Spring配置文件和mybatis详解
目录
- 1.配置文件
- 1.1 概述
- 1.2 properties
- 1.3 yml
- 1.4 优缺点对比
- 1.5 @Value注解
- 2.myBATis
- 2.1 概述
- 2.2 前置操作
- 2.3 注解
- 2.3.1 配置
- 2.3.2 CRUD
- 2.3.3 @Param
- 2.4 XML
- 2.4.1 配置
- 2.4.2 示例
- 2.5 动态SQL
- 2.5.1 trim标签
- 2.5.2 if标签
- 2.5.3 where标签
- 2.5.4 set标签
- 2.5.5 foreach标签
- 2.5.6 include标签
- 2.6 主键返回
- 2.7 预编译/即时SQL
1.配置文件
1.1 概述
计算机配置文件:用于存储系统、应用程序的设置信息,通常以文本或结构化数据格式(如jsON、XML、INI等)保存。其核心功能包括但不限于:
- 参数定制:允许用户或管理员调整软件或硬件的运行参数
- 环境适配:根据不同设备或场景加载特定配置(如开发/生产环境)
- 持久化存储:确保重启后设置仍生效
SpringBoot配置文件:SpringBoot支持多种类型的配置文件,常见的格式包括properties、yaml和yml,主要用于集中管理应用程序的各种配置参数,简化部署和开发过程中的环境切换
- YAML和YML本质上是相同的文件格式,只是文件扩展名的不同,两者在功能和使用上没有区别
1.2 properties
- properties配置文件是最早期的配置⽂件格式,也是创建SpringBoot项⽬默认的配置⽂件
- 采用常见的键值对格式(key=value)
- 支持
#开头的注释
#应用程序名称 spring.application.name=configuration #应用程序端口号 server.port=8080 #数据库连接信息 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/database_name?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root
1.3 yml
- 采用键值对格式(key: value),冒号后必须有空格
- 数据序列化格式,通过缩进表示层级关系
- 支持
#开头的注释
spring:
application:
#应用程序名称
name: configuration
#数据库连接信息
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/database_name?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
#应用程序端口号
server:
port: 8080
1.4 优缺点对比
properties
- 优点:
- 语法简单直观,采用key=value形式,适合初学者快速上手
- 与Java生态兼容性极强
- 缺点:
- 缺乏层次结构,复杂配置时容易冗余。上述配置数据库连接信息时spring.datasource前缀冗余
- 不支持数据类型定义,所有值均为字符串,需手动转换
yml
- 优点:
- 层次化结构清晰,通过缩进表示层级,适合复杂配置场景
- 支持数据类型(如布尔值、数字),减少手动类型转换
- 缺点:
- 格式错误易导致解析失败(容易忽略冒号后空格)
- 部分旧版工具链兼容性较差,需额外依赖解析库
注:SpringBoot同时支持两种格式,混合使用时若key重复,properties优先级高于yml
1.5 @Value注解
作用:是Spring框架提供了一个@Value注解(org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value),用于将外部配置文件中的值注入到Spring管理的Bean中
示例:(properties和yml的读取方式相同)
package org.example.configuration.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class Config {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String applicationName;
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
public void print() {
System.out.println("applicationName=" + applicationName);
System.out.println("port=" + port);
System.out.println("url=" + url);
System.out.println("username=" + username);
System.out.println("password=" + password);
}
}
package org.example.configuration;
import org.example.configuration.config.Config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigurationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(ConfigurationApplication.class, args);
Config config = context.getBean(Config.class);
config.print();
}
}
运行结果:
applicationName=configurationport=8080url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/database_name?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=falseusername=rootpassword=root
2.mybatis
2.1 概述
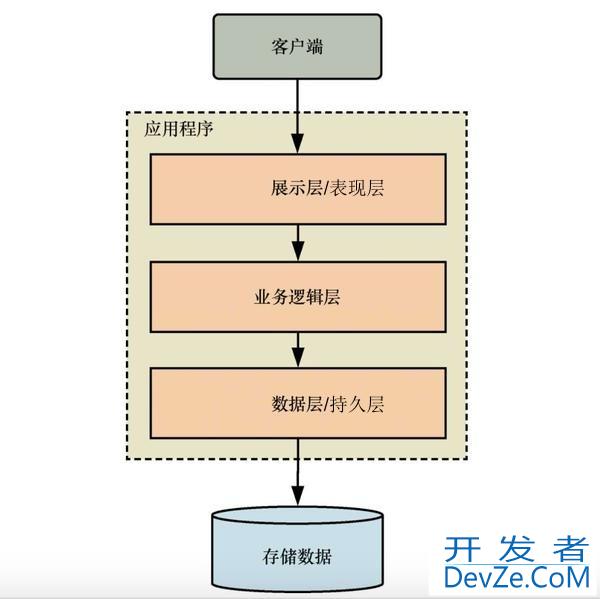
MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,支持自定义 SQL、存储过程、高级映射以及多种配置方式。它消除了几乎所有的JDBC代码和参数的手动设置以及结果集的检索
- 支持存储过程:指的是数据库管理系统(DBMS)允许用户创建、存储和执行存储过程的能力。存储过程是一组预编译的SQL语句,存储在数据库中,可以被应用程序调用执行
- 支持高级映射:指通过配置或注解实现复杂SQL查询结果与Java对象之间的灵活转换。其核心目标是简化数据库关联操作,提升开发效率
- 支持多种配置方式:mybatis支持注解和xml两种配置方式
2.2 前置操作
引入依赖:Spring Web,Mybatis Framework,MySQL Driver,Lombok

在application.properties/yml中添加数据库连接信息:
#应用程序名称 spring.application.name=configuration #应用程序端口号 server.port=8080 #数据库连接信息 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/database_name?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root #自动驼峰转换 mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
spring:
applicaphption:
#应用程序名称
name: configuration
#数据库连接信息
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/database_name?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
#应用程序端口号
server:
port: 8080
mybatis:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #自动驼峰转换
SQL命名规范:采用下划线分隔单词(如order_detail)
Java命名规范:大驼峰/小驼峰
2.3 注解
2.3.1 配置
- 1.创建一个接口,并使用 @Mapper注解 修饰
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface BlogMapper {
//其他代码
}
@Mapper注解:允许开发者直接在接口方法上通过注解配置SQL语句,无需编写XML映射文件。适用于简单SQL场景,能显著减少配置量
- 2.初始化数据
create table blog (id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(128),age int); insert into blog values (null,'刘备',30),(null,'关羽',28),(null,'张飞',25);
- 3.创建对应实体类
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class PersonInfo {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public PersonInfo(Integer id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public PersonInfo() {
}
}
2.3.2 CRUD
import com.example.spring_mybatis.model.PersonInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
@Mapper
public interface BlogMapper {
@Select("select * from blog")
List<PersonInfo> getPersonInfoAll();
@Insert("insert into blog values (#{id},#{name},#{age})")
Integer addPerson(PersonInfo person);
@Update("update blog set name = #{name},age = #{age} where id = #{id}")
Integer updatePerson(PersonInfo personInfo);
@Delete("delete from blog where id = #{id}")
Integer deletePerson(Integer id);
}
按住alt+insert,可在test目录下生成以上方法的测试方法
import com.example.spring_mybatis.model.PersonInfo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class BlogMapperTest {
private final BlogMapper blogMapper;
@Autowired
public BlogMapperTest(BlogMapper blogMapper) {
this.blogMapper = blogMapper;
}
@Test
void getPersonInfoAll() {
List<PersonInfo> personInfoAll = blogMapper.getPersonInfoAll();
log.info("查询成功,personInfoAll:{}",personInfoAll.toString());
//查询成功,personInfoAll:[PersonInfo(id=1, name=刘备, age=30),
//PersonInfo(id=2, name=关羽, age=28),
//PersonInfo(id=3, name=张飞, age=25)]
}
@Test
void addPerson() {
Integer ret = blogMapper.addPerson(new PersonInfo(null, "赵云", 25));
log.info("添加成功,影响行数:{}",ret.toString());//添加成功,影响行数:1
}
@Test
void updatePerson() {
Integer ret = blogMapper.updatePerson(new PersonInfo(1, "刘备", 35));
log.info("更新成功,影响行数:{}",ret.toString());//更新成功,影响行数:1
}
@Test
void deletePerson() {
Integer ret = blogMapper.deletePerson(4);
log.info("删除成功,影响行数:{}",ret.toString());//删除成功,影响行数:1
}
}
2.3.3 @Param
作用:用于在Mapper接口方法中为形式参数指定名称。当方法有多个参数时,通过该注解明确SQL中引用的参数名,避免依赖参数顺序
@Mapper
public interface BlogMapper {
//@Param
@Update("update blog set name = #{name},age = #{age} where id = #{id}")
Integer updatePersonInfo(@Param("id") Integer userId,@Param("name") String userName,@Param("age") Integerpython userAge);
}
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class BlogMapperTest {
private final BlogMapper blogMapper;
@Autowired
public BlogMapperTest(BlogMapper blogMapper) {
this.blogMapper = blogMapper;
}
@Test
void updatePersonInfo() {
Integer ret = blogMapper.updatePersonInfo(1, "刘玄德", 30);
log.info("更新成功,影响行数:{}",ret.toString());//更新成功,影响行数:1
}
}

2.4 xml
2.4.1 配置
- 1.创建一个接口,并使用 @Mapper注解 修饰
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface BlogXMLMapper {
//其他代码
}
- 2.配置mybatis的xml文件路径
mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/**Mapper.xml #配置mybatis的xml文件路径 #标识位于resources/mybatis路径下任何以Mapper结尾的xml文件为mybatis的配置文件

- 3.在resources/mybatis路径下创建以Mapper结尾的xml文件,并添加如下代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--namespace:用于指定该XML文件对应的Java接口或类的全限定名--> <mapper namespace="com.example.spring_mybatis.mapper_blog.BlogXMLMapper"> </mapper>
2.4.2 示例
在接口中声明方法
import com.example.spring_mybatis.model_blog.PersonInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface BlogXMLMapper {
List<PersonInfo> getPersonInfoAll();
}
在对应xml文件中实现接口方法
- id:是MyBatis映射文件中SQL语句的唯一标识符。需与Mapper接口中的方法名一致,保证映射正确
- resultType:指定SQL查询结果映射的Java对象类型,需为全限定类名
<mapper namespace="com.example.spring_mybatis.mapper_blog.BlogXMLMapper">
<select id="getPersonInfoAll" resultType="com.example.spring_mybatis.model_blog.PersonInfo">
select * from blog
</select>
</mapper>
按住alt+insert,可在test目录下生成以上方法的测试方法
import com.example.spring_mybatis.model_blog.PersonInfo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class BlogXMLMapperTest {
private final BlogXMLMapper blogXMLMapper;
@Autowired
public BlogXMLMapperTest(BlogXMLMapper blogXMLMapper) {
this.blogXMLMapper = blogXMLMapper;
}
@Test
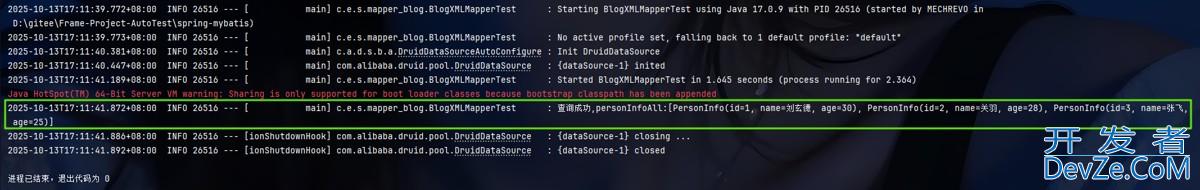
void getPersonInfoAll() {
List<PersonInfo> personInfoAll = blogXMLMapper.getPersonInfoAll();
log.info("查询成功,personInfoAll:{}",personInfoAll.toString());
}
}
运行结果:
2.5 动态SQL
动态SQL:指在程序运行时根据条件或参数动态生成的SQL语句。与静态SQL相比,动态SQL更具灵活性,适用于需要根据不同条件构建查询的场景。例如,在某些web/app进行账号注册时会出现非必填选项
- mybatis的注解和xml两种方式都能实现动态SQL,但xml较为方便,所以下文使用xml来实现动态SQL
2.5.1 trim标签
作用:用于自定义字符串截取规则。包含四个属性:
- prefix:最终结果添加前缀
- suffix:最终结果添加后缀
- prefixOverrides:去除首部指定内容
- suffixOverrides:去除尾部指定内容
2.5.2 if标签
作用:用于条件判断,通常在where或set语句中使用。当test表达式的值为true时,包含标签内的SQL片段
<insert id="addPersonInfo">
insert into blog
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
id,
</if>
<if test="name != null">
name,
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age,
</if>
</trim>
values
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
#{id},
</if>
<if test="name != null">
#{name},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
#{age},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
2.5.3 where标签
作用:替代SQL中的where关键字。当if条件成立时才会加入SQL片段,并自动去除第一个子句的and/or
<select id="getPersonInfoByNameAndAge">
select * from blog
<where>
<if test="name != null">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null">
and age = #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
2.5.4 set标签
作用:用于update语句。当if条件成立时才会加入SQL片段,并自动去除最后一个子句的逗号、
<update id="updatePersonInfo">
update blog
<set>
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age = #{age},
</if>
</set>
<where>
and id = #{id}
</where>
</update>
2.5.5 foreach标签
作用:用于集合遍历。主要属性:
- collection:集合参数名
- item:当前元素变量名
- open/close:包围符号
- sephttp://www.devze.comarator:分隔符
@Test
void getPersonInfoById() {
ArrayList<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
ids.add(3);
List<PersonInfo> personInfoById = blogXMLMapper.getPersonInfoById(ids);
System.out.println(personInfoById);
}
<select id="getPersonInfoById" resultType="com.example.spring_mybatis.model_blog.PersonInfo">
select * from blog
where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(js" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
2.5.6 include标签
作用:用于引用SQL片段,通过refid指定要引用的片段id。需配合sql标签使用,实现代码复用
<sql id="collection">
id,name,age
</sql>
<select id="getPersonInfoAll" resultType="com.example.spring_mybatis.model_blog.PersonInfo">
select
<include refid="collection">
</include>
from blog
</select>
2.6 主键返回
主键返回:指在数据库插入操作后,自动获取刚插入记录的主键值。在mybatis中使用注解和xml都能获取到返回的主键
1.注解实现
@Mapper
public interface BlogMapper {
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id")
@Insert("insert into blog values (#{id},#{name},#{age})")
Integer addPerson(PersonInfo person);
}
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class BlogMapperTest {
private final BlogMapper blogMapper;
@Autowired
public BlogMapperTest(BlogMapper blogMapper) {
this.blogMapper = blogMapper;
}
@Test
void addPerson() {
PersonInfo personInfo = new PersonInfo(null, "黄忠", 60);
Integer ret = blogMapper.addPerson(personInfo);
log.info("添加成功,影响行数:{},返回的主键值:{}",ret.toString(),personInfo.getId());//添加成功,影响行数:1,返回的主键值:6
}
}

2.通过xml实现
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class BlogXMLMapperTest {
private final BlogXMLMapper blogXMLMapper;
@Autowired
public BlogXMLMapperTest(BlogXMLMapper blogXMLMapper) {
this.blogXMLMapper = blogXMLMapper;
}
@Test
void addPersonInfo() {
PersonInfo personInfo = new PersonInfo();
personInfo.setAge(40);
personInfo.setName("曹操");
Integer ret = blogXMLMapper.addPersonInfo(personInfo);
log.info("添加成功,影响行数:{},返回的主键值:{}",ret.toString(),personInfo.getId());//添加成功,影响行数:1,返回的主键值:7
}
}
<insert id="addPersonInfo" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into blog
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
id,
</if>
<if test="name != null">
name,
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age,
</if>
</trim>
values
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="http://www.devze.comid != null">
#{id},
</if>
<if test="name != null">
#{name},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
#{age},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>

2.7 预编译/即时SQL
预编译SQL(Prepared Statements):SQL语句在程序运行前被预先编译并存储在数据库中。执行时只需传递参数,无需重新编译SQL语句
- 安全性高:通过参数化查询避免SQL注入攻击。参数化查询是一种将SQL语句与用户输入数据分离的数据库操作方式,查询语句中使用占位符(如?、@param等)代替直接拼接用户输入,执行时通过预编译机制将参数动态绑定到占位符位置
- 性能优化:编译一次,多次执行,减少数据库开销
即时SQL(Dynamic SQL):在程序运行时动态生成并立即编译执行,每次执行都可能涉及完整的SQL解析和编译过程
- 灵活性高:可根据运行时条件动态拼接SQL语句
- 潜在风险:直接拼接用户输入可能导致SQL注入
- 性能开销:每次执行需重新编译
#占位符会使用预编译机制,将参数值安全地绑定到SQL语句中,防止SQL注入攻击。MyBatis会将#替换为?,然后通过JDBC的预编译功能设置参数值
$占位符直接进行字符串替换,将参数值拼接到SQL语句中,不会进行预编译或转义处理
SQL注入攻击:当恶意输入" 'or 1 = '1 "时
@Select("select * from blog where name= #{name}")
List<UserInfo> queryByName(String name)
预编译SQL会根据参数的类型判断是否需要加引号,上述name参数是String类型,需要加引号,这就是参数化查询的作用。最终SQL:
select * from blog where name = " 'or 1='1 "; # 整个 'or 1='1 会作为name的值
2.即时SQL
@Select("select * from blog where name= '${name}'")
List<UserInfo> queryByName(String name)
即时SQL不会判断参数类型从而是否添加引号,所以需要手动加上单引号。最终SQL:
select * from blog where name = ''or 1 = '1'; # 因为1=1是恒等式,所以该表的数据会被全部查询出来,这就是SQL注入
到此这篇关于Spring配置文件和mybatis的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring配置文件和mybatis内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论