C++入门基础之命名空间、输入输出和缺省参数
目录
- 一.命名空间
- (1)命名空间的定义
- (2)命名空间的使用
- (3)全局域
- 二.输入&&输出
- (1) cout
- (2)cin
- (3)cin cout自动是识别类型
- 三.命名空间的展开
- (1)使用using namespace 命名空间名称引入
- (2)使用using将命名空间中某个成员引入
- 四.缺省参数
- (1)缺省参数概念
- (2)缺省参数分类
- 五.最后
一.命名空间
在C/C++中,变量、函数和后面要学到的类都是大量存在的,这些变量、函数和类的名称将都存
在于全局作用域中,可能会导致很多冲突。使用命名空间的目的是对标识符的名称进行本地化,以避免命名冲突或名字污染,namespace关键字的出现就是针对这种问题的。
例如:
#include<stdio.h>
int rand = 10;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
return 0;
}
这时候代码没有任何问题。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int rand = 10;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
return 0;
}

出现这个问题,我们知道,在头文件<stdlib.h>里面有一个函数rand(),所以头文件展开后就会出现定义冲突的现象。在C++中为了避免这种,利用命名空间。
(1)命名空间的定义
定义命名空间,需要使用到namespace关键字,后面跟命名空间的名字,然后接一对{}即可,{}
中即为命名空间的成员。#include<stdio.h>
namespace ytt
{
int a = 5;
}
int a = 10;
int main()http://www.devze.com
{
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
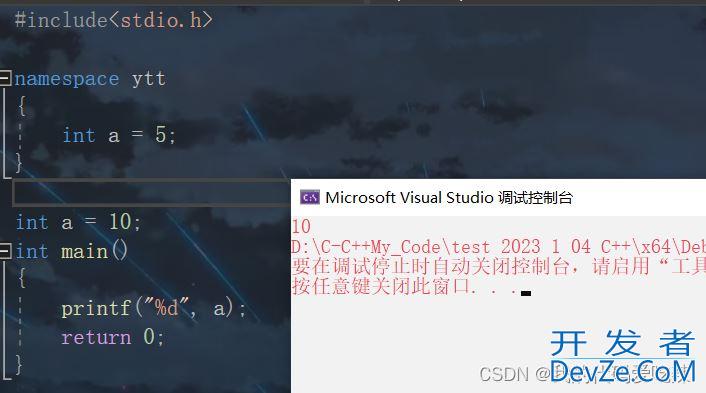
这样就不会有定义冲突的问题了,那如果我们想访问,值为5的那个变量a,又要怎么办呢?
(2)命名空间的使用
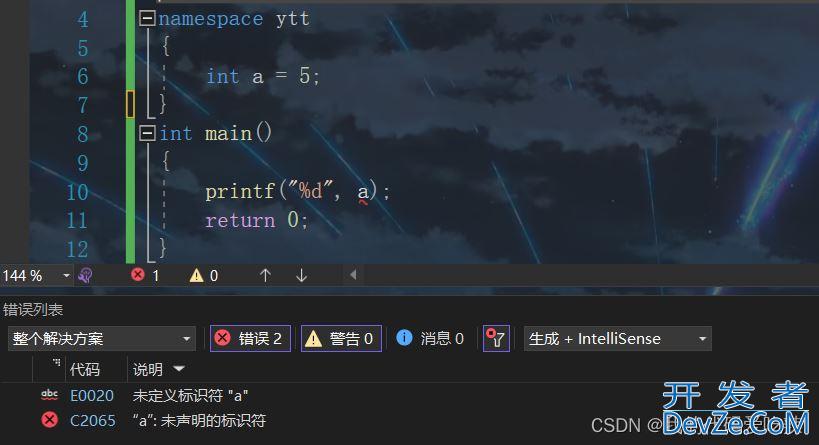
如果直接访问是访问不到的。
1.访问方法
命名空python间的名称 + :: + 命名空间内的变量或者函数。
namespace ytt
{
int a = 5;
int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
int main()
{
printf("a=%d\n", ytt::a);
printf("4+5=%d\n", ytt::Add(4 , 5));
return 0;
}

2.命名空间的嵌套
namespace ytt
{
int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
namespace wq
{
int Max(i编程nt a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
}
}
int main()
{
printf("Max=%d\n", ytt::wq::Max(10, 15));
return 0;
}
嵌套的情况下,就是一层一层访问:

(3)全局域
访问全局域,只需要 :: + 全局变量
namespace ytt
{
int a = 10;
}
int a = 5;
int main()
{
int a = 1;
//局部a
printf("a=%d\n", a);
//全局a
printf("a=%d\n", ytt::a);
//命名空间内的a
printf("a=%d\n", ::a);
return 0;
}
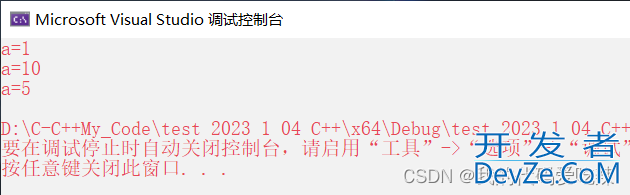
二.输入&&输出
C++的输入输出是函数:cin,cout,被包含在头文件 <IOStream> 中。
(1) cout
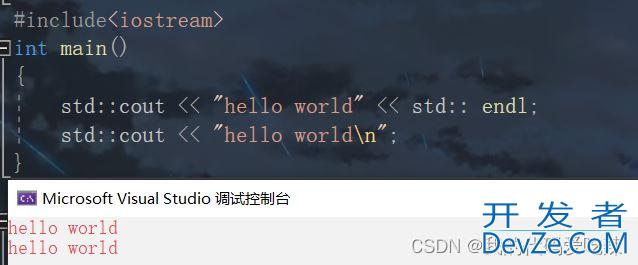
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello world" << std:: endl;
std::cout << "开发者_Go入门hello world\n";
return 0;
}
<<是流插入运算符
有了前面,命名空间的学习,我们也就能看出来了,cout 也是被封装到命名空间 std里面的,endl 是封装在 std 里面的换行符,和 ' \n '是一样的。
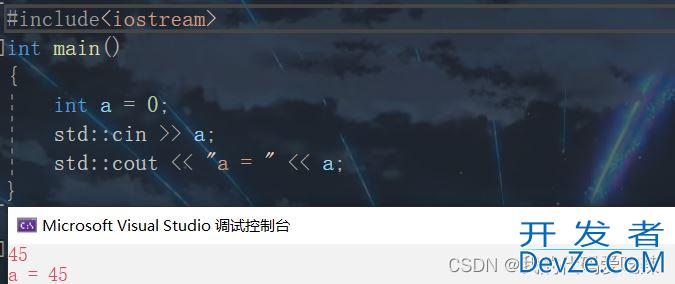
(2)cin
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
std::cin >> a;
std::cout << "a = " << a;
return 0;
}
>>是流提取运算符,cin 也是被封装到命名空间 std里面的。
实际上cout和cin分别是 ostream 和 istream 类型的对象,>>和<<也涉及运算符重载等知识,这些知识我们我们后续才会学习,所以我们这里只是简单学习他们的使用。后面我们还有有一个章节更深入的学习IO流用法及原理。
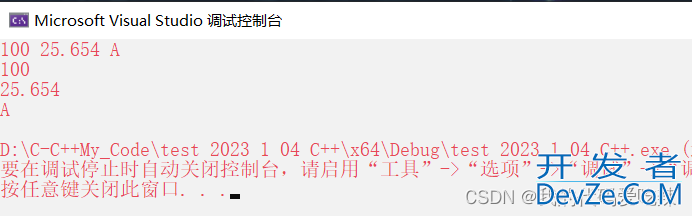
(3)cin cout自动是识别类型
cin cout 相对于 C语言的scnaf printf,少了类型的修饰,所以在C++中,cin 和 cout是可以自动识别类型的。
int main()
{
int a = 0;
double b = 0;
char c = 0;
std::cin >> a >> b >> c;
std::cout << a <<std::endl;
std::cout << b << std::endl;
std::cout << c << std::endl;
return 0;
}
三.命名空间的展开
(1)使用using namespace 命名空间名称引入
我们在写程序的时候,有时候会发生,某个命名空间的变量名,函数名,经常被使用,我们每一次使用都要加上命名空间,会非常麻烦。所以我们使用using namespace 命名空间名称引入。
#include<iostream>
namespace ytt
{
int a = 0;
int b = 2;
}
using namespace ytt;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << a << endl;
cout << b << endl;
return 0;
}
这样使用就是将命名空间的所有定义全部展开,这样虽然使得我们不用每次都去包含命名空间,到那时也使得我们辛辛苦苦建立的命名空间也就没有了意义。因为都在这里展开了,就会发生定义相同的冲突。所以这种使用方法在企业开发时禁止的,我们平时练习代码时,为了方便可以使用。
(2)使用using将命名空间中某个成员引入
上述使用使用using namespace 将整个命名空间展开,会有造成冲突的可能,我们还可以将命名空间的某一成员引入。
#include<iostream>
namespace ytt
{
int a = 0;
int b = 2;
}
using ytt::a;
using ytt::b;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
cout << a << endl;
cout << b << endl;
return 0;
}
四.缺省参数
(1)缺省参数概念
缺省参数是声明或定义函数时为函数的参数指定一个缺省值。在调用该函数时,如果没有指定实参则采用该形参的缺省值,否则使用指定的实参。
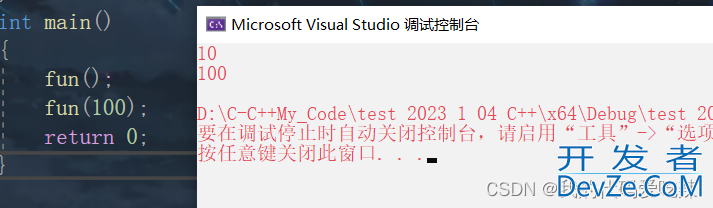
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void fun(int a = 10)
{
cout << apython << endl;
}
int main()
{
fun(); //没传参数,使用缺省参数
fun(100);//传了参数,就使用传的参数
return 0;
}
(2)缺省参数分类
1.全缺省参数
void Func(int a = 10, int b = 20, int c = 30)
{
cout<<"a = "<<a<<endl;
cout<<"b = "<<b<<endl;
cout<<"c = "<<c<<endl;
}
调用时:
void Func(int a = 10, int b = 20, int c = 30)
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
}
int main()
{
Func(); //true
Func(1); //true
Func(1, 2); //true
Func(1, 2, 3); //true
Func(, 1, 2); //error
Func(1, , 3); //error
return 0;
}
带有缺省参数的函数,传参数时必须从左往右连续,不能跳着给参数。
2.半缺省参数
void Func(int a, int b = 10, int c = 20)
{
cout<<"a = "<<a<<endl;
cout<<"b = "<<b<<endl;
cout<<"c = "<<c<&编程客栈lt;endl;
}
3.注意:
1. 半缺省参数必须从右往左依次来给出,不能间隔着给
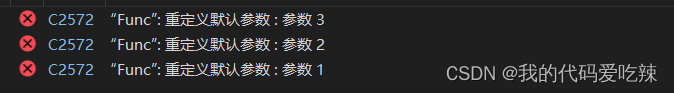
2. 缺省参数不能在函数声明和定义中同时出现
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//函数声明
void Func(int a = 10, int b = 20, int c = 30);
int main()
{
Func(); //true
return 0;
}
//函数定义
void Func(int a = 10, int b = 20, int c = 30)
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
}
3. 缺省值必须是常量或者全局变量
五.最后
到此这篇关于C++入门基础之命名空间、输入输出和缺省参数的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++命名空间、输入输出和缺省参数内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论