Android动态加载布局实现技巧介绍
目录
- 使用限定符
- 使用最小宽度限定符
使用限定符
在平板上面大多数时候采用的双页的模式,程序会在左侧列表上显示一个包含子项列表,右侧的面版会显示详细的内容的因为平板具有足够大的屏幕.完全能够显示两页的内容.但是在手机上手机只能显示一页的内容,因此需要两个页面分开显示.
- 在运行时判断程序应该使用双页模式还是单页模式,需要借助限定符==(qualifier)==来进行实现.
- 在layout/activity_main.XML中只包含一个Fragment,即单页模式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
javascript android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFrag"
android:name="com.zb.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
创建一个layout_large目录,在这个目录下创建一个同样名为activity_main.xml的文件,但是在该布局当中包含两个Fragment,即双页模式.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFrag"
android:name="com.zb.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/rightFrag"
android:name="com.zb.fragmenttest.RightFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="matc开发者_开发培训h_parent"
android:layout_weight="3" />
</LinearLayout>
- 解决在Android开发中layout_large目录下不能创建xml文件的方法:https://blog.csdn.net/CEVERY/article/details/86593814
- 其中large就是一个限定符,那些屏幕被认为是large的设备就睡加载layout_large文件夹下的布局,小屏幕设备则还是会加载layout文件夹下面的布局.
- 这样就可以实现动态加载布局的功能.
- 安卓中常见的限定符
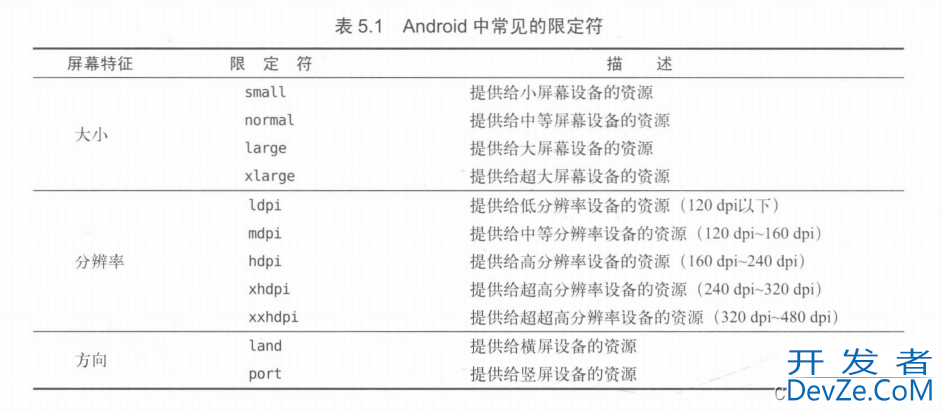
使用最小宽度限定符
- 最小宽度限定符,允许我们对屏幕的宽度指定一个最小值(以dp为单位)
- 然后以这个最小值为临界点.屏幕宽度大于这个值得设备就加载一个布局
- 屏幕宽度小于这个值得就加载另外一个布局
- 在res目录下新家一个layout-sw600dp文件夹,然后在这个文件夹下面建一个activity_main.xml布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LineajavascriptrLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="manGiJhztch_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFragjavascript"
android:name="com.zb.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:name="com.zb.fragmenttest.RightFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3" />
</LinearLayout>
这就意味着,当程序运行在屏幕宽度大于等于600dp的设备上时,会加载layout_sw600dp/activity_main布局,当程序运行在屏幕宽度小于600编程客栈dp的设备上的时候,则仍然加载默认的layout/activity_main布局.
到此这篇关于Android动态加载布局实现技巧介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android动态加载布局内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论