Pytest Fixture参数讲解及使用
Fixture参数详解及使用
Fixture的调用方式:
@pytest.fixture(scope = "function",params=None,autouse=False,ids=None,name=None)
参数详解:1、SCOPE
用于控制Fixture的作用范围作用类似于Pytest的setup/teardown默认取值为function(函数级别),控制范围的排序为:session > module > class > function| 取值 | 范围 说明 |
|---|---|
| function | 函数级 每一个函数或方法都会调用 |
| class | 函数级 模块级 每一个.py文件调用一次 |
| module | 模块级 每一个.py文件调用一次 |
| session | 会话级 每次会话只需要运行一次,会话内所有方法及类,模块都共享这个方法 |
作用范围举例:
scope = “function”
语法:@pytest.fixture() #或者 @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
场景一:做为参数传入
import pytest
# fixture函数(类中) 作为多个参数传入
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("打开浏览器")
a = "account"
return a
@pytest.fixture()
def logout():
print("关闭浏览器")
class TestLogin:
#传入lonin fixture
def test_001(self, login):
print("001传入了loging fixture")
assert login == "account"
#传入logout fixture
def test_002(self, logout):
print("002传入了logout fixture")
def test_003(self, login, logout):
print("003传入了两个fixture")
def test_004(self):
print("004未传入仍何fixture哦")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
运行结果:
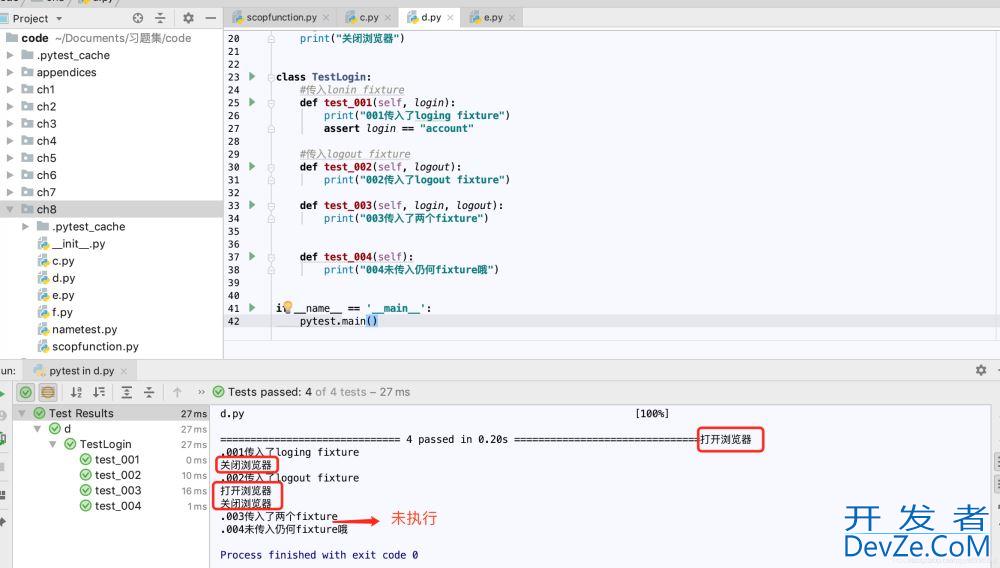
从运行结果可以看出,fixture做为参数传入时,会在执行函数之前执行该fixture函数。再将值传入测试函数做为参数使用,这个场景多用于登录
场景二、Fixture的相互调用
代码:import pytest
# fixtrue作为参数,互相调用传入
@pytest.fixture()
def account():
a = "account"
print("第一层fixture")
return a
#Fixture的相互调用一定android是要在测试类里调用这层fixture才会生次,普通函数单独调用是不生效的
@pytest.fixture()
def login(account):
print("第二层fixture")
class TestLogin:
def test_1(self, login):
print("直接使用第二层fixture,返回值为{}".format(login))
def test_2(self, account):
print("只调用account fixture,返回值为{}".format(account))
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
运行结果:
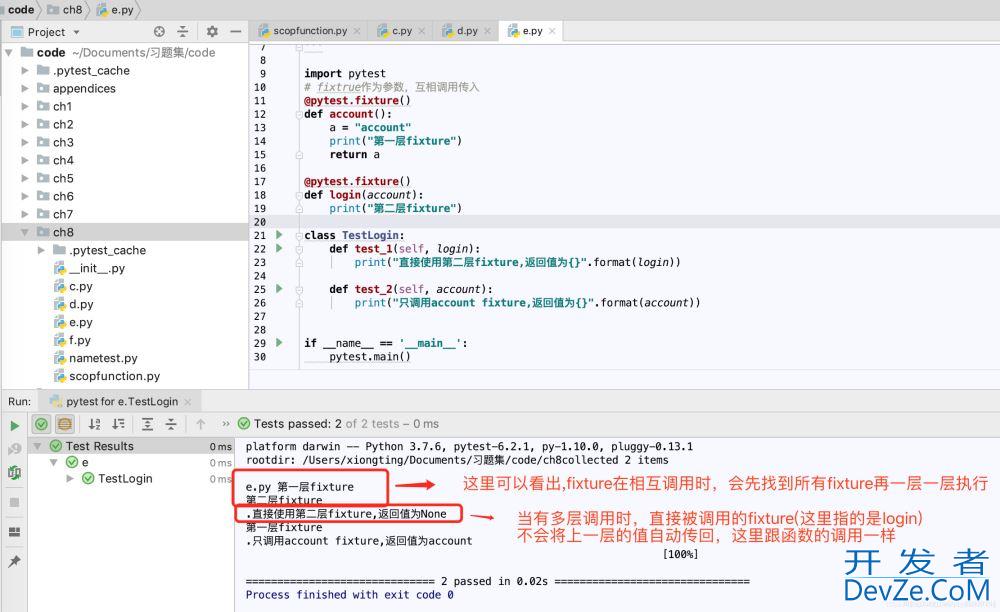
注:
1.即使fixture之间支持相互调用,但普通函数直接使用fixture是不支持的,一定是在测试函数内调用才会逐级调用生效
2.有多层fixture调用时,最先执行的是最后一层fixture,而不是先执行传入测试android函数的fixture3.上层fixture的值不会自动return,这里就类似函数相互调用一样的逻辑
scope = “class”:
**当测试类内的每一个测试方法都调用了fixture,fixture只在该class下所有测试用例执行前执行一次
**测试类下面只有一些测试方法使用了fixture函数名,这样的话,fixture只在该class下第一个使用fixture函数的测试用例位置开始算,后面所有的测试用例执行前只执行一次。而该位置之前的测试用例就不管。
语法
@pytest.fixture(scope='class')
场景一、
import pytest
# fixture作用域 scope = 'class'
@pytest.fixture(scope='class')
def login():
print("scope为class")
class TestLogin:
def test_1(self, login):
print("用例1")
def test_2(self, login):
print("用例2")
def test_3(self, login):
print("用例3")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
运行结果:
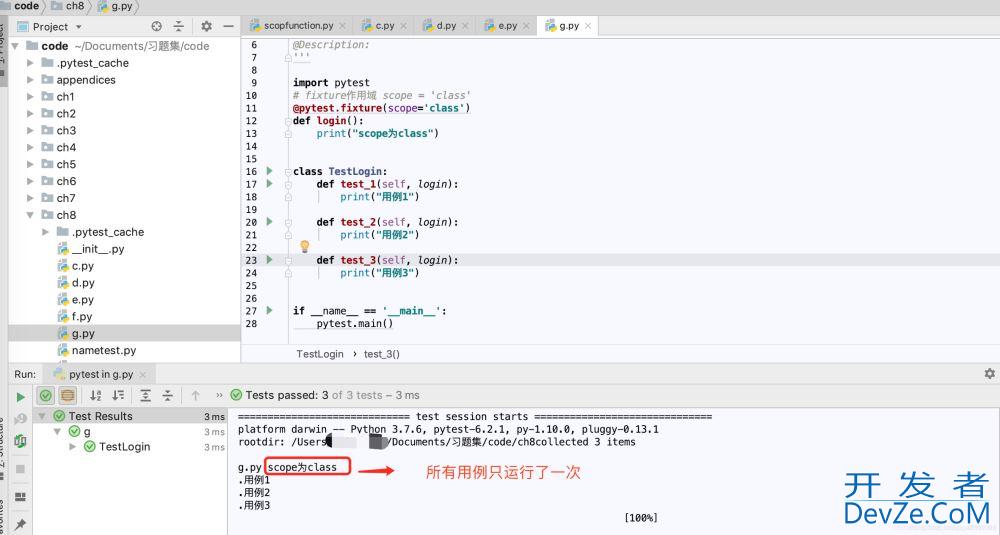
场景二、
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope='class')
def login():
a = '123javascript'
printpython("输入账号密码登陆")
class TestLogin:
def test_1(self):
print("用例1")
def test_2(self, login):
prijsnt("用例2")
def test_3(self, login):
print("用例3")
def test_4(self):
print("用例4")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
运行结果:
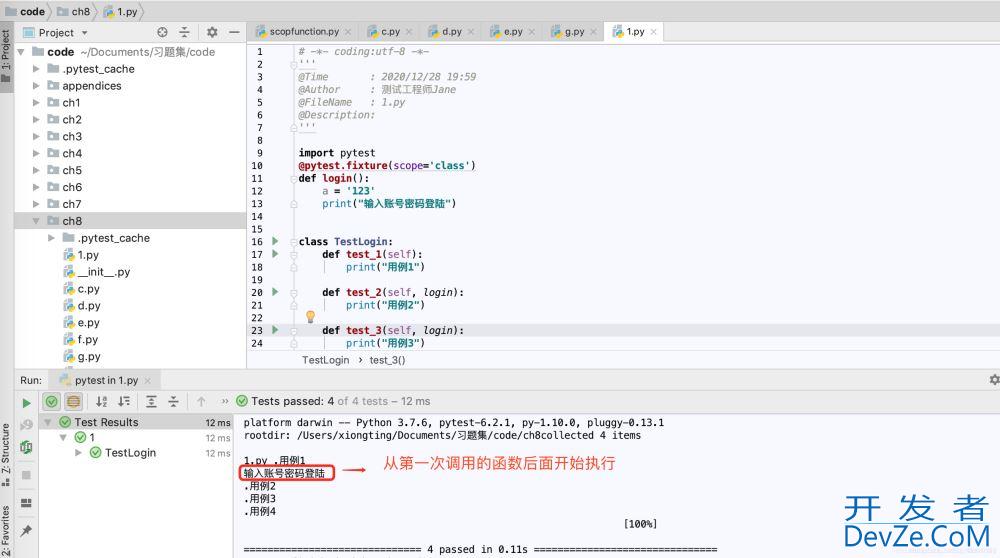
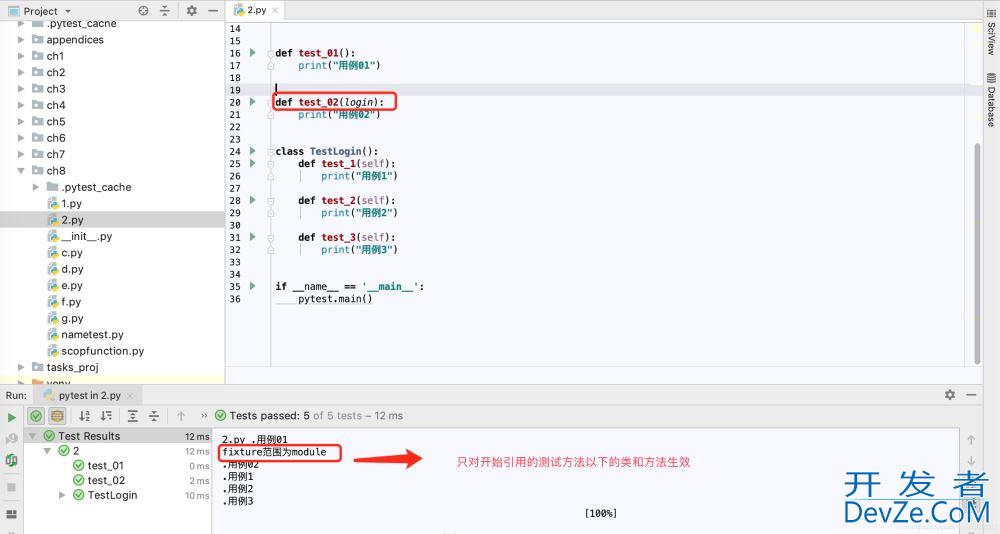
scope = “module”:与class开发者_C开发相同,只从.py文件开始引用fixture的位置生效
import pytest
# fixture scope = 'module'
@pytest.fixture(scope='module')
def login():
print("fixture范围为module")
def test_01():
print("用例01")
def test_02(login):
print("用例02")
class TestLogin():
def test_1(self):
print("用例1")
def test_2(self):
print("用例2")
def test_3(self):
print("用例3")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
运行结果:
scope = “session”:用法将在conftest.py文章内详细介绍
session的作用范围是针对.py级别的,module是对当前.py生效,seesion是对多个.py文件生效session只作用于一个.py文件时,作用相当于module所以session多数与contest.py文件一起使用,做为全局Fixture2、params:Fixture的可选形参列表,支持列表传入默认None,每个param的值fixture都会去调用执行一次,类似for循环
可与参数ids一起使用,作为每个参数的标识,详见ids被Fixture装饰的函数要调用是采用:Request.param(固定写法,如下图)举个栗子: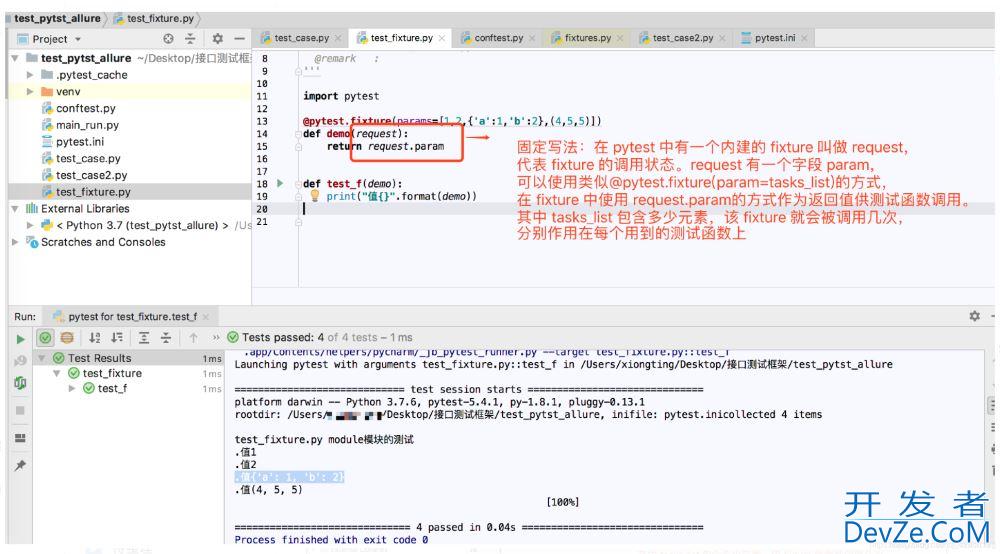
3、ids:
用例标识ID与params配合使用,一对一关系
举个栗子:未配置ids之前,用例: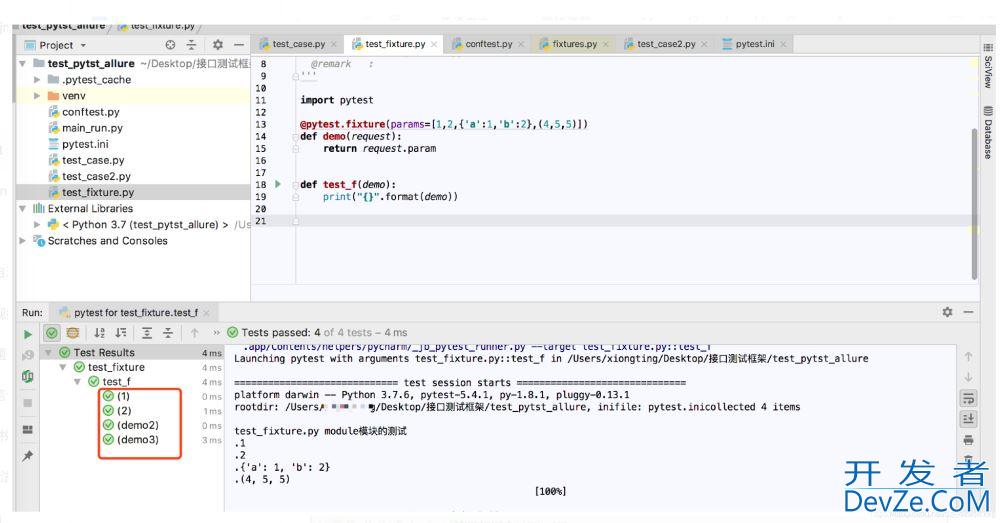
配置了IDS后:
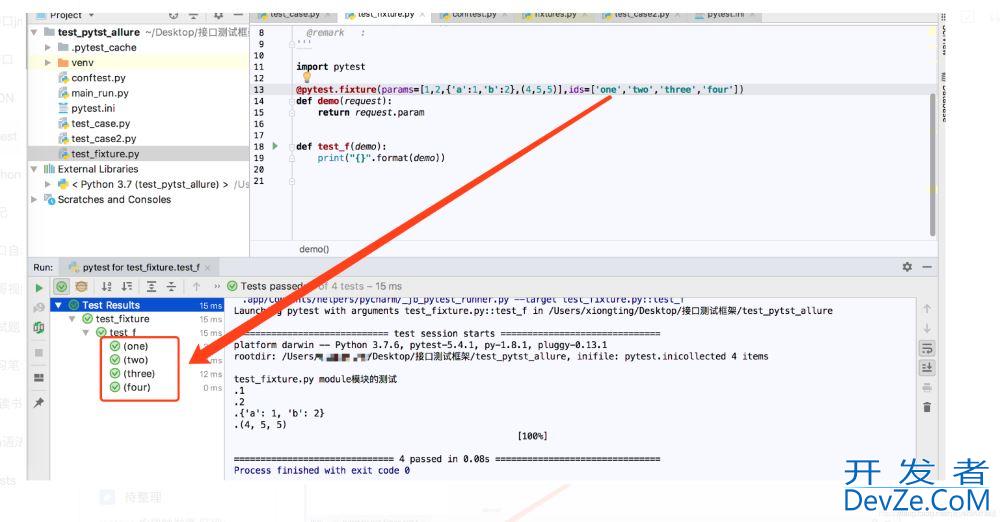
4、autouse:
默认False若为True,刚每个测试函数都会自动调用该fixture,无需传入fixture函数名由此我们可以总结出调用fixture的三种方式: 1.函数或类里面方法直接传fixture的函数参数名称 2.使用装饰器@pytest.mark.usefixtures()修饰 3.autouse=True自动调用,无需传仍何参数,作用范围跟着scope走(谨慎使用)让我们来看一下,当autouse=ture的效果: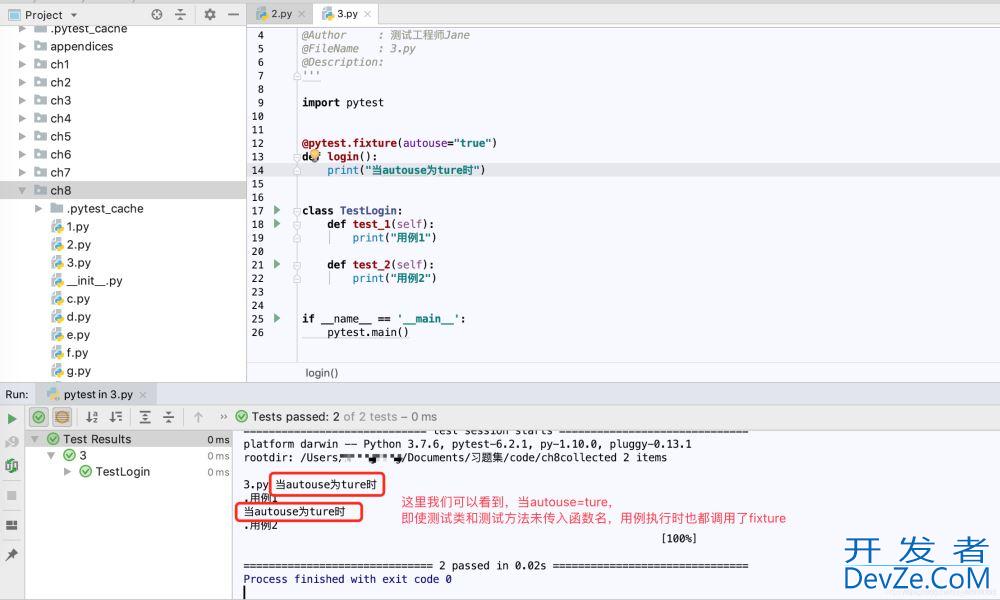
5、Name:
fixture的重命名
通常来说使用 fixture 的测试函数会将 fixture 的函数名作为参数传递,但是 pytest 也允许将fixture重命名如果使用了name,那只能将name传如,函数名不再生效调用方法:@pytest.mark.usefixtures(‘fixture1’,‘fixture2’)举栗:
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(name="new_fixture")
def test_name():
pass
#使用name参数后,传入重命名函数,执行成功
def test_1(new_fixture):
print("使用name参数后,传入重命名函数,执行成功")
#使用name参数后,仍传入函数名称,会失败
def test_2(test_name):
print("使用name参数后,仍传入函数名称,会失败")
运行结果:

到此这篇关于Pytest之Fixture参数详解及使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Pytest Fixture使用内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论