How to find nth occurrence of character in a string?
Similar to a question posted here, am looking for a solution in Java.
That is, how to find the index of nth occurrence of a character/string from a string?
Example: "/folder1/folder2/folder3/". In this case, if I ask for 3rd occurrence of slash (/), it appears before folder3, and I expect to return this index position. My actual intention is to substring it from nth occurrence of a character.
Is there any con开发者_Python百科venient/ready-to-use method available in Java API or do we need to write a small logic on our own to solve this?
Also,
- I quickly searched whether any method is supported for this purpose at Apache Commons Lang's StringUtils, but I don't find any.
- Can regular expressions help in this regard?
If your project already depends on Apache Commons you can use StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf, otherwise, here's an implementation:
public static int ordinalIndexOf(String str, String substr, int n) {
int pos = str.indexOf(substr);
while (--n > 0 && pos != -1)
pos = str.indexOf(substr, pos + 1);
return pos;
}
This post has been rewritten as an article here.
I believe the easiest solution for finding the Nth occurrence of a String is to use StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf() from Apache Commons.
Example:
StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf("aabaabaa", "b", 2) == 5
Two simple options occur:
- Use
charAt()repeatedly - Use
indexOf()repeatedly
For example:
public static int nthIndexOf(String text, char needle, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++)
{
if (text.charAt(i) == needle)
{
n--;
if (n == 0)
{
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
That may well not perform as well as using indexOf repeatedly, but it's possibly simpler to get right.
You can try something like this:
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(from3rd("/folder1/folder2/folder3/"));
}
private static Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(/[^/]*){2}/([^/]*)");
public static String from3rd(String in) {
Matcher m = p.matcher(in);
if (m.matches())
return m.group(2);
else
return null;
}
}
Note that I did some assumptions in the regex:
- the input path is absolute (i.e. starts with "/");
- you do not need the 3rd "/" in the result.
As requested in a comment, I'll try to explain the regex: (/[^/]*){2}/([^/]*)
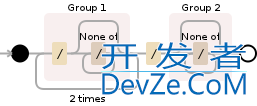
/[^/]*is a/followed by[^/]*(any number of characters that are not a/),(/[^/]*)groups the previous expression in a single entity. This is the1st group of the expression,(/[^/]*){2}means that the group must match extactly{2}times,[^/]*is again any number of characters that are not a/,([^/]*)groups the previos expression in a single entity. This is the2nd group of the expression.
This way you have only to get the substring that matches the 2nd group: return m.group(2);
Image courtesy by Debuggex
I made a few changes to aioobe's answer and got a nth lastIndexOf version, and fix some NPE problems. See code below:
public int nthLastIndexOf(String str, char c, int n) {
if (str == null || n < 1)
return -1;
int pos = str.length();
while (n-- > 0 && pos != -1)
pos = str.lastIndexOf(c, pos - 1);
return pos;
}
([.^/]*/){2}[^/]*(/)
Match anything followed by / two times, then again. The third one is the one you want
The Matcher state can be used to tell where the last / is
May be you could achieve this through String.split(..) method also.
String str = "";
String[] tokens = str.split("/")
return tokens[nthIndex] == null
Nowadays there IS support of Apache Commons Lang's StringUtils,
This is the primitive:
int org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf(CharSequence str, CharSequence searchStr, int ordinal)
for your problem you can code the following: StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf(uri, "/", 3)
You can also find the last nth occurrence of a character in a string with the lastOrdinalIndexOf method.
public static int nth(String source, String pattern, int n) {
int i = 0, pos = 0, tpos = 0;
while (i < n) {
pos = source.indexOf(pattern);
if (pos > -1) {
source = source.substring(pos+1);
tpos += pos+1;
i++;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
return tpos - 1;
}
Another approach:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "/folder1/folder2/folder3/";
int index = nthOccurrence(str, '/', 3);
System.out.println(index);
}
public static int nthOccurrence(String s, char c, int occurrence) {
return nthOccurrence(s, 0, c, 0, occurrence);
}
public static int nthOccurrence(String s, int from, char c, int curr, int expected) {
final int index = s.indexOf(c, from);
if(index == -1) return -1;
return (curr + 1 == expected) ? index :
nthOccurrence(s, index + 1, c, curr + 1, expected);
}
This answer improves on @aioobe 's answer. Two bugs in that answer were fixed.
1. n=0 should return -1.
2. nth occurence returned -1, but it worked on n-1th occurences.
Try this !
public int nthOccurrence(String str, char c, int n) {
if(n <= 0){
return -1;
}
int pos = str.indexOf(c, 0);
while (n-- > 1 && pos != -1)
pos = str.indexOf(c, pos+1);
return pos;
}
My solution:
/**
* Like String.indexOf, but find the n:th occurance of c
* @param s string to search
* @param c character to search for
* @param n n:th character to seach for, starting with 1
* @return the position (0-based) of the found char, or -1 if failed
*/
public static int nthIndexOf(String s, char c, int n) {
int i = -1;
while (n-- > 0) {
i = s.indexOf(c, i + 1);
if (i == -1)
break;
}
return i;
}
public class Sam_Stringnth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="abcabcabc";
int n = nthsearch(str, 'c', 3);
if(n<=0)
System.out.println("Character not found");
else
System.out.println("Position is:"+n);
}
public static int nthsearch(String str, char ch, int n){
int pos=0;
if(n!=0){
for(int i=1; i<=n;i++){
pos = str.indexOf(ch, pos)+1;
}
return pos;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
}
APACHE IMPLEMENTATION (copy-paste: don't import a whole library for one function!)
Here is the exact Apache Commons implementation decoupled from their StringUtils library (so that you can just copy paste this and don't have to add a dependency for the library for just one function):
/**
* <p>Finds the n-th index within a String, handling {@code null}.
* This method uses {@link String#indexOf(String)} if possible.</p>
* <p>Note that matches may overlap<p>
*
* <p>A {@code null} CharSequence will return {@code -1}.</p>
*
* @param str the CharSequence to check, may be null
* @param searchStr the CharSequence to find, may be null
* @param ordinal the n-th {@code searchStr} to find, overlapping matches are allowed.
* @param lastIndex true if lastOrdinalIndexOf() otherwise false if ordinalIndexOf()
* @return the n-th index of the search CharSequence,
* {@code -1} if no match or {@code null} string input
*/
private static int ordinalIndexOf(final String str, final String searchStr, final int ordinal, final boolean lastIndex) {
if (str == null || searchStr == null || ordinal <= 0) {
return -1;
}
if (searchStr.length() == 0) {
return lastIndex ? str.length() : 0;
}
int found = 0;
// set the initial index beyond the end of the string
// this is to allow for the initial index decrement/increment
int index = lastIndex ? str.length() : -1;
do {
if (lastIndex) {
index = str.lastIndexOf(searchStr, index - 1); // step backwards thru string
} else {
index = str.indexOf(searchStr, index + 1); // step forwards through string
}
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
found++;
} while (found < ordinal);
return index;
}
/* program to find nth occurence of a character */
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CharOccur1
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Scanner scr=new Scanner(System.in);
int position=-1,count=0;
System.out.println("enter the string");
String str=scr.nextLine();
System.out.println("enter the nth occurence of the character");
int n=Integer.parseInt(scr.next());
int leng=str.length();
char c[]=new char[leng];
System.out.println("Enter the character to find");
char key=scr.next().charAt(0);
c=str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++)
{
if(c[i]==key)
{
count++;
position=i;
if(count==n)
{
System.out.println("Character found");
System.out.println("the position at which the " + count + " ocurrence occurs is " + position);
return;
}
}
}
if(n>count)
{
System.out.println("Character occurs "+ count + " times");
return;
}
}
}
The code returns the nth occurrence positions substring aka field width. Example. if string "Stack overflow in low melow" is the string to search 2nd occurance of token "low", you will agree with me that it 2nd occurance is at subtring "18 and 21". indexOfOccurance("Stack overflow in low melow", low, 2) returns 18 and 21 in a string.
class Example{
public Example(){
}
public String indexOfOccurance(String string, String token, int nthOccurance) {
int lengthOfToken = token.length();
int nthCount = 0;
for (int shift = 0,count = 0; count < string.length() - token.length() + 2; count++, shift++, lengthOfToken++)
if (string.substring(shift, lengthOfToken).equalsIgnoreCase(token)) {
// keeps count of nthOccurance
nthCount++;
if (nthCount == nthOccurance){
//checks if nthCount == nthOccurance. If true, then breaks
return String.valueOf(shift)+ " " +String.valueOf(lengthOfToken);
}
}
return "-1";
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Example example = new Example();
String string = "the man, the woman and the child";
int nthPositionOfThe = 3;
System.out.println("3rd Occurance of the is at " + example.indexOfOccurance(string, "the", nthPositionOfThe));
}
}
public static int findNthOccurrence(String phrase, String str, int n)
{
int val = 0, loc = -1;
for(int i = 0; i <= phrase.length()-str.length() && val < n; i++)
{
if(str.equals(phrase.substring(i,i+str.length())))
{
val++;
loc = i;
}
}
if(val == n)
return loc;
else
return -1;
}
//scala
// throw's -1 if the value isn't present for nth time, even if it is present till n-1 th time. // throw's index if the value is present for nth time
def indexOfWithNumber(tempString:String,valueString:String,numberOfOccurance:Int):Int={
var stabilizeIndex=0
var tempSubString=tempString
var tempIndex=tempString.indexOf(valueString)
breakable
{
for ( i <- 1 to numberOfOccurance)
if ((tempSubString.indexOf(valueString) != -1) && (tempIndex != -1))
{
tempIndex=tempSubString.indexOf(valueString)
tempSubString=tempSubString.substring(tempIndex+1,tempSubString.size) // ADJUSTING FOR 0
stabilizeIndex=stabilizeIndex+tempIndex+1 // ADJUSTING FOR 0
}
else
{
stabilizeIndex= -1
tempIndex= 0
break
}
}
stabilizeIndex match { case value if value <= -1 => -1 case _ => stabilizeIndex-1 } // reverting for adjusting 0 previously
}
indexOfWithNumber("bbcfgtbgft","b",3) // 6
indexOfWithNumber("bbcfgtbgft","b",2) //1
indexOfWithNumber("bbcfgtbgft","b",4) //-1
indexOfWithNumber("bbcfgtbcgft","bc",1) //1
indexOfWithNumber("bbcfgtbcgft","bc",4) //-1
indexOfWithNumber("bbcfgtbcgft","bc",2) //6
It looks like the string you want to substring is a file path. Can't you just split by / and then consume the array entries from the point of interest onward? For example,
String folders = "/folder1/folder2/folder3/".split('/');
StringBuilder subStringed = new StringBuilder('/');
for (int i = 2; i < folders.length; i++) {
subStringed.append(folders[i]).append('/').;
}
System.out.println(subStringed.toString());
static int nthOccurrenceOfChar(String str, int n, char ch) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
if (str.charAt(i) == ch && ++count == n)
return i;
return -1;
}
Yes, Regular Expressions definetly help in this regard!
To get a substring of everything after the nth occurrence, use this simple one-liner:
public static String afterNthOccurance(String string, char ch, int n) {
return string.replaceAll("^([^"+ch+"]*"+ch+"){"+n+"}", "");
}
For anyone who actually wants the index of the nth occurance, you can use this:
public static int nthIndex(String string, char ch, int n) {
return string.length()-string.replaceAll("^([^"+ch+"]*"+ch+"){"+n+"}", "").length()-1;
}
 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论