SpringBoot的SPI机制源码解析
目录
- 一、从Java类加载机制说起
- 1.1 双亲委派模型
- 1.2 双亲委派模型缺陷
- 1.3 使用线程上下文类加载器(ContextClassLoader)加载
- 1.4 使用类加载器加载资源文件,比如jar包
- 二、Spring中SPI机制实现
- 2.1 SPI机制
- 2.1.1 SPI思想
- 2.1.2 SPI约定
- 2.2 SPI使用案例
- 2.3 Springboot中的类SPI扩展机制
- 三、源码分析
- 3.1 getSpringFactoriesInstances
- 3.2 SpringFactoriesLoader
- 3.3 loadFactoryNames
- 3.3.1 spring-boot-2.2.2.RELEASE.jar
- 3.3.2 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.2.RELEASE.jar
- 3.4 loadSpringFactories
- 3.5 createSpringFactoriesInstances
一、从java类加载机制说起
java中的类加载器负载加载来自文件系统、网络或者其他来源的类文件。jvm的类加载器默认使用的是双亲委派模式。
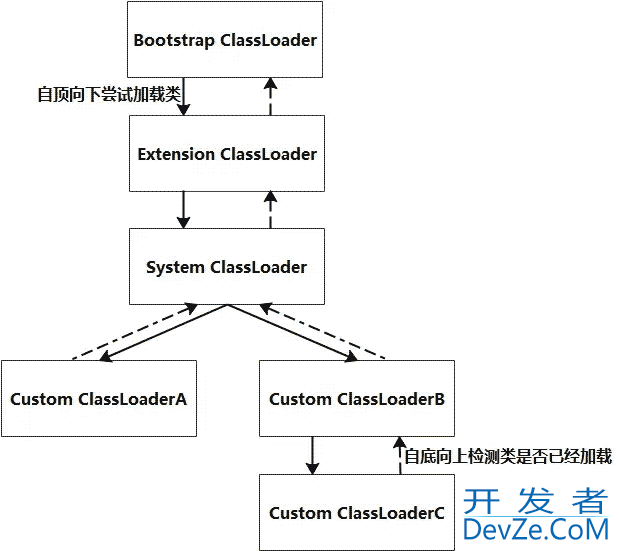
三种默认的类加载器Bootstrap ClassLoader、Extension ClassLoader和System ClassLoader(Application ClassLoader)每一个类加载器都确定了从哪些位置加载文件。于此同时我们也可以通过继承java.lang.classloader实现自己的类加载器。
- Bootstrap ClassLoader:负责加载JDK自带的rt.jar包中的类文件,是所有类加载的父类
- Extension ClassLoader:负责加载java的扩展类库从jre/lib/ect目录或者java.ext.dirs系统属性指定的目录下加载类,是System ClassLoader的父类加载器
- System ClassLoader:负责从classpath环境变量中加载类文件
1.1 双亲委派模型
当一个类加载器收到类加载任务时,会先交给自己的父加载器去完成,因此最终加载任务都会传递到最顶层的BootstrapClassLoader,只有当父加载器无法完成加载任务时,才会尝试自己来加载。
具体:根据双亲委派模式,在加载类文件的时候,子类加载器首先将加载请求委托给它的父加载器,父加载器会检测自己是否已经加载过类,如果已经加载则加载过程结束,如果没有加载的话则请求继续向上传递,直至Bootstrap ClassLoader。如果请求向上委托过程中,如果始终没有检测到该类已经加载,则Bootstrap ClassLoader开始尝试从其对应路劲中加载该类文件,如果失败则由子类加载器继续尝试加载,直至发起加载请求的子加载器为止。
采用双亲委派模式可以保证类型加载的安全性,不管是哪个加载器加载这个类,最终都是委托给顶层的BootstrapClassLoader来加载的,只有父类无法加载时,自己才尝试加载,这样就可以保证任何的类加载器最终得到的都是同样一个Object对象
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) {
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// 首先,检查该类是否已经被加载,如果从JVM缓存中找到该类,则直接返回
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
// 遵循双亲委派的模型,首先会通过递归从父加载器开始找,
// 直到父类加载器是BootstrapClassLoader为止
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {}
if (c == null) {
// 如果还找不到,尝试通过findClass方法去寻找
// findClass是留给开发者自己实现的,也就是说
// 自定义类加载器时,重写此方法即可
c = findClass(name);
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
1.2 双亲委派模型缺陷
在双亲委派模型中,子类加载器可以使用父类加载器已经加载的类,而父类加载器无法使用子类加载器已经加载的。这就导致了双亲委派模型并不能解决所有的类加载器问题。
**案例:**Java 提供了很多服务提供者接口(Service Provider Interface,SPI),允许第三方为这些接口提供实现。常见的 SPI 有 JDBC、JNDI、JAXP 等,这些SPI的接口由核心类库提供,却由第三方实现,这样就存在一个问题:SPI 的接口是 Java 核心库的一部分,是由BootstrapClassLoader加载的;SPI实现的Java类一般是由AppClassLoader来加载的。BootstrapClassLoader是无法找到 SPI 的实现类的,因为它只加载Java的核心库。它也不能代理给AppClassLoader,因为它是最顶层的类加载器。也就是说,双亲委派模型并不能解决这个问题。
1.3 使用线程上下文类加载器(ContextClassLoader)加载
如果不做任何的设置,Java应用的线程的上下文类加载器默认就是AppClassLoader。在核心类库使用SPI接口时,传递的类加载器使用线程上下文类加载器,就可以成功的加载到SPI实现的类。线程上下文类加载器在很多SPI的实现中都会用到。
通常我们可以通过Thread.currentThread().getClassLoader()和Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()获取线程上下文类加载器。
1.4 使用类加载器加载资源文件,比如jar包
类加载器除了加载class外,还有一个非常重要功能,就是加载资源,它可以从jar包中读取任何资源文件,比如,ClassLoader.getResources(String name)方法就是用于读取jar包中的资源文件。
//获取资源的方法
public Enumeration<URL> getResources(String name) throws IOException {
Enumeration<URL>[] tmp = (Enumeration<URL>[]) new Enumeration<?>[2];
if (parent != null) {
tmp[0] = parent.getResources(name);
} else {
tmp[0] = getBootstrapResources(name);
}
tmp[1] = findResources(name);
return new CompoundEnumeration<>(tmp);
}
它的逻辑其实跟类加载的逻辑是一样的,首先判断父类加载器是否为空,不为空则委托父类加载器执行资源查找任务,直到BootstrapClassLoader,最后才轮到自己查找。而不同的类加载器负责扫描不同路径下的jar包,就如同加载class一样,最后会扫描所有的jar包,找到符合条件的资源文件。
// 使用线程上下文类加载器加载资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// Array.class的完整路径
String name = "java/sql/Array.class";
Enumeration<URL> urls = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(name);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
System.out.println(url.toString());
}
}
二、Spring中SPI机制实现
2.1 SPI机制
2.1.1 SPI思想
SPI的全名为Service Provider Interface.这个是针对厂商或者插件的。
SPI的思想:系统里抽象的各个模块,往往有很多不同的实现方案,比如日志模块的方案,XML解析模块、jdbc模块的方案等。面向的对象的设计里,我们一般推荐模块之间基于接口编程,模块之间不对实现类进行硬编码。一旦代码里涉及具体的实现类,就违反了可拔插的原则,如果需要替换一种实现,就需要修改代码。为了实现在模块装配的时候能不在程序里动态指明,这就需要一种服务发现机制。
java spi就是提供这样的一个机制:为某个接口寻找服务实现的机制。
2.1.2 SPI约定
当服务的提供者,提供了服务接口的一种实现之后,在jar包的META-INF/services/目录里同时创建一个以服务接口命名的文件。该文件里就是实现该服务接口的具体实现类。而当外部程序装配这个模块的时候,就能通过该jar包META-INF/services/里的配置文件找到具体的实现类名,并装载实例化,完成模块的注入。通过这个约定,就不需要把服务放在代码中了,通过模块被装配的时候就可以发现服务类了。
2.2 SPI使用案例
common-logging apache最早提供的日志的门面接口。只有接口,没有实现。具体方案由各提供商实现, 发现日志提供商是通过扫描 META-INF/services/org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory配置文件,通过读取该文件的内容找到日志提工商实现类。只要我们的日志实现里包含了这个文件,并在文件里制定 LogFactory工厂接口的实现类即可。
2.3 Springboot中的类SPI扩展机制
在springboot的自动装配过程中,最终会加载META-INF/spring.factories文件,而加载的过程是由SpringFactoriesLoader加载的。从CLASSPATH下的每个Jar包中搜寻所有META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,然后将解析properties文件,找到指定名称的配置后返回。需要注意的是,其实这里不仅仅是会去ClassPath路径下查找,会扫描所有路径下的Jar包,只不过这个文件只会在Classpath下的jar包中。
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
// spring.factories文件的格式为:key=value1,value2,value3
// 从所有的jar包中找到META-INF/spring.factories文件
// 然后从文件中解析出key=factoryClass类名称的所有value值
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
// 取得资源文件的URL
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
// 遍历所有的URL
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
// 根据资源文件URL解析properties文件,得到对应的一组@Configuration类
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
// 组装数据,并返回
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
三、源码分析
先找到一个入口类getSpringFactoriesInstances
3.1 getSpringFactoriesInstances
根据类型获取META-INF/spring.factories文件中对应的实现类
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(tyhttp://www.devze.compe, new Class<?>[]{});
}
private <T> Collection编程客栈<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
//从META-INF/spring.factories中加载对应类型的类的自动配置类
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 加载上来后反射实例化
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 对实例列表进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
3.2 SpringFactoriesLoader
我们看看它的源码(精简):
public abstract class SpringFactoriesLoader {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoriesLoader.class);
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
}
}
这个类我们有利于我们继续往下找线索的代码是这一行:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
有了这一行代码,我们大致就可以猜出来这个SpringFactoriesLoader类大概是干嘛的了吧?它的两个核心方法一个是用来寻找spring.factories文件中的Factory名称的,一个是用来寻找类的。
3.3 loadFactoryNames
在该方法里,首先拿到ClassLoader,然后加载FactoryNames,加载类型(type)为ApplicationContextInitializer,类加载器(classLoader)为刚刚拿到的类加载器,返回值放入一个Set中,为的是确保没有重复的FactoryName,这是因为在之后加载的两个spring.factories配置文件中有两个重复的FactoryName。
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
这一步是为了使用给定的ClassLoader去给定的FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION中加载全部的工厂类
可以看到,加载的配置文件在META-INF下,名称为spring.factories,该配置文件一共有两个,且配置文件中,每个段落第一行为Key,后边为value,读取时会通过key将所有的value拿出来
在配置文件中我们发现,key和value都是包名加类名的字符串,因此Springboot在读取文件后,是通过反射生成的类
3.3.1 spring-boot-2.2.2.RELEASE.jar
该配置文件内容如下:
# PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Error Reporters org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationjsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor # Failure Analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer # FailureAnalysisReporters org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
3.3.2 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.2.RELEASE.jar

该配置文件内容如下:
# Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaLuationReportLoggingListener # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer # Auto Configuration Import Listeners org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener # Auto Configuration Import Filters org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition # Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BATch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudServiceConnectorsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconjsfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.Redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.rest.RestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.androidautoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedwebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration # Failure analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayMigrationScriptMissingFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autocwww.devze.comonfigure.session.NonUniqueSessionRepositoryFailureAnalyzer # Template availability providers org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure开发者_开发培训.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.JSPTemplateAvailabilityProvider
3.4 loadSpringFactories
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//到缓存中读取
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
//如果存在则直接返回
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
//获取所以jar包META-INF/spring.factories对应的URL
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
//遍历数据
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
//获取到资源数据
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
//加载配置文件
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
//遍历解析配置文件
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
//将spring.factories配置文件数据放进结果集
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
//加入缓存
cache.put(classLoader, result);
//返回结果
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
读取完spring.factories后,把读取到的内容(13个key)存储到枚举类中,然后遍历枚举类,将里边内容都add到一个map(result)里边去,最后把classloader以及遍历的结果都放入cache中,提高加载资源的效率。
3.5 createSpringFactoriesInstances
目前已经取出所有的配置,但还没有进行初始化,该方法是实例化对象的
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
//获取构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
//实例化对象
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
//加入instances实例列表
instances.add(instance);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
以上就是SpringBoot的SPI机制源码解析的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot SPI机制的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论