(X, Y int, Color string) string {
Radius := 30
Circle := "<circle cx=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X) + "\" cy=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y) +
"\" r=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Radius) + "\" stroke=\"black\" stroke-width=" +
"\"2\" fill=\"" + Color + "\" />"
return Circle
}
func XmlText(X, Y int, DATA string) string {
iFontSize, tColor := 20, "red"
Text := "<text x=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X) + "\" y=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y) +
"\" fill=\"" + tColor + "\" font-size=\"" + strconv.Itoa(iFontSize) +
"\" text-anchor=\"middle\" dominant-baseline=\"middle\">" + DATA + "</text>"
return Text
}
func XmlLine(X1, Y1, X2, Y2 int) string {
Line := "<line x1=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X1) + "\" y1=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y1) +
"\" x2=\"" + strconv.Itoa(X2) + "\" y2=\"" + strconv.Itoa(Y2) +
"\" style=\"stroke:black;stroke-width:2\" />"
return Line
}
TreeInfo()写入二叉树结点信息,其中DataLevel是层序遍历的结果,也可以用它来作图。
Info2XML()就是把上述方法所得信息,转化成SVG的xml代码;
ShowSVG()生成并显示图形,svg的xml如下:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" version="1.1" width="680" height="400">
<a xlink:href="https://blog.csdn.net/boysoft2002" target="_blank">
<text x="5" y="20" fill="blue">Hann's CSDN Homepage</text></a>
<g id="0,0,0">
<circle cx="320" cy="60" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="orange" />
<text x="320" y="60" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">*</text>
<line x1="299" y1="81" x2="160" y2="130" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
<line x1="341" y1="81" x2="480" y2="130" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
</g>
<g id="0,-4,1">
<circle cx="160" cy="160" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="orange" />
<text x="160" y="160" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">*</text>
<line x1="139" y1="181" x2="80" y2="230" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
<line x1="181" y1="181" x2="240" y2="230" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
</g>
<g id="0,-6,2">
<circle cx="80" cy="260" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="orange" />
<text x="80" y="260" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">/</text>
<line x1="59" y1="281" x2="40" y2="330" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
<line x1="101" y1="281" x2="120" y2="330" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
</g>
<g id="0,-7,3">
<circle cx="40" cy="360" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="lightgreen" />
<text x="40" y="360" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-basel开发者_Go培训ine="middle">1</text>
<LEAF/>
</g>
<g id="0,-5,3">
<circle cx="120" cy="360" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="lightgreen" />
<text x="120" y="360" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">3</text>
<LEAF/>
</g>
<g id="0,-2,2">
<circle cx="240" cy="260" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="lightgreen" />
<text x="240" y="260" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">5</text>
<LEAF/>
</g>
<g id="0,4,1">
<circle cx="480" cy="160" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="orange" />
<text x="480" y="160" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">*</text>
<line x1="459" y1="181" x2="400" y2="230" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
<line x1="501" y1="181" x2="560" y2="230" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
</g>
<g id="0,2,2">
<circle cx="400" cy="260" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="orange" />
<text x="400" y="260" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">*</text>
<line x1="379" y1="281" x2="360" y2="330" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
<line x1="421" y1="281" x2="440" y2="330" style="stroke:black;stroke-width:2" />
</g>
<g id="0,1,3">
<circle cx="360" cy="360" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="lightgreen" />
<text x="360" y="360" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">6</text>
<LEAF/>
</g>
<g id="0,3,3">
<circle cx="440" cy="360" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="lightgreen" />
<text x="440" y="360" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">6</text>
<LEAF/>
</g>
<g id="0,6,2">
<circle cx="560" cy="260" r="30" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="lightgreen" />
<text x="560" y="260" fill="red" font-size="20" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">3.14</text>
<LEAF/>
</g>
</svg>
扩展
多棵二叉树同时展示,Info2SVG()可以设置起始位置
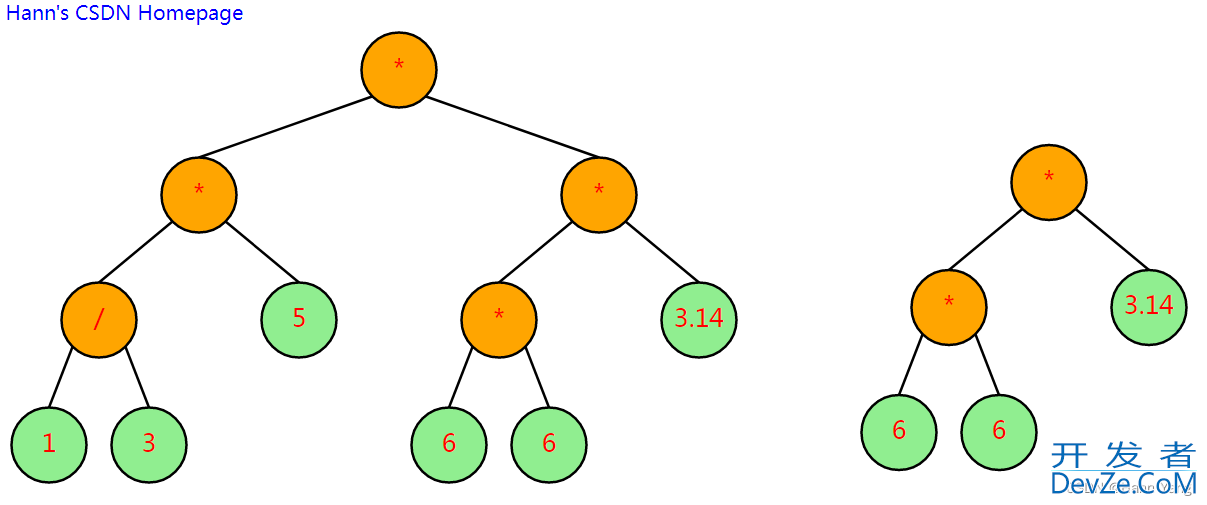
左右并列展示
tree2 := Build("*", "*", 3.14, 6, 6)
tree2.TreeInfo()
tree2.Info2SVG()
tree2.ShowSVG("tree2")
//左右并列展示
tree2.Info2SVG(tree.Info.SvgWidth, tree.Info.SpaceY)
tree.Info.SvgXml += tree2.Info.SvgXml
tree.Info.SvgWidth += tree2.Info.SvgWidth
tree.ShowSVG("tree12")
tree.Info2SVG() //恢复tree原状
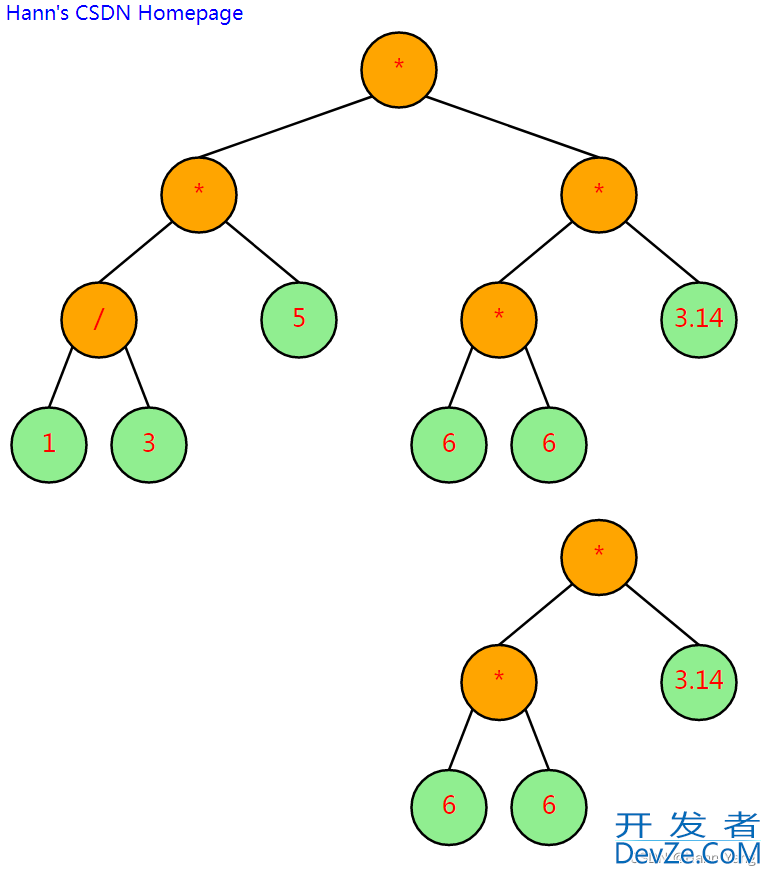
上下并列展示
//上下并列展示
tree2.Info2SVG(tree.Info.SvgWidth-tree2.Info.SvgWidth, tree.Info.SvgHeight)
tree.Info.SvgXml += tree2.Info.SvgXml
tree.Info.SvgHeight += tree2.Info.SvgHeight
tree.ShowSVG("tree123")
tree.Info2SVG() //恢复tree原状
以上2段代码放在前文源代码的main()函数中测试。
总结回顾
结点显示的代码固定了文字和圆形的大小颜色,如果读者愿意自己动手的话,可以尝试把这些要素设成参数或者增加biTreeInfo结构的属性。
到此这篇关于Go语言数据结构之二叉树可视化详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Go语言 二叉树可视化内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论