一文详解MySQL表的约束
目录
- 1. 空属性
- 2. 默认值
- 3. 列描述
- 4. zerofill
- 5. 主键
- 5.1 指定主键
- 5.2 主键约束
- 5.3 删除主键
- 5.4 追加主键
- 5.5 复合主键
- 6. 自增长
- 6.1 索引
- 7. 唯一键
- 8. 外键
- 8.1 如何理解外键约束
- 9. 综合案例
- 9.1 创建商品表
- 9.2 创建客户表
- 9.3 创建购买表
- 9.4 主键和外键
- 9.5 插入数据
- 9.6 验证外键和关联查询
表的约束:表中一定要有各种约束,通过约束,让我们未来插入数据库表中的数据是符号预期的。
约束的本质是通过技术手段,倒逼程序员,插入正确的数据。反过来,站在 mysql 的视角,凡是插入进来的数据,都是符合数据约束的!
所以约束的最终目标:保证数据的完整性和可预期性。
真正约束字段的是数据类型,但是数据类型约束很单一,需要有一些额外的约束,更好的保证数据的合法性,从业务逻辑角度保证数据的正确性。比如有一个字段是 email,要求是唯一的。
表的约束很多,这里主要介绍如下几个: null / not null、default、comment、zerofill、primary key、auto_increment、unique key。
1. 空属性
两个值:null(默认的)和 not null(不为空)。
数据库默认字段基本都是字段为空,但是实际开发时,尽可能保证字段不为空,因为数据为空没办法参与运算。
mysql> select null; +------+ | NULL | +------+ | NULL | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select 1+null; +--------+ | 1+null | +--------+ | NULL | +--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
案例:创建一个班级表,包含班级名和班级所在的教室。
站在正常的业务逻辑中:
- 如果班级没有名字,你不知道你在哪个班级。
- 如果教室名字可以为空,就不知道在哪上课。
所以我们在设计数据库表的时候,一定要在表中进行限制,满足上面条件的数据就不能插入到表中。这就是 “约束”。
先建表:
mysql> create table if not exists myclass(
-> class_name varchar(20) not null,
-> class_room varchar(20) not null,
-> other varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc myclass;
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| class_name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| class_room | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| other | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
我们先做全列插入:
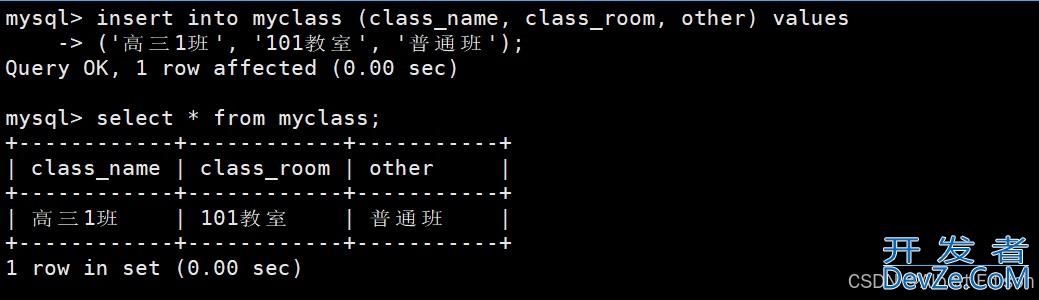
mysql> insert into myclass (class_name, class_room, other) values
-> ('高三1班', '101教室', '普通班');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from myclass;
+------------+------------+python-----------+
| class_name | class_room | other |
+------------+------------+-----------+
| 高三1班 | 101教室 | 普通班 |
+------------+------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into myclass (class_name, class_room) values ('高三3班', '103教室');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from myclass;
+------------+------------+-----------+
| class_name | class_room | other |
+------------+------------+-----------+
| 高三1班 | 101教室 | 普通班 |
| 高三3班 | 103教室 | NULL |
+------------+------------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结果如下:
继续插入数据:
mysql> insert into myclass (class_name, class_room) values ('高三3班', '103教室');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from myclass;
+------------+------------+-----------+
| class_name | class_room | other |
+------------+------------+-----------+
| 高三1班 | 101教室 | 普通班 |
| 高三3班 | 103教室 | NULL |
+------------+------------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结果如下:
如果没有给教室数据,或者数据为空,则会插入失败:
mysql> insert into myclass (class_name) values ('高三4班');
ERROR 1364 (HY000): Field 'class_room' doesn't have a default value
mysql> insert into myclass (class_name, class_room) values ('高三4班', NULL);
ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'class_room' cannot be null
2. 默认值
默认值:某一种数据会经常性的出现某个具体的值,可以在一开始就指定好,在需要真实数据的时候,用户可以选择性的使用默认值。
案例:建立一张人物信息表
mysql> create table if not exists t1(
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> age tinyint unsigned default 18,
-> gender char(1) default '男'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc t1;
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | 18 | |
| gender | char(1) | YES | | 男 | |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
我们先做全列插入:
mysql> insert into t1 (name, age, gender) values ('小红', 19, '女');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t1;
+--------+------+--------+
| name | age | gender |
+--------+------+--------+
| 小红 | 19 | 女 |
+--------+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
结果如下:

然后做缺省插入:
mysql> insert into t1 (name) values ('李四');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t1;
+--------+------+--------+
| name | age | gender |
+--------+------+--------+
| 小红 | 19 | 女 |
| 李四 | 18 | 男 |
+--------+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
可以看到,数据在插入的时候不给该字段赋值,就使用默认值。
我们重新建一张表,然后把 gender 字段,既设置了 not null,又设置了 default
mysql> create table if not exists t2(
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> age tinyint default 18,
-> gender char(1) not null default '男'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc t2;
+--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(4) | YES | | 18 | |
| gender | char(1) | NO | | 男 | |
+--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
思考一下:如果不指定 gender 的值会怎么样呢?
mysql> insert into t2 (name, age, gender) values ('小明', 20, '男');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t2 (name, age) values ('小红', 22);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from t1;
+--------+------+--------+
| name | age | gender |
+--------+------+--------+
| 小红 | 19 | 女 |
| 李四 | 18 | 男 |
+--------+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结果如下,可以看到 default 和 not null 不冲突,而是互相补充的。
另外,只有设置了 default 的列,才可以在插入值的时候,对列进行省略
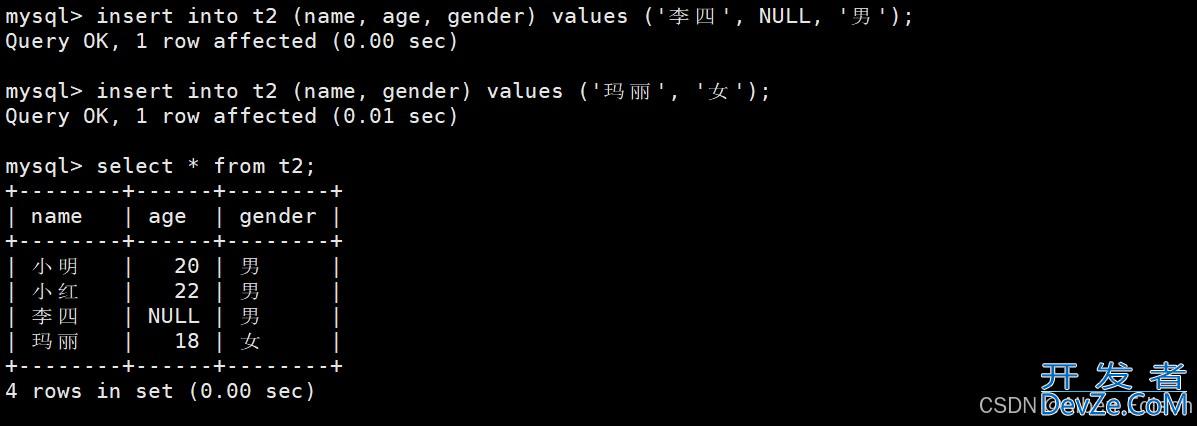
mysql> insert into t2 (name, age, gender) values ('李四', NULL, '男');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t2 (name, gender) values ('玛丽', '女');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from t2;
+--------+------+--------+
| name | age | gender |
+--------+------+--------+
| 小明 | 20 | 男 |
| 小红 | 22 | 男 |
| 李四 | NULL | 男 |
| 玛丽 | 18 | 女 |
+--------+------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结果如下:
另外,如果我们建表不指定约束,那么 MySQL 会默认给我们添加 default null,也就是可以省略。

3. 列描述
列描述:comment,没有实际含义,专门用来描述字段,会根据表创建语句保存,用来给程序员或 DBA 来进行了解。
还是先建一张表
mysql> create table if not exists t4(
-> name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名',
-> age tinyint unsigned default 18 comment '年龄',
-> gender char(1) default '男' comment '性别'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
注意:not null 和 defalut 一般不需要同时出现,因为 default 本身有默认值,不会为空。
我们可以插入一行数据,来验证看看:
mysql> insert into t4 (name) values ('android小明');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t4;
+--------+------+--------+
| name | age | gender |
+--------+------+--------+
| 小明 | 18 | 男 |
+--------+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
然后通过 desc 会发现查看不到注释信息:
mysql> desc t4; +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | | age | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | 18 | | | gender | char(1) | YES | | 男 | | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
我们要通过 show 才可以看到:
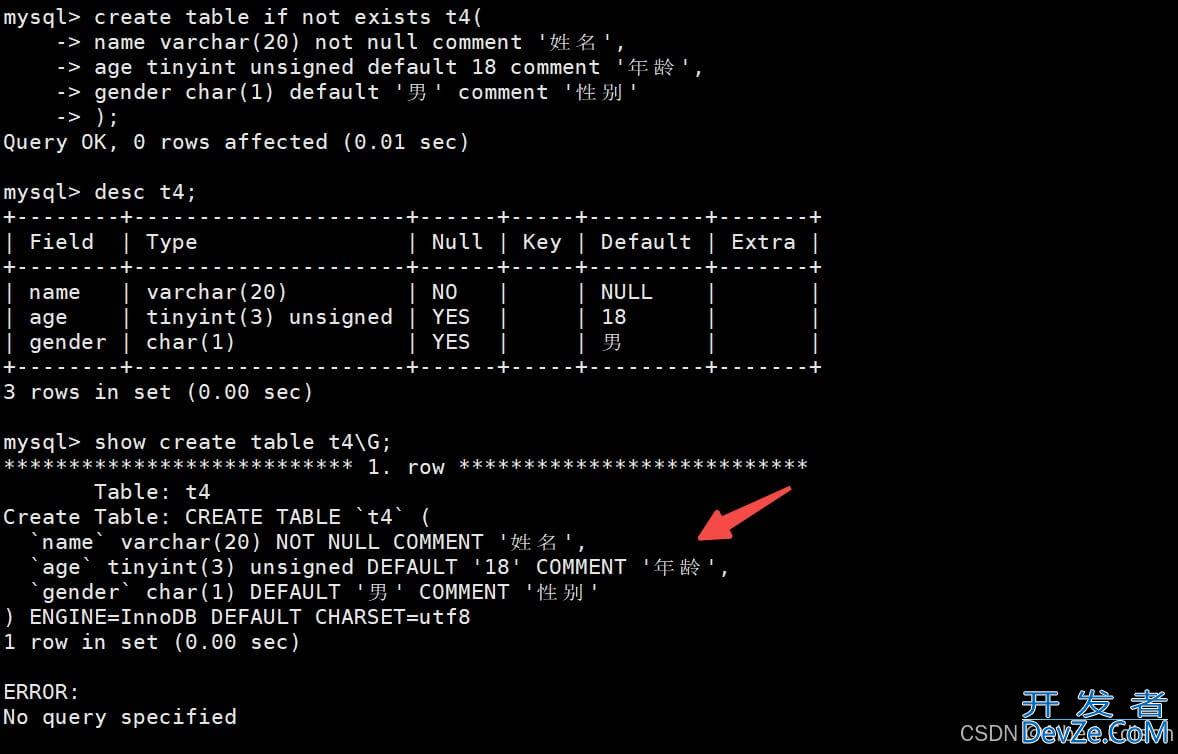
4. zerofill
刚开始学习数据库时,很多人对数字类型后面的长度很迷茫。我们先建一张表,通过 show 看看 t5 表的建表语句:
mysql> create table if not exists t5(
-> a int unsigned not null,
-> b int unsigned not null
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc t5;
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| a | int(10) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| b | int(10) unsigned | NO |编程客栈 | NULL | |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show create table t5\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t5
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t5` (
`a` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`b` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
结果如下:

可以看到 int(10) 这个代表什么意思呢?整型不是 4 字节码?这个 10 又代表什么呢?其实没有 zerofill 这个属性,括号内的数字 10 是毫无意义的。
a 和 b 列就是前面插入的数据,如下:
mysql> insert into t5 (a, b) values (1, 2); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t5; +---+---+ | a | b | +---+---+ | 1 | 2 | +---+---+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
但是对列添加了 zerofill 属性后,显示的结果就有所不同了。修改 t5 表的属性:
mysql> alter table t5 modify b int unsigned zerofill not null;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show create table t5\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t5
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t5` (
`a` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`b` int(10) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
对 b 列添加了 zerofill 属性,再进行查找,返回如下结果:
mysql> select * from t5; +---+------------+ | a | b | +---+------------+ | 1 | 0000000002 | +---+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
我们插入一行数据也能看到结果:

这次可以看到 b 的值由原来的 2 变成 0000000002,这就是 zerofill 属性的作用,如果宽度小于设定的宽度(这里设置的是 10),自动填充 0。
要注意的是,这只是最后显示的结果,在 MySQL 中实际存储的还是 2。为什么是这样呢?我们可以用 hex 函数来证明。
mysql> select b, hex(b) from t5; +------------+--------+ | b | hex(b) | +------------+--------+ | 0000000002 | 2 | | 0000000200 | C8 | +------------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
可以看出数据库内部存储的还是 2,0000000002 只是设置了 zerofill 属性后的一种格式化输出而已。
5. 主键
主键:primary key 用来唯一的约束该字段里面的数据,不能重复,不能为空,一张表中最多只能有一个主键;主键所在的列通常是整数类型。
5.1 指定主键
创建表的时候直接在字段上指定主键。
mysql> create table if not exists test_key (
-> id int unsigned primary key comment '学号不能为空',
-> name varchar(20) not null
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc test_key;
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到主键默认不能为空:

5.2 主键约束
主键对应的字段中不能重复,一旦重复,操作失败。
mysql> insert into test_key values (1, '小明'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from test_key; +----+--------+ | id | name | +----+--------+ | 1 | 小明 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into test_key values (1, '小红'); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY' mysql> insert into test_key values (2, '小红'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from test_key; +----+--------+ | id | name | +----+--------+ | 1 | 小明 | | 2 | 小红 | +----+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
另外,我们还可以根据主键来查找和修改:
mysql> select * from test_key where id=2; +----+--------+ | id | name | +----+--------+ | 2 | 小红 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> update test_key set name='玛丽' where id=2; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.30 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from test_key; +----+--------+ | id | name | +----+--------+ | 1 | 小明 | | 2 | 玛丽 | +----+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
5.3 删除主键
我现在把 test_key 表的主键给删除掉
mysql> alter table test_key drop primary key; Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.05 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> desc test_key; +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(10) unsigned | NO | | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
此时,可以插入 id 相同的值了:

5.4 追加主键
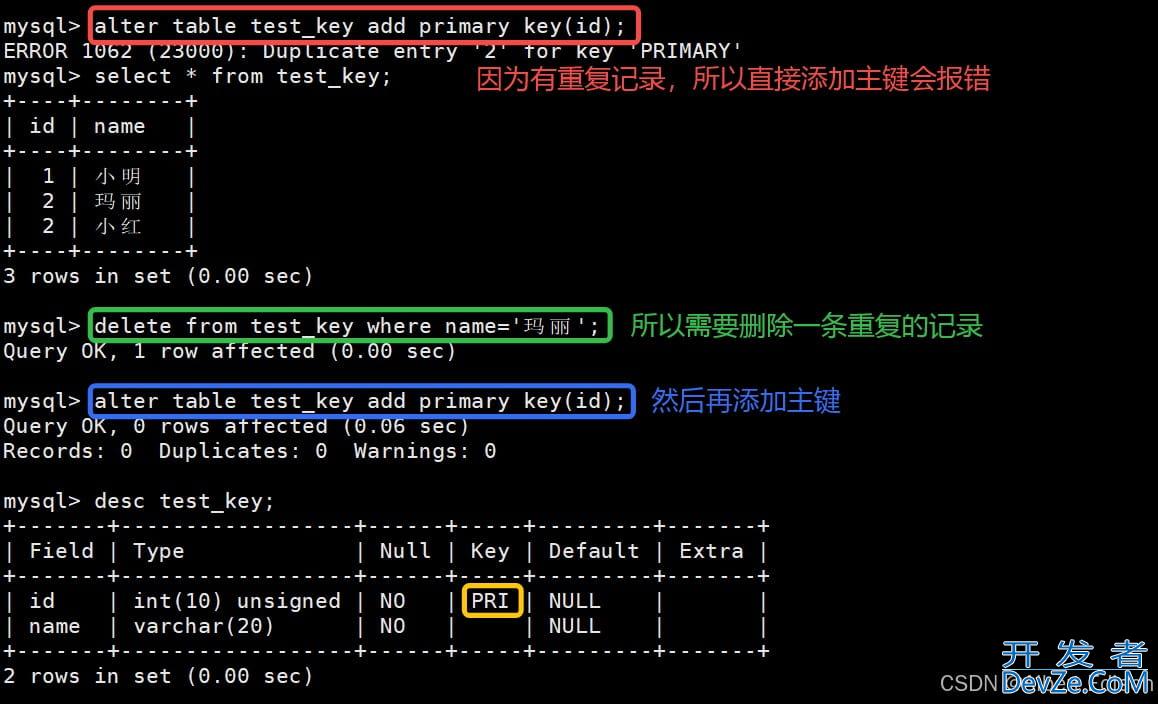
当表创建好以后,但是没有主键的时候,可以再次追加主键。
我们可以给 test_key 的 id 重新添加主键,但是记得把表里面重复的记录给删除掉
mysql> alter table test_key add primary key(id); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> desc test_key; +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
结果如下:
5.5 复合主键
在创建表的时候,在所有字段之后,使用 primary key(主键字段列表)来创建主键,如果有多个字段作为主键,可以使用复合主键。
也就是说,一个主键可以被添加到一列,或者多列上。
案例如下,我建一张课程表,然后把学号和课程号都设置主键
mysql> create table pick_course (
-> id int unsigned comment '学号',
-> course char(10) comment '课程代码',
-> score tinyint unsigned comment '成绩',
-> primary key(id, course)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc pick_course;
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| course | char(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| score | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注意:有两个 PRI 不代表有两个主键,而是说明这两个都是主键,也就是说,它俩合起来才算一个主键。
插入数据进行验证:
mysql> insert into pick_course values(001, 085410, 90); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into pick_course values(002, 085410, 85); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into pick_course values(001, 085411, 95); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from pick_course; +----+--------+-------+ | id | course | score | +----+--------+-------+ | 1 | 85410 | 90 | | 1 | 85411 | 95 | | 2 | 85410 | 85 | +----+--------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into pick_course values(001, 085410, 100); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1-85410' for key 'PRIMARY' mysql> insert into pick_course values(002, 085410, 100); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '2-85410' for key 'PRIMARY'
可以看到 id 和 course 必须为不同的值,才可以插入数据:

6. 自增长
auto_increment:当对应的字段,不给值,会自动的被系统触发,系统会从当前字段中已经有的最大值 +1 操作,得到一个新的不同的值。通常和主键搭配使用,作为逻辑主键。
自增长的特点:
- 任何一个字段要js做自增长,前提是本身是一个索引(key 一栏有值)。
- 自增长字段必须是整数。
- 一张表最多只能有一个自增长。
先创建一个表
mysql> create table if not exists t6 (
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc t6;
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
然后开始插入数据
mysql> insert into t6(name) values ('a');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t6(name) values ('b');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t6(name) values ('c');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t6;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | a |
| 2 | b |
| 3 | c |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
如果不指定 id 的话,是默认从 1 开始的,但是我们指定 id 为 1000 的话,那么下次 id 就会变为 1001:
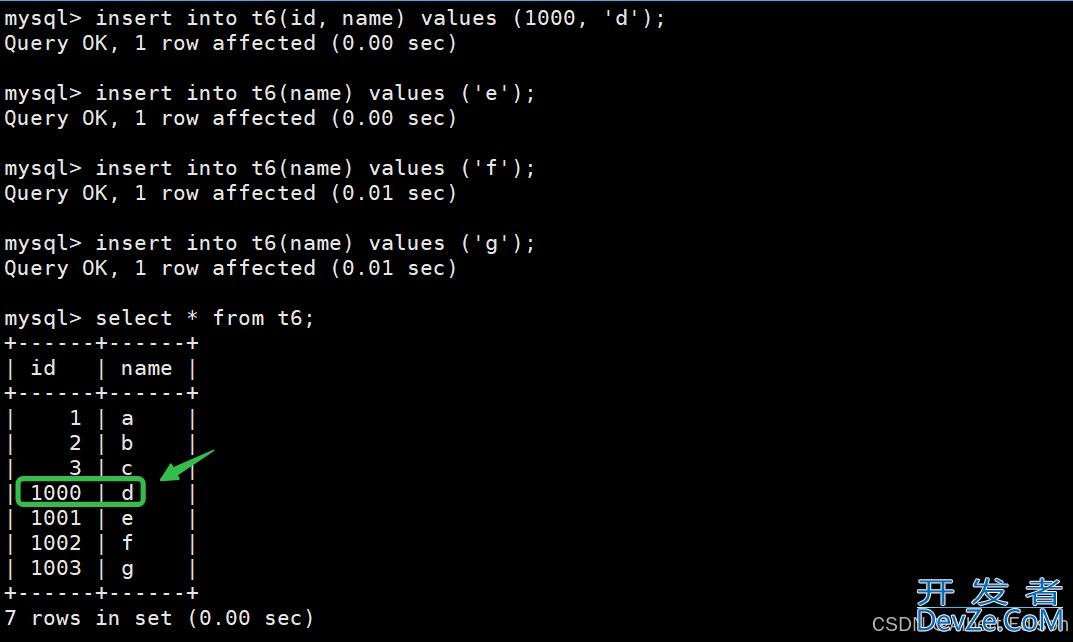
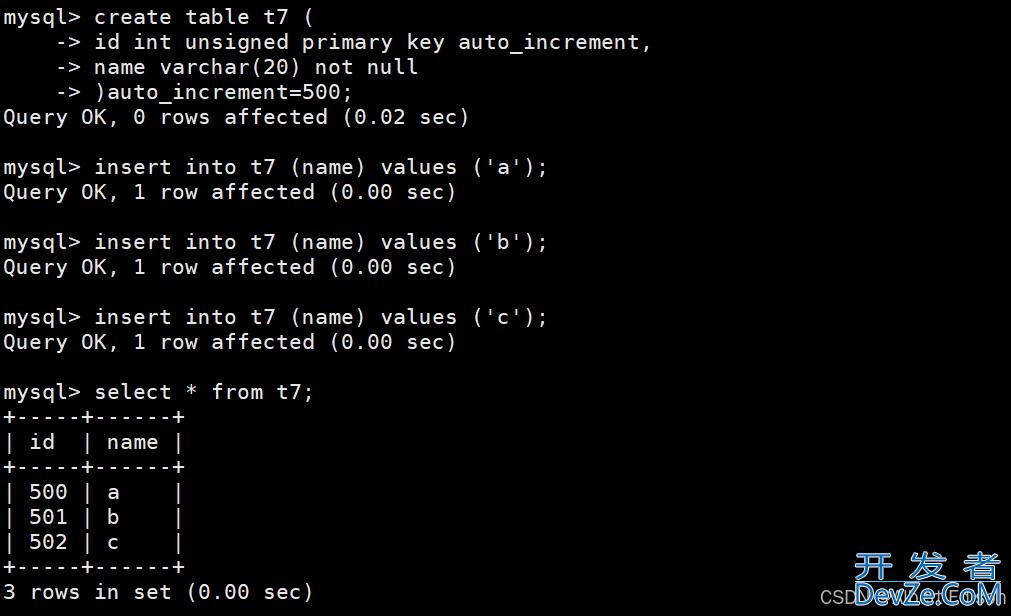
另外,我们在建表的时候,还可以指定 auto_increment 的初始值:
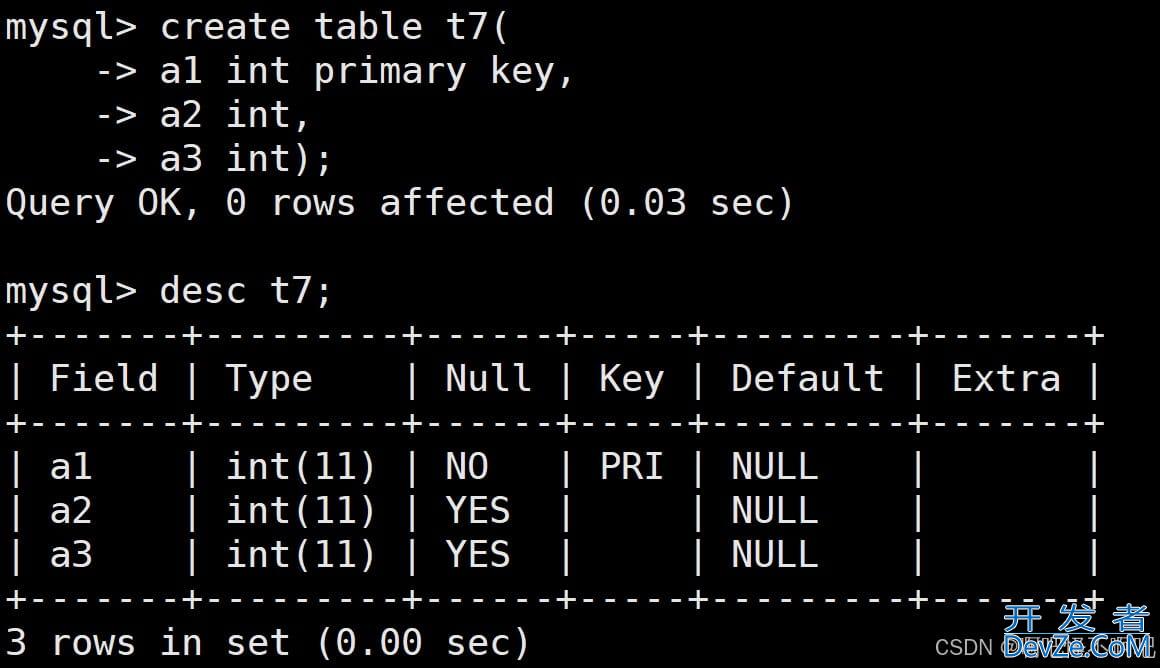
mysql> create table t7 (
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null
-> )auto_increment=500;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
结果如下:
在插入后获取上次插入的 AUTO_INCREMENT 的值(批量插入获取的是第一个值)
mysql> select last_insert_id(); +------------------+ | last_insert_id() | +------------------+ | 3 | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
6.1 索引
这里可以简单的谈一下索引。
在关系数据库中,索引是一种单独的、物理的对数据库表中一列或多列的值进行排序的一种存储结构,它是某个表中一列或若干列值的集合和相应的指向表中物理标识这些值的数据页的逻辑指针清单。
索引的作用相当于图书的目录,可以根据目录中的页码快速找到所需的内容。索引提供指向存储在表的指定列中的数据值的指针,然后根据您指定的排序顺序对这些指针排序。
数据库使用索引以找到特定值,然后顺指针找到包含该值的行。这样可以使对应于表的 SQL 语句执行得更快,可快速访问数据库表中的特定信息。
7. 唯一键
一张表中有往往有很多字段需要唯一性,数据不能重复,但是一张表中只能有一个主键:唯一键就可以解决表中有多个字段需要唯一性约束的问题。
唯一键的本质和主键差不多,唯一键允许为空,而且可以多个为空,空字段不做唯一性比较。
我们先建立一张拥有唯一键的学生表
mysql> create table stu (
-> id char(20) unique comment '这是一个学生的唯一键',
-> name varchar(32) not null
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc stu;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | char(20) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
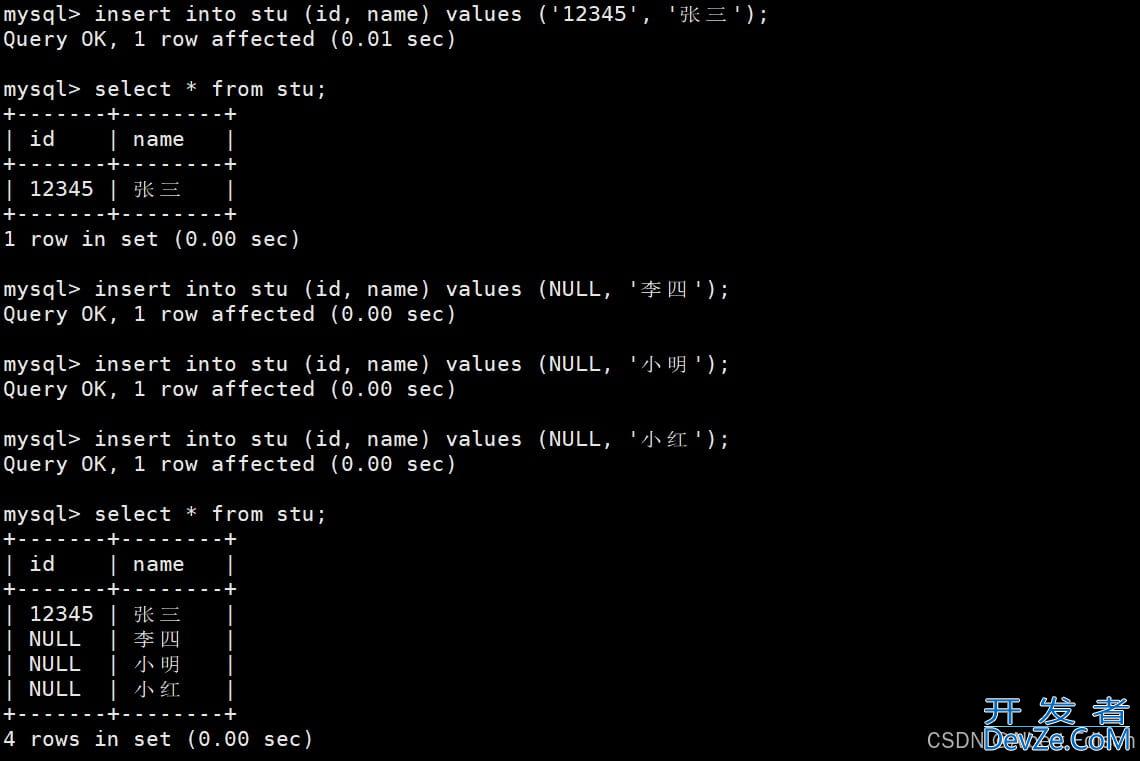
然后进行数据的插入:
mysql> insert into stu (id, name) values ('12345', '张三');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from stu;
+-------+--------+
| id | name |
+-------+--------+
| 12345 | 张三 |
+-------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu (id, name) values (NULL, '李四');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
结果如下:
我们再来建一张表:
mysql> create table student(
-> id char(20) primary key,
-> name varchar(32) not null,
-> telphone char(20) unique key,
-> qq varchar(64) unique key
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc student;
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | char(20) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | |
| telphone | char(20) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| qq | varchar(64) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
当我们设置了唯一键可以,可以避免一些未定义或者误操作,从而保证插入表里面的数据不一样:

关于唯一键和主键的区别:
- 我们可以简单理解成,主键更多的是标识唯一性的。
- 而唯一键更多的是保证在业务上,不要和别的信息出现重复。
乍一听好像没啥区别,我们举一个例子,假设一个场景:
- 比如在公司,我们需要一个员工管理系统,系统中有一个员工表,员工表中有两列信息,一个身份证号码,一个是员工工号,我们可以选择身份号码作为主键。
- 而我们设计员工工号的时候,需要一种约束:而所有的员工工号都不能重复。具体指的是在公司的业务上不能重复,我们设计表的时候,需要这个约束,那么就可以将员工工号设计成为唯一键。
- 一般而言,我们建议将主键设计成为和当前业务无关的字段,这样,当业务调整的时候,我们可以尽量不会对主键做过大的调整。
8. 外键
外键用于定义主表和从表之间的关系:外键约束主要定义在从表上,主表则必须是有主键约束或 unique 约束。当定义外键后,要求外键列数据必须在主表的主键列存在或为 null。
语法:
foreign key (字段名) references 主表(列)
案例如下图所示:
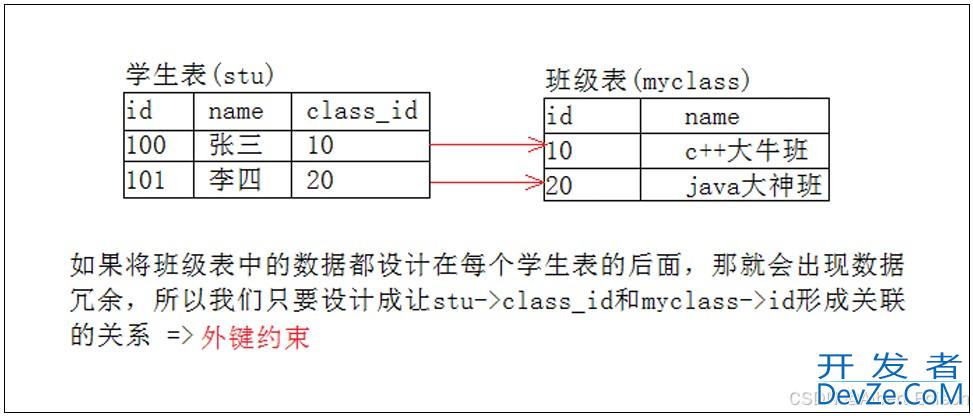
对上面的示意图进行设计:
- 先创建主键表
mysql> create table if not exists class (
-> id int primary key,
-> name varchar(32) not null
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc class;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 再创建从表
指明我们的外键列为 class_id,并且将外键这一列和我们的主表当中的 id 列建立我们的外键约束关系
mysql> create table if not exists student (
-> id int unsigned primary key,
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> telphone varchar(32) unique key,
-> class_id int,
-> foreign key(class_id) references class(id)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> desc student;
+----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| telphone | varchar(32) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| class_id | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
+----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 正常插入数据
先在对 class 表插入数据
mysql> desc class; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into class values (1, '人工智能101'), (2, '人工智能102'); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from class; +----+-----------------+ | id | name | +----+-----------------+ | 1 | 人工智能101 | | 2 | 人工智能102 | +----+-----------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
然后再对学生表插入数据
mysql> insert into student (id, name, telphone, class_id) values (212001, '张三', '12345', 1); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into student (id, name, telphone, class_id) values (212002, '李四', '12346', 2); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | id | name | telphone | class_id | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | 212001 | 张三 | 12345 | 1 | | 212002 | 李四 | 12346 | 2 | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 插入一个班级号为 3 的学生,因为没有这个班级,所以插入不成功
mysql> insert into student (id, name, telphone, class_id) values (212003, '王五', '12347', 3); ERROR 1452 (23000): Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails (`test_db`.`student`, CONSTRAINT `student_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`id`))
- 假设我现在要删除 人工智能101班,但是因为班里面有学生,所以无法删除,这就是外键约束
mysql> select * from student; +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | id | name | telphone | class_id | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | 212001 | 张三 | 12345 | 1 | | 212002 | 李四 | 12346 | 2 | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from class; +----+-----------------+ | id | name | +----+-----------------+ | 1 | 人工智能101 | | 2 | 人工智能102 | +----+-----------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> delete from class where id=1; ERROR 1451 (23000): Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`test_db`.`student`, CONSTRAINT `student_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`id`))
我们只有把班级里面的学生删除,然后删除班级
mysql> delete from student where id=212001; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | id | name | telphone | class_id | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | 212002 | 李四 | 12346 | 2 | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> delete from class where id=1; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from class; +----+-----------------+ | id | name | +----+-----------------+ | 2 | 人工智能102 | +----+-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- 插入班级 id 为 null,比如来了一个学生,目前还没有分配班级
mysql> insert into student values(212003, '赵六', '12349', null); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | id | name | telphone | class_id | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ | 212002 | 李四 | 12346 | 2 | | 212003 | 赵六 | 12349 | NULL | +--------+--------+----------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
所以外键的本质:
- 1、产生关联。
- 2、增加约束,来整体保证表跟表之间的完整性。
8.1 如何理解外键约束
首先我们承认,这个世界是数据很多都是相关性的。
理论上,上面的例子,我们不创建外键约束,就正常建立学生表,以及班级表,该有的字段我们都有。
此时,在实际使用的时候,可能会出现什么问题?
有没有可能插入的学生信息中有具体的班级,但是该班级却没有在班级表中?
比如计算机学院的人工智能专业只开了【人工智能 1 班】和【人工智能 2 班】,但是在上课的学生里面竟然有【人工智能 3 班】的学生(这个班目前并不存在),这很明显是有问题的。
因为此时两张表在业务上是有相关性的,但是在业务上没有建立约束关系,那么就可能出现问题。
解决方案就是通过外键完成的。建立外键的本质其实就是把相关性交给 MySQL 去审核了,提前告诉 MySQL 表之间的约束关系,那么当用户插入不符合业务逻辑的数据的时候,MySQL 不允许你插入。
9. 综合案例
有一个商店的数据,记录客户及购物情况,有以下三个表组成:
1️⃣ 商品表 goods:
- 商品编号 goods_id
- 商品名 goods_name
- 单价 unitprice
- 商品类别 category
- 供应商 provider
2️⃣ 客户表 customer:
- 客户号 customer_id
- 姓名 name
- 住址 address
- 邮箱 email
- 性别 sex
- 身份证 card_id
3️⃣ 购买表 purchase:
- 购买订单号 order_id
- 客户号 customer_id
- 商品号 goods_id
- 购买数量 nums
要求:
- 每个表的主外键
- 客户的姓名不能为空值
- 邮箱不能重复
- 客户的性别(男,女)
先创建一个数据库:
mysql> create database if not exists store; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> use store; Database changed
9.1 创建商品表
mysql> create table if not exists goods (
-> goods_id int primary key auto_increment comment '商品编号',
-> goods_name varchar(32) not null comment '商品名称',
-> unitprice int not null default 0 comment '单价,单位分',
-> category varchar(12) comment '商品分类',
-> provider varchar(64) not null comment '供应商名称'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc goods;
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| goods_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| goods_name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | |
| unitprice | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| category | varchar(12) | YES | | NULL | |
| provider | varchar(64) | NO | | NULL | |
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注意:
- 主键(Primary Key):goods_id
- 外键(Foreign Key):无(此表是被引用方)。
9.2 创建客户表
mysql> create table if not exists customer (
-> customer_id int primary key auto_increment comment '客户编号',
-> name varchar(32) not null comment '客户姓名',
-> address varchar(256) comment '客户地址',
-> email varchar(64) unique key comment '电子邮箱',
-> sex enum('男', '女') not null comment '性别',
-> card_id char(18) unique key comment '身份证'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc customer;
+-------------+-------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+-------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| customer_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | |
| address | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(64) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| sex | enum('男','女') | NO | | NULL | |
| card_id | char(18) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
+-------------+-------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注意:
- 主键(Primary Key):customer_id
- 外键(Foreign Key):无(此表是被引用方)。
- 唯一约束(Unique Key):email、card_id。
9.3 创建购买表
mysql> create table if not exists purchase (
-> order_id int primary key auto_increment comment '订单号',
-> customer_id int comment '客户编号',
-> goods_id int comment '商品编号',
-> nums int default 0 comment '购买数量',
-> foreign key (customer_id) references customer(customer_id),
-> foreign key (goods_id) references goods(goods_id)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc purchase;
+-------------+---------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+---------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| order_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| customer_id | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| goods_id | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| nums | int(11) | YES | | 0 | |
+-------------+---------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注意:
- 主键(Primary Key):order_id
- 外键(Foreign Key):
- customer_id → 关联到 customer.customer_id,表示 “谁买的”。
- goods_id → 关联到 goods.goods_id,表示 “买的什么”。
9.4 主键和外键
| 表名 | 主键 | 外键 | 外键关联 |
|---|---|---|---|
| goods | goods_id | — | — |
| customer | customer_id | — | — |
| purchase | order_id | customer_id, goods_id | customer(customer_id), goods(goods_id) |
关系图示:
customer (客户表)
│
│ customer_id ←───┐
│ │
└──────────────────▶ purchase (购买表) ───▶ goods (商品表)
▲ │
│ goods_id │
└──────────────────────┘
注意:
- 一个客户(customer)可以有多笔订单(purchase)。
- 一个商品(goods)可以被多笔订单购买。
- 所以这是一个 多对多关系,中间的 purchase 表是 关联表。
9.5 插入数据
插入商品表 goods
mysql> insert into goods (goods_name, unitprice, category, provider) values
-> ('苹果', 500, '水果', '青岛果业有限公司'),
-> ('香蕉', 300, '水果', '海南香蕉集团'),
-> ('牛奶', 450, '饮品', '伊利实业股份有限公司'),
-> ('洗发水', 1200, '日用品', '宝洁公司'),
-> ('牙膏', 800, '日用品', '高露洁公司');
Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from goods;
+----------+------------+-----------+-----------+--------------------------------+
| goods_id | goods_name | unitprice | category | provider |
+----------+------------+-----------+-----------+--------------------------------+
| 1 | 苹果 | 500 | 水果 | 青岛果业有限公司 |
| 2 | 香蕉 | 300 | 水果 | 海南香蕉集团 |
| 3 | 牛奶 | 450 | 饮品 | 伊利实业股份有限公司 |
| 4 | 洗发水 | 1200 | 日用品 | 宝洁公司 |
| 5 | 牙膏 | 800 | 日用品 | 高露洁公司 |
+----------+------------+-----------+-----------+--------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
插入客户表 customer
mysql> insert ipythonnto customer (name, address, email, sex, card_id) values
-> ('张三', '北京市海淀区中关村1号', 'zhangsan@example.com', '男', '110101199001010011'),
-> ('李四', '上海市浦东新区世纪大道100号', 'lisi@example.com', '女', '310101199212123456'),
-> ('王五', '广州市天河区花城大道88号', 'wangwu@example.com', '男', '440101198805056789');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+-----+--------------------+
| customer_id | name | address | email | sex | card_id |
+-------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+-----+--------------------+
| 1 | 张三 | 北京市海淀区中关村1号 | zhangsan@example.com | 男 | 110101199001010011 |
| 2 | 李四 | 上海市浦东新区世纪大道100号 | lisi@example.com | 女 | 310101199212123456 |
| 3 | 王五 | 广州市天河区花城大道88号 | wangwu@example.com | 男 | 440101198805056789 |
+-------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+-----+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
插入购买表 purchase(需要使用上面插入的主键)
mysql> insert into purchase (customer_id, goods_id, nums) values
-> (1, 1, 5), -- 张三 买了 5 个 苹果
-> (1, 3, 2), -- 张三 买了 2 盒 牛奶
-> (2, 2, 10), -- 李四 买了 10 根 香蕉
-> (2, 4, 1), -- 李四 买了 1 瓶 洗发水
-> (3, 5, 3); -- 王五 买了 3 支 牙膏
Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from purchase;
+----------+-------------+----------+------+
| order_id | customer_id | goods_id | nums |
+----------+-------------+----------+------+
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 10 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
+----------+-------------+----------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
9.6 验证外键和关联查询
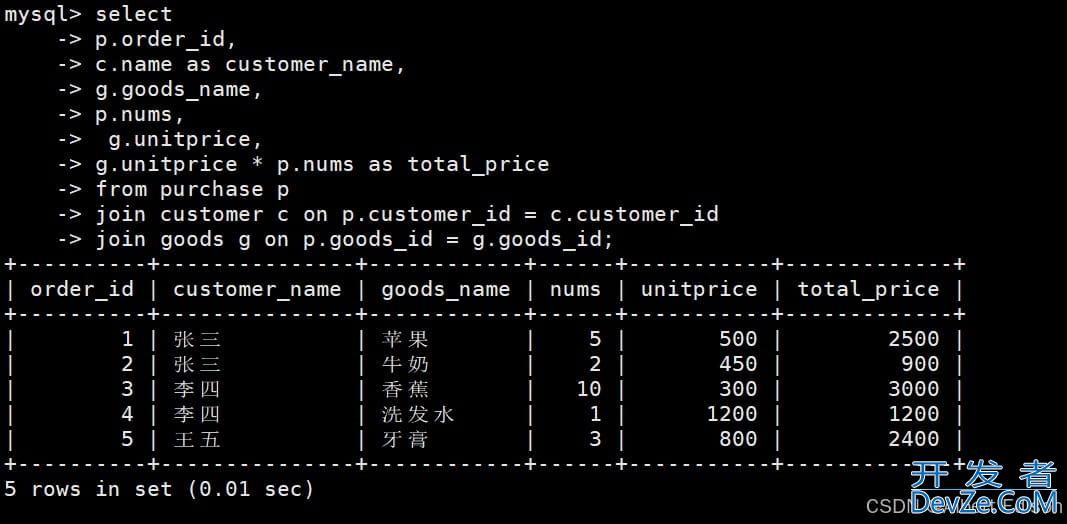
执行以下 SQL 语句看看结果是否正确:
-- 查询所有订单及关联信息
mysql> select
-> p.order_id,
-> c.name as customer_name,
-> g.goods_name,
-> p.nums,
-> g.unitprice,
-> g.unitprice * p.nums as total_price
-> from purchase p
-> join customer c on p.customer_id = c.customer_id
-> join goods g on p.goods_id = g.goods_id;
查询结果如下:
到此这篇关于MySQL表的约束的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql表的约束内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!



 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论