java异步编程CompletableFuture使用示例详解
目录
- 一、简单介绍
- 二、常见操作
- 1、使用默认线程池
- 2、使用自定义线程池
- 3、获取线程的执行结果
- 三、处理异步结算的结果
- 四、异常处理
- 五、组合 CompletableFuture
- 六、并行运行多个 CompletableFuture
- 七、案例
- 1、从多个平台获取书价格
- 2、从任意一个平台获取结果就返回
一、简单介绍
CompletableFuture 同时实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口。
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T>
CompletableFuture 除了提供了更为好用和强大的 Future 特性之外,还提供了函数式编程的能力。
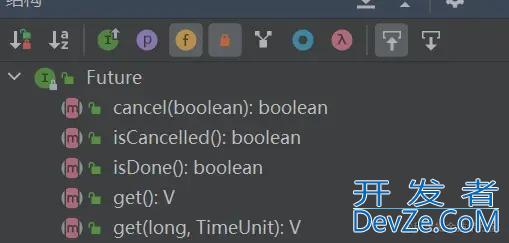
Future 接口有 5 个方法:
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) :尝试取消执行任务。
boolean isCancelled() :判断任务是否被取消。
boolean isDone() : 判断任务是否已经被执行完成。
get() :等待任务执行完成并获取运算结果。
get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) :多了一个超时时间。
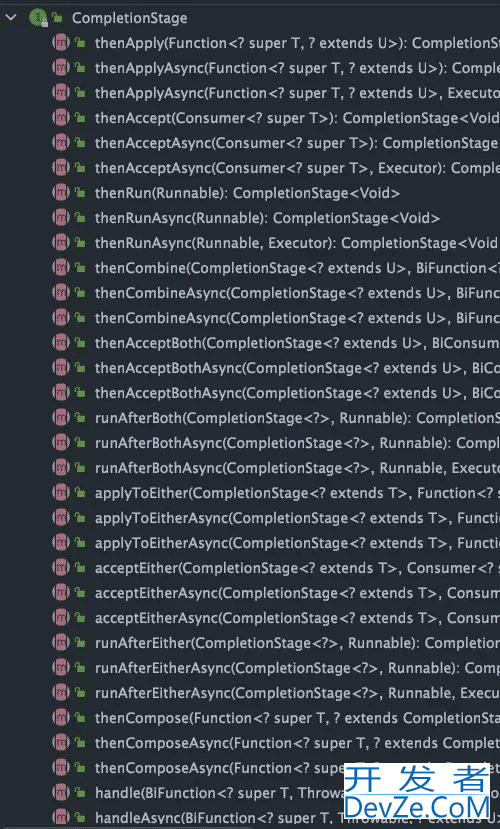
CompletionStage<T> 接口中的方法比较多,CompletableFuture 的函数式能力就是这个接口赋予的。从这个接口的方法参数你就可以发现其大量使用了 Java8 引入的函数式编程。
二、常见操作
1、使用默认线程池
// 使用默认的线程池,ForkJoinPool
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("come in");
System.out.println("是否为守护线程: " + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("is ending");
return "hello";
});
System.out.println("I am main thread");
输出如下:
I am main thread
come in是否为守护线程: true
从输出结果可以看出,使用默认的线程池,启动是线程是守护线程,如果主线程执行完毕,会导致守护线程结束。 导致 is ending 无法输出。
2、使用自定义线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 使用自定义线程池
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("come in");
System.out.println("是否为守护线程: " + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("is ending");
return "hello";
},executorService);
System.out.println("I am main thread");
// 关闭线程池
executorService.shutdown();
输出如下:
I am main thread
come in是否为守护线程: false当前线程名称:pool-1-thread-1is ending
可以看出,使用自定义线程池,创建出来的线程不是守护线程。
3、获取线程的执行结果
1、 get()
会阻塞当前主线程,等待任务线程执行完成,获取任务线程结果
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 使用自定义线程池
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("come in");
System.out.println("是否为守护线程: " + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("is ending");
return "hello";
},executorService);
System.out.println("I am main thread");
System.out.println("等待线程执行结束");
// 阻塞等待任务执行完成。
String s = completableFuture.get();
System.out.println("线程执行结果为:" + s);
executorService.shutdown();
输出为:
I am main thread
等待线程执行结束come in是否为守护线程: false当前线程名称:pool-1-thread-1is ending线程执行结果为:hello
2、getNow(defaultValue)
如果线程执行完成,获取线程的执行结果,如果没有执行完,获取传递的默认结果值 defaultValue 。
3、whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
异步回调,获取线程的执行结果。
completableFuture.whenComplete((v,e)->{
// 没有异常
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("执行结果为:" + v);
}
});
异常返回的处理。
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 使用自定义线程池
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("come in");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int i = 10 / 0;
return "hello";
},executorService);
completableFuture.whenComplete((v,e)->{
// 没有异常
if (e == null)编程客栈 {
System.out.println("执行结果为:" + v);
} else {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println("异常了,要处理拉");
}
});
executorService.shutdown();
输出结果如下:
come in
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero异常了,要处理拉
三、处理异步结算的结果
当我们获取到异步计算的结果之后,还可以对其进行进一步的处理,比较常用的方法有下面几个:
thenApply()
thenAccept()
thenRun()
whenComplete()
thenApply() 方法接受一个 Function 实例,用它来处理结果。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
return 10;
}).thenApply((s)->{
return s + 20;
}).thenApply(s->{
return s+ 30;
}).whenComplete((v,e)->{
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("结果为:" + v);
}
});
// 等待线程执行完毕
Thread.sleep(2000);
输出结果为:
结果为:60
如果你不需要从回调函数中获取返回结果,可以使用 thenAccept() 或者 thenRun()。这两个方法的区别在于 thenRun() 不能访问异步计算的结果。
四、异常处理
可以通过 handle() 方法来处理任务执行过程中可能出现的抛出异常的情况。
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");
}
return "hello!";
}).handle((res, ex) -> {
// res 代表返回的结果
// ex 的类型为 Throwable ,代表抛出的异常
return res != null ? res : ex.getMessage();
});
System.out.println(future.get());
输出如下:
java.lang.RuntimeException: Computation error!
如果你想让 CompletableFuture 的结果就是异常的话,可以使用 completeExceptionally() 方法为其赋值。
五、组合 CompletableFuture
你可以使用 thenCompose() 按顺序链接两个 CompletableFuture 对象。
CompletableFuture<String> future
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!")
.thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + "world!"));
System.out.println(future.get());
输出如下:
hello!world!
在实际开发中,这个方法还是非常有用的。比如说,我们先要获取用户信息然后再用用户信息去做其他事情。
和 thenCompose() 方法类似的还有 thenCombine() 方法, thenCombine() 同样可以组合两个 CompletableFuture 对象。
thenCompose() 可以两个 CompletableFuture 对象,并将前一个任务的返回结果作为下一个任务的参数,它们之间存在着先后顺序。
thenCombine() 会在两个任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果合并。两个任务是并行执行的,它们之间并没有先后依赖顺序。
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!")
// 两个任务并行执行,执行完,进行合并操作
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> "world!"), (s1, s2) -> s1 + s2)
.thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + "nice!"));
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
输出如下:
hello!world!nice!
六、并行运行多个 CompletableFuture
你可以通过 CompletableFuture 的 allOf()这个静态方法来并行运行多个 CompletableFuture 。
实际项目中,我们经常需要并行运行多个互不相关的任务,这些任务之间没有依赖关系,可以互相独立地运行。
比说我们要读取处理 6 个文件,这 6 个任务都是没有执行顺序依赖的任务,但是我们需要返回给用户的时候将这几个文件的处理的结果进行统计整理。像这种情况我们就可以使用并行运行多个 CompletableFuture 来开发者_JS培训处理。
示例代码如下:
CompletableFuture<Void> task1 =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//自定义业务操作
});
......
CompletableFuture<Void> task6 =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//自定义业务操作
});
......
CompletableFuture<Void> headerFuture=CompletableFuture.allOf(task1,.....,task6);
try {
headerFuture.join();
} catch (Exception ex) {
......
}
System.out.println("all done. ");
------
经常和 allOf() 方法拿来对比的是 anyOf() 方法。
allOf() 方法会等到所有的 CompletableFuture 都运行完成之后再返回 anyOf() 方法不会等待所有的 CompletableFuture 都运行完成之后再返回,只要有一个执行完成即可!
七、案例
模拟:平台商城,查询商品价格
class PlatShopping {
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 平台名称
private String name;
public PlatShopping(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取书籍名称
* @param bookName 书名
* @return
*/
public Double getPrice(String bookName) {
try {
// 模拟查询
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return Math.random() * 100;
}
1、从多个平台获取书价格
构造多个平台查询价格
public static void main(String[] args) throws
InterruptedException,
ExecutionException {
PlatShopping jd = new PlatShopping("京东");
PlatShopping taobao = new PlatShopping("淘宝");
PlatShopping tianmao= new PlatShopping("天猫");
List<PlatShopping> platShoppings = new ArrayList<>();
platShoppings.add(jd);
platShoppings.add(taobao);
platShoppings.add(tianmao);
long c1 = currentTimeMillis();
String allPlatPrice = getAllPlatPrice(platShoppings,"java高级编程");
System.out.println(String.format("总耗时:%d", currentTimeMillis()- c1));
System.out.println(allPlatPrice);
}
获取所有的书价格结果(顺序执行)
private static String getAllPlatPrice(List<PlatShopping> platShoppings, String bookName) {
return platShoppings.stream().map(p->{
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
}).collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
}
输出结果如下: 效率低
总耗时:3077
京东 上 java高级编程 的价格 60.47淘宝 上 java高级编程 的价格 89.12天猫 上 java高级编程 的价格 79.15
使用并行,硬编码处理。
private static String getAllPlatPrice(List<PlatShopping> platShoppings, String bookName) {
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(0);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
CompletableFuture<String> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(1);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
CompletableFuture<String> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(2);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
return task1.thenCombineAsync(task2,(s1,s2)->{
return s1 + s2;
}).thenCombineAsync(task3,(s1,s2) -> {
return s1 + s2;
}).join();
}
}
输出结果如下:
总耗时:1065
京东 上 java高级编程 的价格 65.41 淘宝 上 java高级编程 的价格 35.13&nbandroidsp;天猫 上 java高级编程 的价格 19.70
使用allOf
private static String getAllPlatPrice(List<PlatShopping> platShoppings, String bookName) {
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(0);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
CompletableFuture<String> task2 = ComplpythonetableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(1);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
CompletableFuture<String> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(2);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 等待三个都执行完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2, task3).join();
// 获取结果
stringBuilder.append(task1.join()).append(task2.join()).append(task3.join());
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
输出结果如下:
总耗时:1064
京东 上 java高级编程 的价格 46.49 淘宝 上 java高级编程 的价格 4.59 天猫 上 java高级编程 的价格 74.47
使用流
private static String getAllPlatPrice(List<PlatShopping> platShoppings, String bookName) {
// 批量提交任务,返回并行任务的集合列表
List<CompletableFuture<String>> completableFutureList = platShoppings.stream().map(p -> {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f", p.getName(), bookName, p.getPrice(bookName));
return data;
});
return completableFuture;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 分别获取每个任务的结果,再进行聚合
String result = completableFutureList.stream().map(c -> c.join())
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
return result;
}
运行结果如下:
总耗时:1062
京东 上 java高级编程 的价格 69.99淘宝 上 java高级编程 的价格 58.18天猫 上 java高级编程 的价格 5.05
2、从任意一个平台获取结果就返回
构造多平台,
public static void main(String[] args) throws
InterruptedException,
ExecutionException {
PlatShopping jd = new PlatShopping("京东");
PlatShopping taobao = new PlatShopping("淘宝");
PlatShopping tianmao= new PlatShopping("天猫");
List<PlatShopping> platShoppings = new ArrayList<>();
platShoppings.add(jd);
platShoppings.add(taobao);
platShoppings.add(tianmao);
long c1 = currentTimeMillis();
String onePrice = getOnePrice(platShoppings,"java高级编程");
System.out.println(String.format("总耗时:%d", currentTimeMillis()- c1));
System.out.println(onePrice);
}
使用anyOf
private static String getOnePrice(List<PlatShopping> platShoppings, String bookName) {
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(0);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
Co编程mpletableFuture<String> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(1);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
CompletableFuture<String> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(2);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
Object join = CompletableFuture.anyOf(task1, task2, task3).join();
return (String) join;
}
输出如下:
总耗时:1063
京东 上 java高级编程 的价格 www.devze.com4.93
使用 applyToEitherAsync
private static String getOnePrice(List<PlatShopping> platShoppings, String bookName) {
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(0);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
});
String result = task1.applyToEitherAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(1);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
}), (t) -> t).applyToEitherAsync(
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
PlatShopping p = platShoppings.get(2);
Double price = p.getPrice(bookName);
String data = String.format("%s 上 %s 的价格 %.2f \n", p.getName(), bookName, price);
return data;
}),
(t) -> t
).join();
return result;
}
输出如下:
总耗时:1063
京东 上 java高级编程 的价格 52.31
另外,建议可以看看京东的 asyncToolopen in new window 这个并发框架,里面大量使用到了 CompletableFuture 。
以上就是java异步编程CompletableFuture使用示例详解的详细内容,更多关于java异步CompletableFuture的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论