Label Propagation算法原理示例解析
目录
- 1. 概述
- 2. Label Propagation算法
- 2.1. Label Propagation算法概述
- 2.2. Label Propagation算法原理
- 3.3. Label Propagation算法过程
- 3. 实验
- 3.1. 数据描述
- 3.2. 实验代码
- 3.3. 代码解析
- 4. 实验结果
1. 概述
对于社区,没有一个明确的定义,有很多对社区的定义,如社区是指在一个网络中,有一组节点,它们彼此都相似,而组内的节点与网络中的其他节点则不相似。更为一般的可以表述为:社区是指网络中节点的集合,这些节点内部连接较为紧密而外部连接较为稀疏。
基于上述的形象的表示,出现了很多的社区划分算法,如Fast Unfolding算法[1],Fast Unfolding算法是基于模块度的算法,模块度相当于对上述社区的形象描述的一种抽象表示,成为优化的主要目标。但是模块度的计算相对较为复杂,这也成为限制基于模块度算法在大规模图数据上的应用。
Label Propagation算法[2]是一种基于标签传播的局部社区划分算法,相比较而言其简单的计算过程,能够在大规模的图数据上应用。
2. Label Propagation算法
2.1. Label Propagation算法概述
Label Propagation算法是一种基于标签传播的局部社区划分算法。对于网络中的每一个节点,在初始阶段,Label Propagation算法对每一个节点一个唯一的标签,在每一个迭代的过程中,每一个节点根据与其相连的节点所属的标签改变自己的标签,更改的原则是选择与其相连的节点中所属标签最多的社区标签为自己的社区标签,这便是标签传播的含义。随着社区标签的不断传播,最终紧密连接的节点将有共同的标签。
Label Propagation算法最大的优点是其算法过程比较简单,想比较于优化模块度的过程,算法速度非常快。Label Propagation算法利用网络的结构指导标签的传播过程,在这个过程中无需优化任何函数。在算法开始前我们不必要知道社区的个数,随着算法的迭代,在最终的过程中,算法将自己决定社区的个数。
2.2. Label Propagation算法原理
对于Label Propagation算法,假设对于节点x,其邻居节点为x1,x2,⋯,xk,对于每一个节点,都有其对应的标签,标签代表的是该节点所属的社区。在算法迭代的过程中,节点x根据其邻居节点更新其所属的社区。更新的规则是选择节点x的邻居节点中,所属社区最多的节点对应的社区为其新的社区。
上述便是Label Propagation算法的核心概念。在初始节点,令每一个节点都属于唯一的社区,当社区的标签在节点间传播的过程中,紧密相连的节点迅速地取得一致的标签。具体过程如下图所示:

这样的过程不断地持续下去,直到所有可能聚集到一起的节点都具有了相同的社区标签。在传播过程的最终,具有相同社区标签的节点被划到相同的社区中称为一个个独立的社区。
在标签传播的过程中,节点的标签的更新过程可以分为两种,即:
- 同步更新
- 异步更新
同步更新是指对于节点xxx,在第ttt代时,根据其所有邻居节点在第t−1代时的社区标签对其标签进行更新。即:

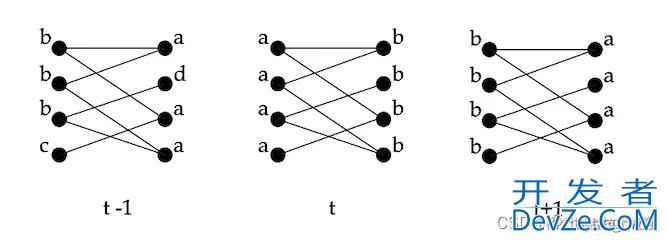
在上图中,两边的标签会在社区标签aaa和社区标签bbb不停地震荡。

这样的停止条件可以使得最终能够获得强壮的社区(Strong Community),但是社区并不是唯一的。对于Strong Community,其要求对于每一个节点,在其社区内部的邻居节点严格大于社区外部的邻居节点,然而Label Propagation算法能够保证对于每一个节点,在其所属的社区内有足够多的邻居节点。
3.3. Label Propagation算法过程

3. 实验
3.1. 数据描述
实验过程中使用的数据为参考[1]中使用的数据,其结构如下所示:
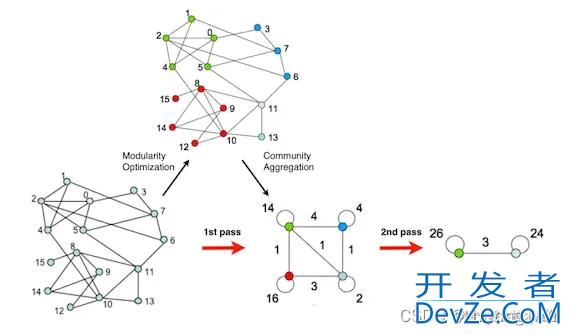
其在Fast Unfolding算法的划分结果为:
- 社区1:节点0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
- 社区2:节点8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15
3.2. 实验代码
#####################################
# Author:zhaozhiyong
# Date:20151205
# Fun:Label Propagation
# Fix:已经用python3重新修改
##################android###################
import random
def loadData(filePath):
f = open(filePath)
vector_dict = {}
edge_dict = {}
for line in f.readlines():
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
for i in range(2):
if lines[i] not in vector_dict:
#put the vector into the vector_dict
vector_dict[lines[i]] = int(lines[i])
#put the edges into the edge_dict
edge_list = []
if len(lines) == 3:
edge_list.append(lines[1-i]+":"+lines[2])
else:
edge_list.append(lines[1-i]+":"+"1")
edge_dict[lines[i]] = edge_list
else:
edge_list = edge_dict[lines[i]]
if len(lines) == 3:
edge_list.append(lines[1-i]+":"+lines[2])
else:
edge_list.append(lines[1-i]js+":"+"1")
edge_dict[lines[i]] = edge_list
return vector_dict, edge_dict
def get_max_community_label(vector_dict, adjacency_node_list):
label_dict = {}
# generate the label_dict
for node in adjacency_node_list:
node_id_weight = node.strip().split(":")
node_id = node_id_weight[0]
node_weight = int(node_id_weight[1])
if vector_dict[node_id] not in label_dict:
label_dict[vector_dict[node_id]] = node_weight
else:
label_dict[vector_dict[node_id]] += node_weight
# find the max label
sort_list = sorted(label_dict.items(), key = lambda d: d[1], reverse=True)
return sort_list[0][0]
def check(vector_dict, edge_dict):
for node in vector_dict.keys():
adjacency_node_list = edge_dict[node]
node_label = vector_dict[node]
label_check = {}
for ad_node in adjacency_node_list:
node_id_weight = ad_node.strip().split(":")
node_id = node_id_weight[0]
if vector_dict[node_id] not in label_check:
label_check[vector_dict[node_id]] = 1
else:
label_check[vector_dict[node_id]] += 1
sort_list = sorted(label_check.items(), key = lambda d: d[1], reverse=True)
if node_label == sort_list[0][0]:
continjsue
else:
return 0
return 1
def label_propagation(vector_dict, edge_dict):
#initial, let every vjavascriptector belongs to a community
t = 0
#for every node in a random order
while True:
if (check(vector_dict, edge_dict) == 0):
t = t+1
print("----------------------------------------")
print("iteration: ", t)
for node in vector_dict.keys():
adjacency_node_list = edge_dict[node]
vector_dict[node] = get_max_community_label(vector_dict, adjacency_node_list)
print(vector_dict)
else:
break
return vector_dict
if __name__ == "__main__":
vector_dict, edge_dict=loadData("./cd_data.txt")
dict_key_list = list(vector_dict.keys())
random.shuffle(dict_key_list)
new_vector_dict = {开发者_Python培训}
for key in dict_key_list:
new_vector_dict[key] = vector_dict.get(key)
print("original community: ", new_vector_dict)
vec_new = label_propagation(new_vector_dict, edge_dict)
print("---------------------------------------------------------")
print("the final result: ")
community_dict = {}
for key in vec_new.keys():
if vec_new[key] not in community_dict:
community_dict[vec_new[key]] = []
community_dict[vec_new[key]].append(str(key))
for key in community_dict.keys():
print("community-" + str(key) + " ---> " + str(community_dict[key]))
3.3. 代码解析
上述的实验代码中主要包括4个部分其一为loadData()函数,其目的是从文件中读入数据,取得点的信息,边的信息;
第二个是label_propagation()函数,其目的是Label Propagation算法的整个迭代过程,期中会调用两个函数,即get_max_community_label()函数和check()函数,get_max_community_label()函数的目的是在对每个节点遍历其邻居节点的过程中,选择出最大的社区标签,check()函数的目的是判断算法是否迭代结束。
4. 实验结果

参考文献
[1] Blondel V D, Guillaume J L, Lambiotte R, et al. Fast unfolding of communities in large netwojsrks[J]. Journal of statistical mechanics: theory and experiment, 2008, 2008(10): P10008.
[2] Raghavan U N, Albert R, Kumara S. Near linear time algorithm to detect community structures in large-scale networks[J]. Physical review E, 2007, 76(3): 036106.
以上就是Label Propagation算法原理示例解析的详细内容,更多关于Label Propagation算法的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论