怎样给Kafka新增分区
目录
- 给Kafka新增分区
- 1、修改 topic 的分区
- 2、迁移数据
- 3、迁移
- 4、验证
- Kafka分区原理机制
- 分区结构
- 分区优点
- 分区策略
- 根据分区策略实现消息的顺序消费
- 默认分区策略源码
- 总结
给Kafka新增分区
数据量猛增的时候,需要给 kafka 的 topic 新增分区,增大处理的数据量,可以通过以下步骤
1、修改 topic 的分区
kafka-topics --zookeeper hadoop004:2181 --alter --topic flink-test-04 --partitions 3
2、迁移数据
生成迁移计划,手动开发者_JAVA学习新建一个 json 文件
{
"topics": [
{"topic": "flink-test-03"}
],
"version": 1
}
生成迁移计划
kafka-reassign-partitions --zookeeper hadoop004:2181 --topics-to-move-json-file topic.json --broker-list “120,121,122” --generate
Current partition replica assignment:
{"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"flink-test-02","partition":5,"replicas":[120]},{"topic":"flink-test-02","partition":0,"replicas":[121]},{"topic":"flink-test-02","partition":2,"replicas":[120]},{"topic":"flink-test-02","partition":1,"replicas":[122]},{"topic":"flink-test-02","partition":4,"replicas":[122]},{"topic":"flink-test-02","partition":3,"replicas":[121]}]}
新建一个文件reassignment.json,保存上边这些信息
3、迁移
kafka-reassign-partitions --zookeeper hadoop004:2181 --reassignment-json-file reassignment.json --execute
4、验证
kafka-reassign-partitions --zookeeper hadoop004:2181 --reassignment-json-file reassignment.json --verify
Kafka分区原理机制
分区结构
kafka的消息总共是三层结构
Topic(第一层结构,表示一个主题)-> Partition(分区,每个消息可以有多个分区) -> 消息实例(具体的消息文本等等,一个消息实例只可能在www.devze.com一个分区里面,不会出现在多个分区中)
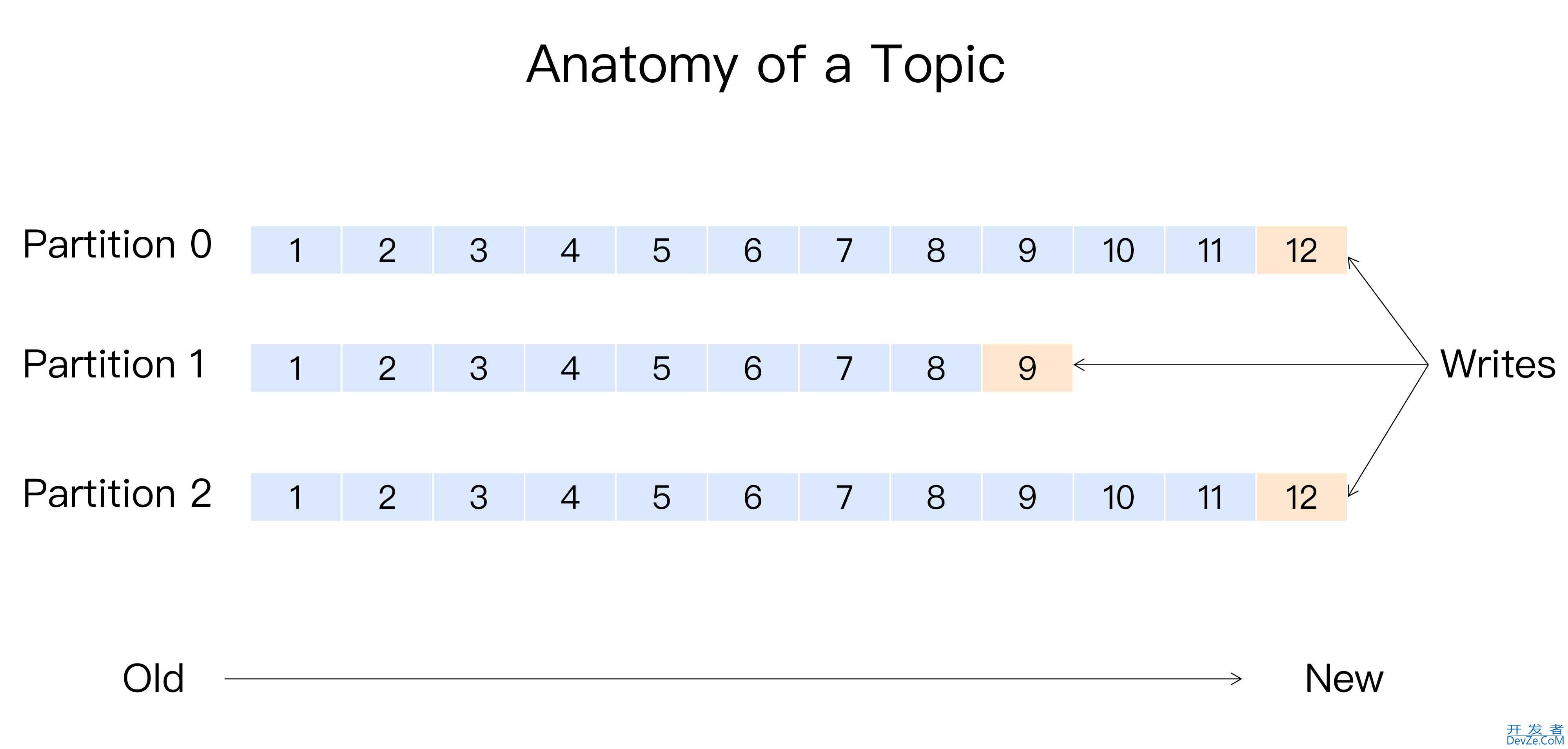
分区优点
分区其实是一个负载均衡的思想。如此设计能使每一个分区独自处理单独的读写请求,提高吞吐量。
分区策略
- 轮询策略Round-robin(未指定key新版本默认策略)
- 随机策略Randomness(老版本默认策略)
- 消息键排序策略Key-ordering(指定了key,则使用该策略)
- 根据地理位置进行分区
- 自定义分区 需要在生产者端实现org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Partitioner接口,并配置一下实现类的全限定名
根据分区策略实现消息的顺序消费
可以只设置一个分区,这样子消息都是放在一个partition,肯定是先进先出进行消费,然而这种场景无法利用kafka多分区的高吞吐量以及负载均衡的优势。
将需要顺序消费的消息设置key,这个时候根据默认的分区策略,kafka会将所有的相同的key放在一个partition上面,这样既可以使用kafka的partition又可以实现顺序消费。
默认分区策略源码
/**
* 编程客栈The default partitioning strategy:
* <ul>
* <li>If a partition is specified in the record, use it
* <li>If no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key
* <li>If no partition or key is present choose a partition in a round-robin fashion
*/
public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, AtomicInteger> topicCounterMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current wZZtbcluster metadata
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
int numPartitions = partitions.sijavascriptze();
if (keyBytes == null) {
int nextValue = nextValue(topic);
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (availablePartitions.size() > 0) {
int part = Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % availablePartitions.size();
return availablePartitions.get(part).partition();
} else {
// no partitions are available, give a non-available partition
return Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % numPartitions;
}
} else {
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
}
private int nextValue(String topic) {
AtomicInteger counter = topicCounterMap.get(topic);
if (null == counter) {
counter = new AtomicInteger(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
AtomicInteger currentCounter = topicCounterMap.putIfAbsent(topic, counter);
if (currentCounter != null) {
counter = currentCounter;
}
}
return counter.getAndIncrement(php);
}
public void close() {}
}
从类注释当中已经很明显的看出来分区逻辑
3. 如果指定了分区,则使用指定分区
4. 如果没有指定分区,但是有key,则使用hash过的key放置消息
5. 如果没有指定分区,也没有key,则使用轮询
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论