Android ViewStub使用方法学习
目录
- 前言
- 1.ViewStub的优势
- 2.ViewStub的使用
- 属性 功能
- 简单实战
- 1.viewstub就是动态加载试图
- 2.看一个简单的demo
- 3.当调用第二次inflate的时候,会报错:
- 文末
- android ViewStub的使用注意事项
前言
当渲染一个活动时,这个活动的布局可能会有很多visible为invisible和gone的情况,虽然这些控件虽然现在不显示在屏幕上,但是系统在加载这个布局文件时还是会加载它的,这就影响了这个页面的加载效率,因为这些不可见的控件提前加载它们并没有什么实际的意义,反而会编程客栈减缓页面的加载时间,所以为了解决这个问题可以使用ViewStub来懒加载暂时不显示的布局.
1.ViewStub的优势
简单来说, ViewStub可以做到按需加载一个布局,我们可以控制它加载的时机,而不是在Activity的onCreate方法中去加载.即懒加载
2.ViewStub的使用
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/text"
android:layout="@layout/text_view_stub"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/textView3"
android:layout_marginTop="180dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="100dp"/>
属性 功能
android:inflatedId="@+id/text" 为我们要加载的布局提供一个id android:layout 我们需要加载的布局 除此之外
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/textView3"
android:layout_marginTop="180dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="100dp"/>
这些代表我们懒加载的布局在父布局的位置,如果懒加载的布局有相同的属性,将会被覆盖
//通过id得到viewStub对象 ViewStub viewStub = findViewById(R.id.stub); //动态加载布局 viewStub.inflate();
简单实战
1.viewstub就是动态加载试图
也就是在我们的app启动绘制页面的时候,他不会绘制到view树中;当在代码中执行inflate操作后,她才会被添加到试图中。其实ViewStub就是一个宽高都为0的一个View,它默认是不可见的,只有通过调用setVisibility函数或者Inflate函数才 会将其要装载的目标布局给加载出来,从而达到延迟加载的效果,这个要被加载的布局通过android:layout属性来设置。最终目的是把app加载页面的速度提高了,使用户体验更好。
2.看一个简单的demo
viewstub.XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/inflatedStart"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
&lpythont;TextView
android:id="@+id/hello_tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:text="DATA EMPTY!"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
activity_myviewstub.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="inflate"
android:text="inflate" />
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="setData"
android:text="setdata"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="hide"
android:text="hide"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="show"
android:text="show"/>
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/vs"
android:inflatedId="@+id/inflatedStart"
python android:layout="@layout/viewstub"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
MyViewStubActivity.Java
package com.ysl.myandroidbase.viewstub;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewStub;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.ysl.myandroidbase.R;
public class MyViewStubActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ViewStub viewStub;
private TextView textView;
private View inflate;
private ConstraintLayout constraintLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_myviewstub);
viewStub = findViewById(R.id.vs);
//textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);空指针,因为viewstub没有inflate
}
public void inflate(View view){
if (inflate == null) {//inflate只会进行一次,当第二次调用的时候,就会抛异常;也可以try catch进行处理
inflate = viewStub.inflate();
constraintLayout = findViewById(R.id.inflatedStart);
System.out.println(constraintLayout);
System.out.println("viewStub-------->"+viewStub);
textView = viewStub.findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);//获取到的textview是空的;
System.out.println("viewStub textView-------->"+textView);//null
textView = constraintLayout.findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);
System.out.println("constraintLayout textView-------->"+textView);
textView = findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);
System.out.println("textView-------->"+textView);
}
}
public void setData(View view){
if (constraintLayout != null) {
textView = constraintLayout.findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);
textView.setText("HAVE DATA !!!");
}
}
public void hide(View view){
viewStub.setVisibility(View.GONE);
// if (constraintLayout != null){
// constraintLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
// }
}
public void show(View view){
viewStub.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// if (constraintLayout != null){
// constraintLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// }
}
}
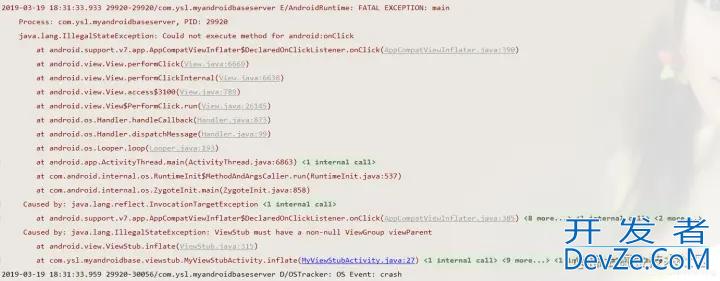
3.当调用第二次inflate的时候,会报错:
编辑切换为居中
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
我们看一下这是为什么?进入viewStub.inflate();的源码:
public View inflate() {
final Viewparent viewParent = getParent();
if (viewParent != null && viewParent instanceof ViewGroup) {
if (mLayoutResource != 0) {
final ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) viewParent;
final View view = inflateViewNoAdd(parent);
replaceSelfWithView(view, parent);
mInflatedViewRef = new WeakReference<>(view);
if (mInflateListener != null) {
mInflateListener.onInflate(this, view);
}
return view;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ViewStub must have a valid layoutResource");
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("ViewStub must have a non-null ViewGroup viewParent");
}
}
可以看到当viewParent为空或者不是viewgroup时才会报这个错误;那么第一次调用的时候,肯定是进去了;发现一个方法replaceSelfWithView(view,parent);view就是我们在布局文件中给viewstub指定的layout所引用的那个布局;parent就是getParent方法得到的,也就是acticity的填充布局LinearLayout;
进去看一下:
private void replaceSelfWithView(View view, ViewGroup parent) {
final int ind编程ex = parent.indexOfChild(this);
parent.removeViewInLayout(this);
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = getLayoutParams();
if (layoutParams != null) {
parent.addView(view, index, layoutParams);
} else {
parent.addView(view, index);
}
}
可以发现parent.removeViewInLayout(this);把this就是viewstub从父布局linearlayout中移除了;parent.addView()就是把view(也就是我们引用的布局)添加到了父布局LinearLayout中。
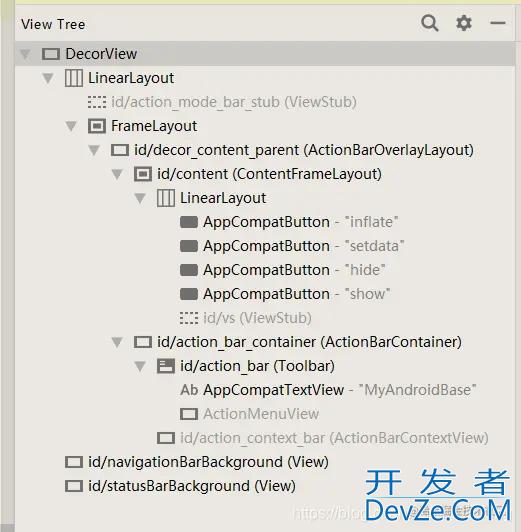
我们用layout inspector来查看一下:
inflate前:可以看到viewstub是灰色的
编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
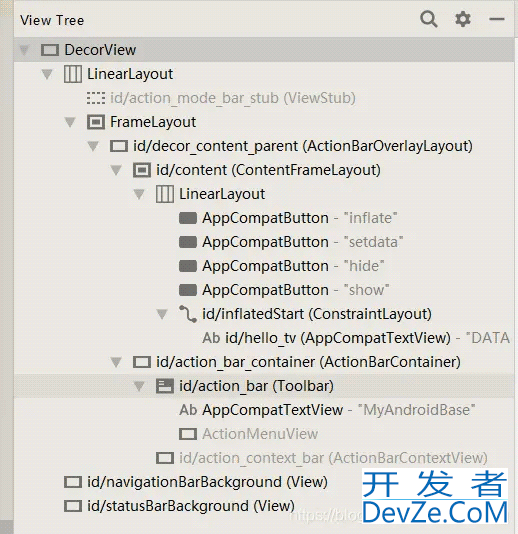
inflate后:可以看到viewstub直接被移除了,把引用布局直接放到view树里了。
编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
所以当我们第二次再调用inflate方法时,viewstub的parent已经为空了;就会抛出此异常;
当调用textView = viewStub.findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);//获取到的textview是空的;
而使用textView = findViewById(R.id.hello_tv);就可以直开发者_Python培训接拿到控件对象了;
当实现引用布局的显示和隐藏时,测试发现使用viewstub的setVisibility()方法可以实现,这是为什么呢?;按理说使用constraintLayout.setVisibility()当然也可以;根据上面的view树结构来看,好像使用引用布局的setVisibility()方法更合理一些;
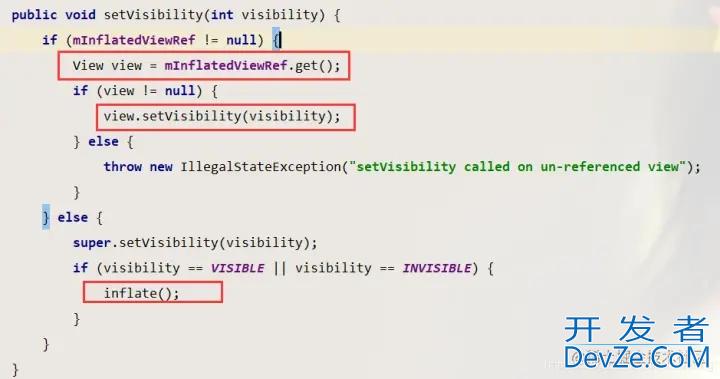
下面我们再来看看viewstub的setVisibility()为什么也可以;跟进源码看看:
编辑切换为居中
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
源码中使用mInflatedViewRef获取到view,然后设置隐藏与显示;mInflatedViewRef是一个view的弱引用WeakReference
其实在上面的inflate方法中已经为其添加了mInflatedViewRef = new WeakReference<>(view);这个view就是viewstub中的引用布局;
所以,使用viewstub可以实现相同的显示或隐藏效果;
从上图的最后一个红色框中可以发现,假设现在我没有调用inflate方法,而是直接点击了show按钮;然后引用布局也可以绘制出来;这就是我在写demo的时候,直接上去点击show按钮,竟然也可以显示的原因。
编辑切换为居中
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
以上就是Android ViewStub的使用与简单的演练;如果想要进阶自己Android技能,可以参考这份《Android核心技术笔记》里面记录有Android的核心技术与其他前沿技术。
文末
Anjsdroid ViewStub的使用注意事项
inflate方法只能调用一次,再次调用会出异常 我们看下inflate方法的源码,一旦第二次调用inflate方法,我们的到viewParent将等于null,会报 throw new IllegalStateException(“ViewStub must have a non-null ViewGroup viewParent”);异常,所以总之一句话,这个懒加载只能加载一次
public View inflate() {
final ViewParent viewParent = getParent();
if (viewParent != null && viewParent instanceof ViewGroup) {
if (mLayoutResource != 0) {
final ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) viewParent;
final View view = inflateViewNoAdd(parent);
replaceSelfWithView(view, parent);
mInflatedViewRef = new WeakReference<>(view);
if (mInflateListener != null) {
mInflateListener.onInflate(this, view);
}
return view;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ViewStub must have a valid layoutResource");
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("ViewStub must have a non-null ViewGroup viewParent");
}
}
以上就是Android ViewStub使用方法学习的详细内容,更多关于Android ViewStub使用的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论