C++中stack和queue的用法及说明
目录
- 前言
- 1.stack的介绍和实现
- 1.1 Stack 的基本概念
- 1.2 Stack 的模拟实现
- 1.3 自定义 Stack 的使用
- 2.queue的介绍和实现
- 2.1 Queue 的基本概念
- 2.2 Queue 的模拟实现
- 2.3 自定义 Queue 的使用
- 3. 设计模式
- 4.priority_queue的介绍和实现
- 4.1 priority_queue的使用
- 4.1.1 C++ 标准库中
- 4.1.2 自定义优先队列
- 5. STL标准库中stack和queue的底层结构
- 6. deque的简单介绍
- 7. 双端队列的模拟实现
- 1. 主类Deque
- 2. 迭代器类Iterator
- 3. 构造函数和常规操作
- 4. 内部实现和辅助函数
- 8. 完整代码及演示
- 总结
前言
在 C++ 中,stack(栈)和 queue(队列)是两种常用的容器适配器,分别用于管理数据的后进先出(LIFO)和先进先出(FIFO)访问模式。
本文将详细介绍这两种数据结构的基本概念、常见操作及其在 C++ 中的实现,并探讨与其相关的设计模式。
1.stack的介绍和实现
1.1 Stack 的基本概念
Stack 是一种后进先出(LIFO, Last In First Out)的数据结构。这意味着最新添加的元素最先被移除。
- 常见的操作包括:
| 函数说明 | 接口说明 |
| stack() | 构造空的栈 |
| empty() | 检测stack是否为空 |
| size() | 返回stack中元素的个数 |
| top() | 返回栈顶元素的引用 |
| push() | 将元素val压入stack中 |
| pop() | 将stack中尾部的元素弹出 |
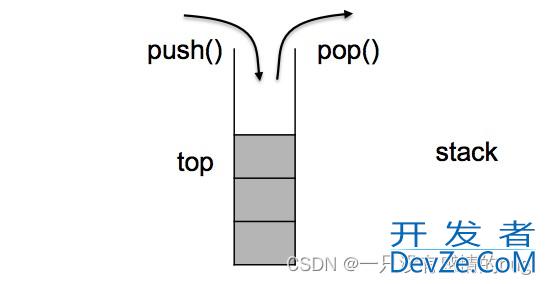
1.2 Stack 的模拟实现
以下是一个基于 C++ 模板的栈实现,默认情况下使用 deque 作为底层容器。通过模板参数,用户可以指定其他支持相同操作的容器类型(如 vector)。
template <class T, class Container = deque<T>> // 缺省值
class MyStack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop() // 不支持 第二个参数是vectot<T>的原因是它没有pop_front(),但仍可以变向的实现
{
// 这样就可以支持vector了,但效率就很低了
// _con.erase(bebin());
_con.pop_back();
}
const T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
1.3 自定义 Stack 的使用
#include "stack_queue.h"
int main()
{
// 栈:
cout << "STACK :" << endl;
bit::MyStack <int, list<int >> st1;
bit::MyStack <int, deque<int >> st2;
st1.push(1);
st1.push(2);
st1.push(3);
st2.push(4);
st2.push(5);
st2.push(6);
while (!st1.empty())
{
cout << st1.top() << " ";
st1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
while (!st2.empty())
{
cout << st2.top() << " ";
st2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
输出:
STACK : 3 2 1 6 5 4
OJ上的使用
最小栈
class MinStack {
stack<int> x_stack;
stack<int> min_stack;
public:
MinStack() {
min_stack.push(INT_MAX);
}
void push(int x) {
x_stack.push(x);
min_stack.push(min(min_stack.top(), x));
}
void pop() {
x_stack.pop();
min_stack.pop();
}
int top() {
return x_stack.top();
}
int getMin() {
return min_stack.top();
}
};
栈的压入、弹出序列
class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int>& pushV, vector<int>& popV) {
if (pushV.size() != popV.size()) return false;
stack<int> stk;
int popIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pushV.size(); ++i) {
stk.push(pushV[i]);
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() == popV[popIndex]) {
stk.pop();
++popIndex;
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
};
逆波兰表达式求值
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> s;
for (size_t i = 0; i < tokens.size(); ++i) {
string& str = tokens[i];
// str为数字
if (!("+" == str || "-" == str || "*" == str || "/" == str)) {
s.push(atoi(str.c_str()));
} else {
// str为操作符
int right = s.top();
s.pop();
int left = s.top();
s.pop();
switch (str[0]) {
case '+':
s.push(left + right);
break;
case '-':
s.push(left - right);
break;
case '*':
s.push(left * right);
break;
case '/':
// 题目说明了不存在除数为0的情况
s.push(left / right);
break;
}
}
}
return s.top();
}
};
用两个栈实现队列
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> A; // 栈 A,用于存储新加入的元素
stack<int> B; // 栈 B,用于反转 A 中的元素以实现队列的 FIFO 特性
public:
// 初始化数据结构
MyQueue() {}
// 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
void push(int x) {
A.push(x); // 直接将元素压入栈 A
}
// 从队列前端移除元素并返回该元素
int pop() {
int peek = this->peek(); // 获取队列前端的元素
B.pop(); // 从栈 B 中移除该元素
return peek; // 返回被移除的元素
}
// 获取队列前端的元素
int peek() {
// 如果栈 B 非空,直接返回栈 B 的栈顶元素
if (!B.empty())
return B.top();
// 如果栈 A 也为空,返回 -1 表示队列为空
if (A.empty())
return -1;
// 将栈 A 中的所有元素移动到栈 B 中,以反转元素顺序
while (!A.empty()) {
B.push(A.top());
A.pop();
}
// 返回栈 B 的栈顶元素,即队列前端的元素
return B.top();
}
// 返回队列是否为空
bool empty() {
// 如果栈 A 和栈 B 都为空,表示队列为空
return A.empty() && B.empty();
}
};
2.queue的介绍和实现
2.1 Queue 的基本概念
Queue 是一种先进先出(FIFO, First In First Out)的数据结构。这意味着最先添加的元素最先被移除。
- 常见的操作包括:
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| queue() | 构造空的队列 |
| empty() | 检测队列是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size() | 返回队列中有效元素的个数 |
| front() | 返回队头元素的引用 |
| back() | 返回队尾元素的引用 |
| push() | 在队尾将元素val入队列 |
| pop() | 将队头元素出队列 |
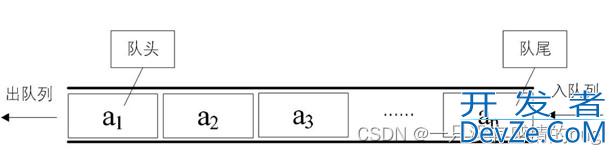
2.2 Queue 的模拟实现
以下是一个基于 C++ 模板的队列实现,默认情况下使用 deque 作为底层容器。通过模板参数,用户可以指定其他支持相同操作的容器类型(如 list)。
// 队列的实现:
template <class T, class Container = deque<T>> // 缺省值
class MyQueue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front();
}
const T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
2.3 自定义 Queue 的使用
#include "stack_queue.h"
int main()
{
// 队列:
cout << "QUEUE :" << endl;
bit::MyQueue <int, list<int >> q1;
bit::MyQueue <int, deque<int >> q2;
q1.push(1);
q1.push(2);
q1.push(3);
q2.push(4);
q2.push(5);
q2.push(6);
while (!q1.empty())
{
cout << q1.front() << " ";
q1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
while (!q2.empty())
{
cout << q2.front() << " ";
q2.pop();
}
return 0;
}
输出:
QUEUE : 1 2 3 4 5 6
OJ上的使用
用两个队列实现栈
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> queue1; // 主队列,用于存储栈中的元素
queue<int> queue2; // 辅助队列,用于帮助元素的重新排列
// 初始化数据结构
MyStack() {}
// 将元素 x 压入栈
void push(int x) {
// 将新元素压入辅助队列
queue2.push(x);
// 将主队列中的所有元素移到辅助队列中
while (!queue1.empty()) {
queue2.push(queue1.front());
queue1.pop();
}
// 交换主队列和辅助队列
swap(queue1, queue2);
}
// 移除并返回栈顶元素
int pop() {
int r = queue1.front(); // 获取栈顶元素
queue1.pop(); // 移除栈顶元素
return r; // 返回栈顶元素
}
// 获取栈顶元素
int top() {
return queue1.front(); // 返回栈顶元素
}
// 判断栈是否为空
bool empty() {
return queue1.empty(); // 返回主队列是否为空
}
};
3. 设计模式
设计模式
- 常见的设计模式共有 23 种。
适配器模式 -- 封装转换
- 适配器模式是一种结构型设计模式,它允许接口不兼容的对象协同工作。
- 栈和队列的实现正是通过适配器模式来封装不同的底层容器(如
deque、vector等),提供统一的接口。
迭代器模式 -- 统一访问方式 (数据结构访问都可以用)
- 迭代器模式是一种行为型设计模式,它提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而不需要暴露该对象的内部表示。
- 在栈和队列的实现中,虽然没有直接使用迭代器模式,但它们的底层容器(如
deque)本身支持迭代器,这使得我们可以通过迭代器访问容器中的元素。
4.priority_queue的介绍和实现
通过对priority_queue的底层结构就是堆,因此此处只需对对进行通用的封装即可。
4.1 priority_queue的使用
使用priority_queue的关键点
- 默认大顶堆:
priority_queue<int>,使用默认的less<int>比较函数,因此它是一个大顶堆。 - 小顶堆:
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>,通过传递greater<int>作为比较函数,使其成为小顶堆。 - 需要指定容器类型:当指定比较函数(如
greater<int>或less<int>)时,也必须显式指定底层容器类型(通常是vector<int>)。
4.1.1 C++ 标准库中
代码 :
// 库中优先队列的使用
#include <IOStream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = { 3,2,7,6,0,4,1,9,8,5 };
// 优先队列(堆)
/*
priority_queue<int> q1;
for (auto e : v)
q1.push(e);
*/
// priority_queue<int> q1(v.begin(), v.end());
int a[] = { 3,2,7,6,0,4,1,9,8,5 };
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));//小堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> q2(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));//大堆
while (!q1.empty())
{
cout << q1.top() << " ";
q1.pop();// 删除堆顶元素
}
cout << endl;
while (!q2.empty())
{
cout << q2.top() << " ";
q2.pop();// 删除堆顶元素
}
return 0;
}
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
4.1.2 自定义优先队列
PriorityQueue.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // for std::swap
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
template<class T>
struct myless
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
struct mygreater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = mygreater<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
priority_queue() = default;
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
// 建堆
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
{
adjust_down(i);
}
}
void adjust_up(int child)
{
Compare comfunc;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (comfunc(_con[child], _con[parent]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
编程客栈 {
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void adjust_down(int parent)
{
Compare comfunc;
int size = _con.size();
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < size)
{
if (child + 1 < size && comfunc(_con[child + 1], _con[child]))
{
child++;
}
if (comfunc(_con[child], _con[parent]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con.front();
}
void pop()
{
if (!_con.empty())
{
swap(_con.front(), _con.back());
_con.pop_back();
if (!_con.empty())
{
adjust_down(0);
}
}
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
test.cpp
#include "PriorityQueue.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
// 默认构造函数,使用初始化列表初始化年、月、日
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year), _month(month), _day(day)
{}
// 重载小于运算符
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
// 重载大于运算符
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
// 重载等于运算符
bool operator==(const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;
}
// 重载不等于运算符
bool operator!=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 输出日期
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Date& d)
{
os << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return os;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 库中的priority_queue使用
void TestPriorityQueue1()
{
Date date1(2023, 6, 9);
Date date2(2024, 1, 1);
Date date3(2018, 9, 10);
priority_queue<Date> q;// 默认大堆
q.push(date1);
q.push(date2);
q.push(date3);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.top() << endl;
q.pop();
}
}
class PDateLess
{
public:
bool operator()(Date* p1, Date* p2)
{
return *p1 < *p2;
}
};
void TestPriorityQueue2()
{
bit::priority_queue<Date*, vector<Date*>, PDateLess> q;
q.push(new Date(2023, 6, 9));
q.push(new Date(2024, 1, 1));
q.push(new Date(2018, 9, 10));
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << *q.top() << endl;
q.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
// 大堆,需要用户在自定义类型中提供比较的重载
// priority_queue<Date*, vector<Date*>, PDateLess> q1;
TestPriorityQueue1();
cout << "-----------------------" << endl;
TestPriorityQueue2();
return 0;
}
输出:
2024-1-1 2023-6-9 2018-9-10 ----------------------- 2018-9-10 2023-6-9 2024-1-1
5. STL标准库中stack和queue的底层结构
虽然stack和queue中也可以存放元素,但在STL中并没有将其划分在容器的行列,而是将其称为容器适配 器,这是因为stack和队列只是对其他容器的接口进行了包装,STL中stack和queue默认使用deque,比如:

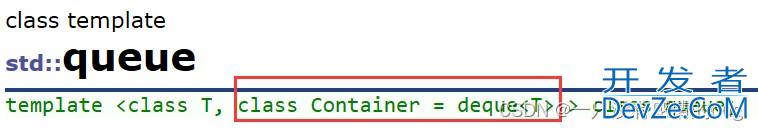
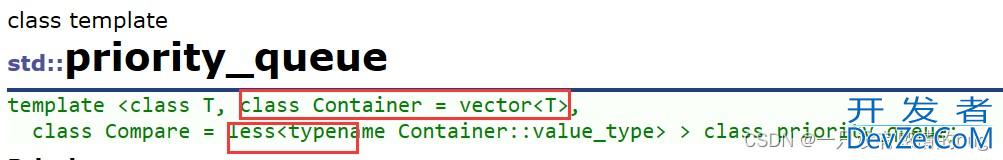
6. deque的简单介绍
deque(双端队列)是一种双开口的“连续”空间的数据结构,双开口的含义是:可以在头尾两端进行插入和删除操作,且时间复杂度为 O(1)。
与 vector 比较,deque 在头部插入时效率更高,因为不需要搬移元素;与 list 比较,deque 的空间利用率更高。
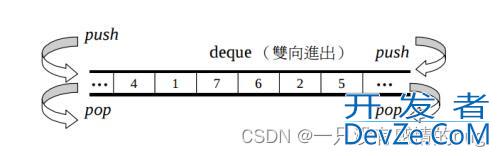
deque并不是真正连续的空间,而是由一段段连续的小空间拼接而成的,实际deque类似于一个动态的二维数组,其底层结构如下图所示:
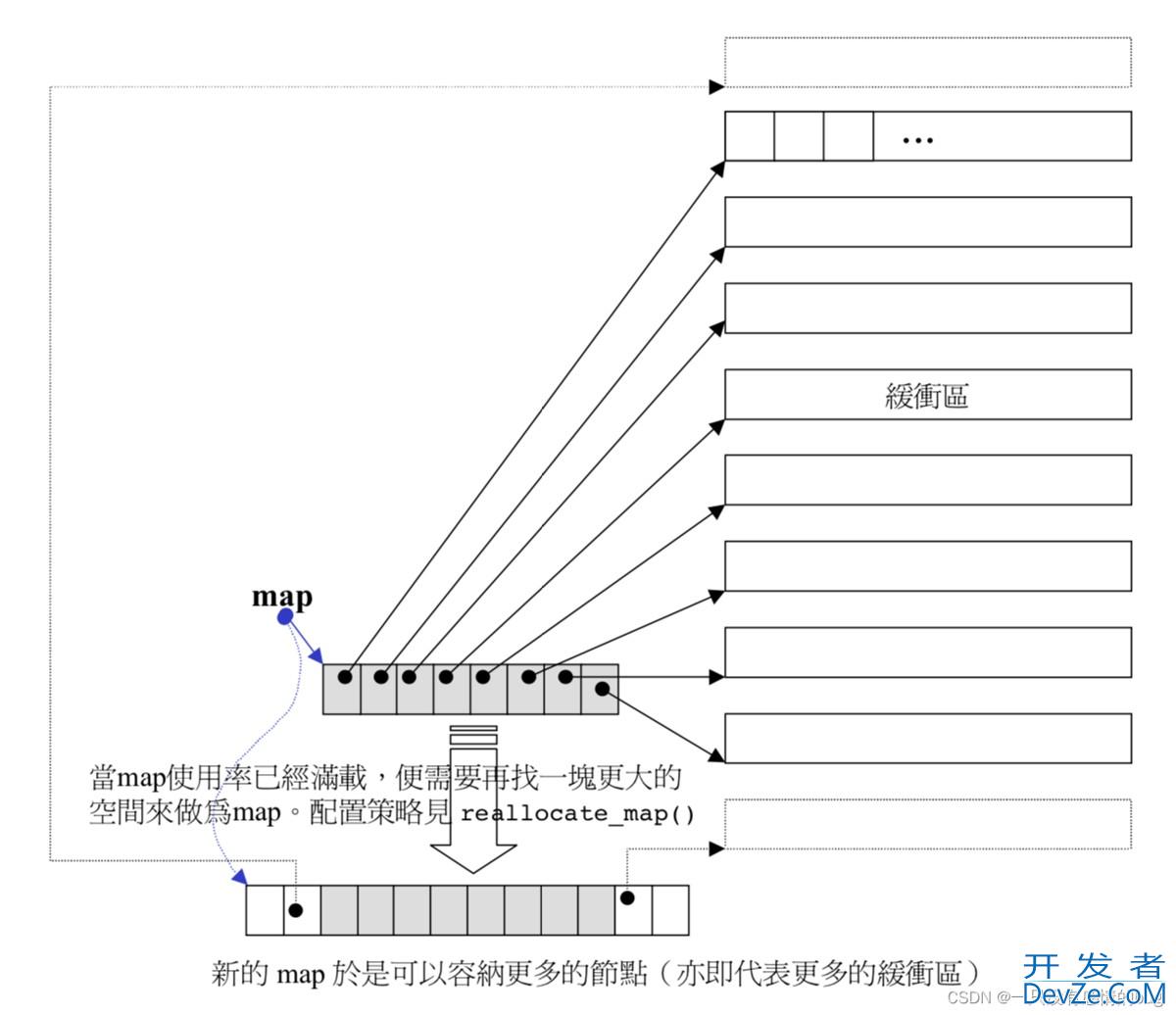
双端队列底层是一段假象的连续空间,实际是分段连续的,为了维护其“整体连续”以及随机访问的假象,落 在了deque的迭代器身上,因此deque的迭代器设计就比较复杂,如下图所示:
那deque是如何借助其迭代器维护其假想连续的结构呢?

deque 的缺陷
deque 有一个致命缺陷:不适合遍历,因为android在遍历时,deque 的迭代器要频繁地检测是否移动到某段小空间的边界,导致效率低下。
而在序列式场景中,可能需要经常遍历。
因此在实际中,需要线性结构时,大多数情况下优先考虑 vector 和 list,deque 的应用并不多。
而目前能看到的一个应用就是,STL 用其作为 stack 和 queue 的底层数据结构。
以下通过对大量数据排序来证明遍历 queue 导致的效率很低
遍历queue的性能比较
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// vector与deque的性能对比(相同的结构,相同的访问)
srand(time(0));
deque<int> dq1;
deque<int> dq2;
int N = 1000000;
for (int i = 0;i < N;++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
dq1.push_back(e);
dq2.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
sort(dq1.begin(), dq1.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
//拷贝到vector
vector<int> v(dq1.begin(), dq1.end());
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
//拷贝回deque
dq2.assign(v.begin(), v.end()); // 迭代区间赋值
int end2 = clock();
cout << "deque sort: " << end1 - begin1 << endl;
cout << "deque copy vector sort, copy back deque: " << end2 - begin2 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
deque sort: 1456 deque copy vector sort, copy back deque: 198
对于大规模数据的访问,显然 deque 效率落入下风。
总结
尽管 deque 在某些方面具有优势,但由于其遍历性能较低和内存管理复杂等缺陷,在需要频繁遍历或要求高效随机访问的场景中,vector 和 list 通常是更好的选择。因此,在实际应用中,deque 的使用相对较少,主要用于特定场景,如 stack 和 queue 的底层数据结构。
为什么选择 deque 作为 stack 和 queue 的底层默认容器?
stack 是一种后进先出的特殊线性数据结构,因此只要具有 push_back() 和 pop_back() 操作的线性结构,都可以作为 stack 的底层容器,比如 vector 和 list 都可以;androidqueue 是先进先出的特殊线性数据结构,只要具有 push_back() 和 pop_front() 操作的线性结构,都可以作为 queue 的底层容器,比如 list。
选择 deque 作为 stack 和 queue 的底层默认容器主要是由于 deque 的特性能够很好地满足这两种数据结构的需求。以下是详细的原因:
1. 只需要在固定的一端或两端进行操作
stack 和 queue 主要在固定的一端或两端进行操作:
stack:后进先出(LIFO),主要在末端进行插入和删除操作。queue:先进先出(FIFO),在前端删除,在末端插入。
由于 deque(双端队列)支持在两端进行高效的插入和删除操作,因此非常适合用于实现 stack 和 queue。
2. 扩展效率
deque vs vector:
- 当
deque扩展时,不需要像vector那样搬移整个数组。deque是分段存储的,扩展时只需增加新的块,而不是搬移整个容器中的元素。 - 这使得
deque在元素增长时具有更高的效率,因为deque避免了大量的内存复制。
3. 内存使用效率
deque vs list:
list是链表结构,虽然在插入和删除时也很高效,但它的节点需要额外的内存来存储指针,并且每次操作都需要动态分配内存,导致内存利用率较低。deque是基于分段的动态数组,内存利用率更高,因为每个块的内存分配是连续的,且不需要额外的指针开销。
4. CPU 缓存命中率
连续内存块带来的优势:
deque的每个块都是连续的内存,尽管整个deque是分段存储的。- 这种设计相比于链表,具有更高的 CPU 缓存命中率,因为访问同一个块中的元素时,能更好地利用 CPU 缓存。
7. 双端队列的模拟实现
1. 主类Deque
这是 deque 的主类,用于实现双端队列的基本操作和管理。
template <typename T>
class Deque {
public:
class Iterator;
Deque(); // 构造函数
void push_back(const T& value); // 在尾部插入元素
void push_front(const T& value); // 在头部插入元素
void pop_back(); // 删除尾部元素
void pop_front(); // 删除头部元素
Iterator begin() const; // 返回双端队列的开始迭代器
Iterator end() const; // 返回双端队列的结束迭代器
bool isEmpty() const; // 判断双端队列是否为空
private:
T** map; // 指向块的指针数组
size_t map_size; // 中控数组的大小
Iterator start; // 开始迭代器
Iterator finish; // 结束迭代器
void allocateblock(bool atFront = false); // 分配新的块
};
2. 迭代器类Iterator
这是 deque 的迭代器类,用于实现遍历双端队列中的元素。
template <typename T>
class Iterator {
public:
T* cur; // 当前元素的指针
T* first; // 当前块的起始位置的指针
T* last; // 当前块的结束位置的指针
T** node; // 指向中控数组中当前块的指针
Iterator(); // 默认构造函数
Iterator(T* cur, T* first, T* last, T** node); // 带参数的构造函数
T& operator*() const; // 解引用操作符
Iterator& operator++(); // 前置自增操作符
Iterator operator++(int); // 后置自增操作符
Iterator& operator--(); // 前置自减操作符
Iterator operator--(int); // 后置自减操作符
bool operator==(const Iterator& other) const; // 相等比较操作符
bool operator!=(const Iterator& other) const; // 不等比较操作符
};
因为 Iterator 类的操作会更新指针成员 cur、start 等,确保它们始终指向有效的内存区域,因此不会出现释放内存导致悬空指针的情况。
在 Deque 类中,Iterator 对象的生命周期受到 Deque 对象的控制,在 Deque 的生命周期内,Iterator 对象的指针成员都是有效的。
3. 构造函数和常规操作
// 前向声明 Iterator 类
class Iterator;
// 默认构造
Deque() : map(nullptr), map_size(0)
{
allocateBlock();
start.node = finish.node = map;
start.cur = finish.cur = *start.node + BLOCK_SIZE / 2;
start.first = finish.first = *start.node;
start.last = finish.last = *start.node + BLOCK_SIZE;
}
// 尾插
void push_back(const T& value)
{
if (finish.cur == finish.last)
{
allocateBlock();
++finish.node;
finish.first = *finish.node;
finish.last = finish.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
finish.cur = finish.first;
}
*finish.cur = value;
++finish.cur;
}
// 头插
void push_front(const T& value)
{
if (start.cur == start.first)
{
allocateBlock(true);
--start.node;
start.first = *start.node;
start.last = start.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
start.cur = start.last;
}
--start.cur;
*start.cur = value;
}
// 尾删
void pop_back() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw std::out_of_range("Deque is empty"); // 异常处理
}
if (finish.cur == finish.first) {
--finish.node;
finish.first = *finish.node;
finish.last = finish.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
finish.cur = finish.last;
}
--finish.cur;
}
// 头删
void pop_front()
{
if (isEmpty())
{
throw std::out_of_range("Deque is empty"); // 异常处理
}
if (start.cur == start.last)
{
++start.node;
start.first = *start.node;
start.last = start.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
start.cur = start.first;
}
++start.cur;
}
Iterator begin() const
{
return start;
}
Iterator end() const
{
return finish;
}
bool isEmpty() const
{
return start == finish;
}
后面我们包装在主类dqeue中,便于管理
4. 内部实现和辅助函数
void allocateBlock(bool atFront = false) // 分配新的块
{
T** new_map = new T * [map_size + 1]; // 中控数组的空间大小+1,存放增加的块
for (size_t i = 0; i < map_size; ++i)
{
new_map[i + (atFront ? 1 : 0)] = map[i]; // 如果 atFront 为 false,则 map 中的内容保持原位置
}
new_map[atFront ? 0 : map_size] = new T[BLOCK_SIZE];// 为新的块分配空间
delete[] map; // 释放旧的 map 内存。
map = n编程客栈ew_map; // map 指向新的指针数组 new_map。
++map_size;
if (atFront) // 如果在前端分配新的块,调整 start 和 finish 迭代器的 node 指针,确保它们指向正确的位置。
{ //这一步是必要的,因为在 map 前端插入新的块后,这将导致原本的所有块指针都需要向后移动一位。
++start.node;
++finish.node;
}
}
8. 完整代码及演示
deque.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept> // 提供了标准化的方式来报告和处理错误
#include <vector>
const size_t BLOCK_SIZE = 8; // 块的大小
template <typename T>
class Deque {
public:
// 前向声明 Iterator 类
class Iterator;
// 默认构造
Deque() : map(nullptr), map_size(0)
{
allocateBlock();
start.node = finish.node = map;
start.cur = finish.cur = *start.node + BLOCK_SIZE / 2;
start.first = finish.first = *start.node;
start.last = finish.last = *start.node + BLOCK_SIZE;
}
// 尾插
void push_back(const T& value)
{
if (finish.cur == finish.last)
{
allocateBlock();
++finish.node;
finish.first = *finish.node;
finish.last = finish.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
finish.cur = finish.first;
}
*finish.cur = value;
++finish.cur;
}
// 头插
void push_front(const T& value)
{
if (start.cur == start.first)
{
allocateBlock(true);
--start.node;
start.first = *start.node;
start.last = start.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
start.cur = start.last;
}
--start.cur;
*start.cur = value;
}
// 尾删
void pop_back() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw std::out_of_range("Deque is empty"); // 异常处理
}
if (finish.cur == finish.first) {
--finish.node;
finish.first = *finish.node;
finish.last = finish.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
finish.cur = finish.last;
}
--finish.cur;
}
// 头删
void pop_front()
{
if (isEmpty())
{
throw std::out_of_range("Deque is empty"); // 异常处理
}
if (start.cur == start.last)
{
++start.node;
start.first = *start.node;
start.last = start.first + BLOCK_SIZE;
start.cur = start.first;
}
++start.cur;
}
Iterator begin() const
{
return start;
}
Iterator end() const
{
return finish;
}
bool isEmpty() const
{
return start == finish;
}
class Iterator {
public:
T* cur; // 当前元素的指针
T* first; // 当前块的起始位置的指针
T* last; // 当前块的结束位置的指针
T** node; // 指向中控数组中当前块的指针
// 默认构造函数
Iterator()
: cur(nullptr), first(nullptr), last(nullptphpr), node(nullptr)
{}
// 带参数的构造函数
Iterator(T* cur, T* first, T* last, T** node)
: cur(cur), first(first), last(last), node(node)
{}
T& operator*() const // 解引用操作符
{
return *cur;
}
Iterator& operator++() // 前置自增操作符
{
++cur;
if (cur == last)
{
++node;
first = *node;
last = first + BLOCK_SIZE;
cur = first;
}
return *this;
}
Iterator operator++(int) // 后置自增操作符
{
Iterator temp = *this;
++(*this);
return temp;
}
Iterator& operator--() // 前置自减操作符
{
if (cur == first)
{
--node;
first = *node;
last = first + BLOCK_SIZE;
cur = last;
}
--cur;
return *this;
}
Iterator operator--(int) // 后置自减操作符
{
Iterator temp = *this;
--(*this);
return temp;
}
bool operator==(const Iterator& other) const // 相等比较操作符
{
return cur == other.cur;
}
bool operator!=(const Iterator& other) const // 不等比较操作符
{
return !(*this == other);
}
};
private:
T** map; // 指向块的指针数组
size_t map_size; // 中控数组的大小
Iterator start; // 开始迭代器
Iterator finish; // 结束迭代器
void allocateBlock(bool atFront = false) // 分配新的块
{
T** new_map = new T * [map_size + 1]; // 中控数组的空间大小+1,存放增加的块
for (size_t i = 0; i < map_size; ++i)
{
new_map[i + (atFront ? 1 : 0)] = map[i]; // 如果 atFront 为 false,则 map 中的内容保持原位置
}
new_map[atFront ? 0 : map_size] = new T[BLOCK_SIZE];// 为新的块分配空间
delete[] map; // 释放旧的 map 内存。
map = new_map; // map 指向新的指针数组 new_map。
++map_size;
if (atFront) // 如果在前端分配新的块,调整 start 和 finish 迭代器的 node 指针,确保它们指向正确的位置。
{ //这一步是必要的,因为在 map 前端插入新的块后,这将导致原本的所有块指针都需要向后移动一位。
++start.node;
++finish.node;
}
}
};
test.cpp
#include "deque.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Deque<int> dq;
dq.push_back(1);
dq.push_back(2);
dq.push_back(3);
dq.push_front(0);
dq.push_front(-1);
for (Deque<int>::Iterator it = dq.begin(); it != dq.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
dq.pop_back();
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front(); // 抛异常
for (Deque<int>::Iterator it = dq.begin(); it != dq.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出
-1 0 1 2 3 1 2
以上便是对C++ 中 stack 和 queue 的底层数据结构和优先队列priority_queue的简单实现。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论