Java Map和Set使用详解(最新推荐)
目录
- Map和Set
- 二叉搜索树
- 查找
- 分析:
- 插入
- 删除
- Map
- Map的使用
- Set
- Set的使用
- 哈希表
- 负载因子的调节(重点)
- 闭散列
- 开散列
- HashMap和HashSet
- 面试题
- HashMap的源码
Map和Set
- map和set用于搜索
- 搜索树,二叉搜索树 -> AVL树 -> 红黑树
- AVL树:高度平衡的二叉搜索树
- TreeMap和TreeSet底层是红黑树,每次存储元素都得进行大小比较
二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树:如果左子树不为空,那么左子树所有节点都小于根节点,如果右子树不为空,那么右子树所有节点都大于根节点,它的左右子树都是二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的
查找
- 比key大往右找,比key小往左找
// 查找
pcuoWlublic boolean search(int key){
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val > key){
cur = cur.left;
}else if(cur.val < key){
cur = cur.right;
}else{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
分析:
- 时间复杂度:最好情况:O(logN),完全二叉树最坏情况:O(N),单分支的二叉树
插入
// 插入
public boolean insert(int key){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(key);
TreeNode parent = null;
if(root == null){
root = node;
return true;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val < key){
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}else if(cur.val > key){
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}else{
// 在二叉搜索树中只能不能有相同的数字,比如5,有一个5就可以了,只要有这个数就可以了
return false;
}
}
if(parent.val < key){
parent.right= node;
}else{
parent.left = node;
}
return true;
}
删除
- 第一种情况:cur.left == null要删除的节点是curcur是根节点cur是某个节点的左边cur是某个节点的右边
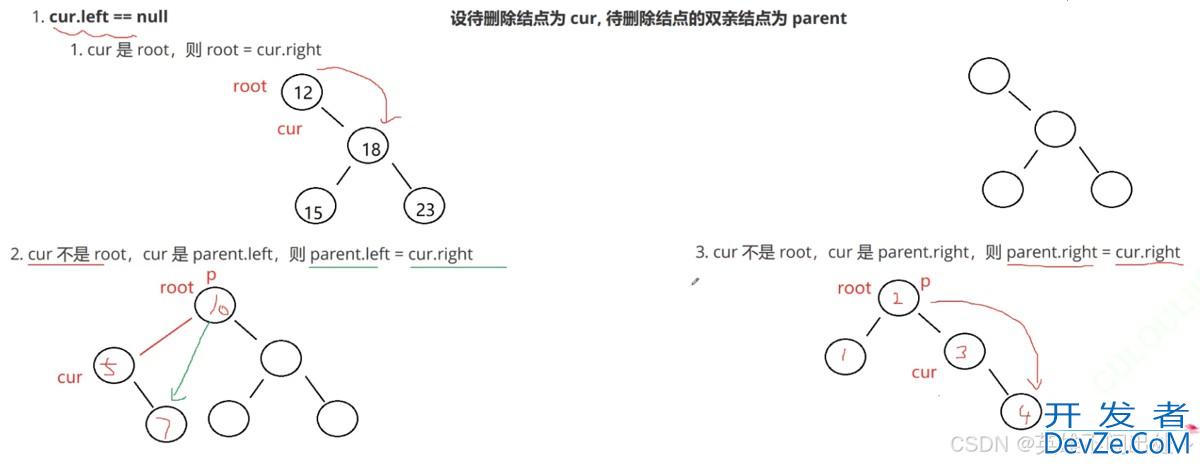
2. 第二种情况:cur.right == null
要删除的节点是curcur是根节点cur是某个节点的左边cur是某个节点的右边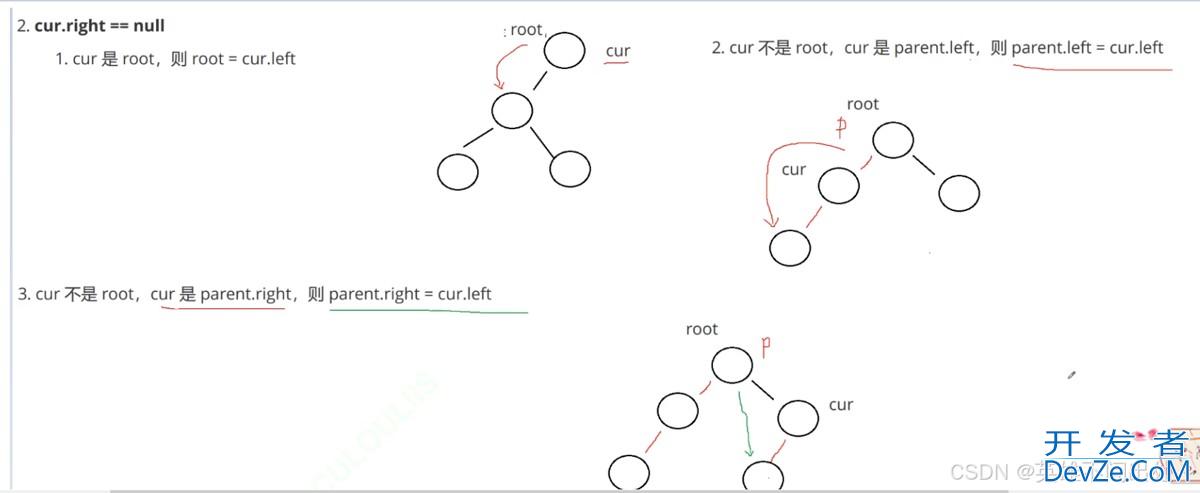
3. 第三种情况:cur.left != null && cur.right != null
使用替换法进行删除替换为左树中最大的值或者是右树中最小的值替换完之后删除这个去替换的值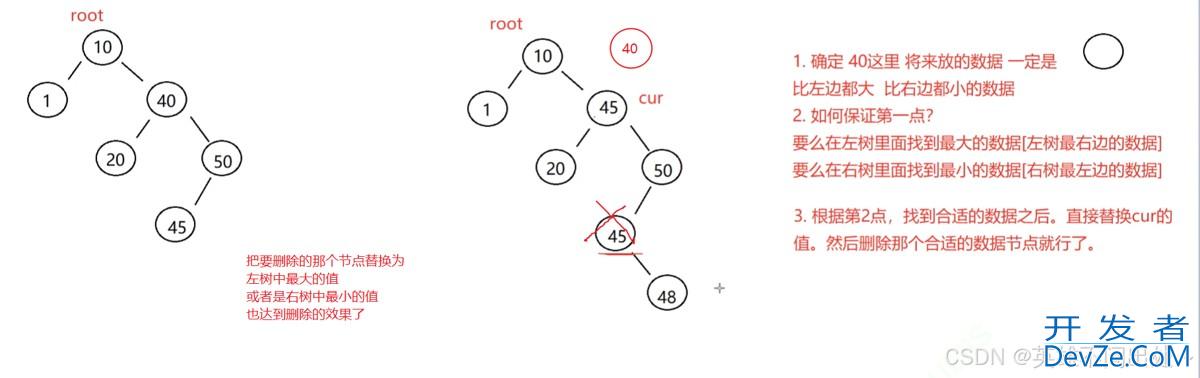

// 删除
private void removeNode(TreeNode cur, TreeNode parent) {
if(cur.left == null){
// 要删除的是根节点
if(cur == root){
root = cur.right;
}else if(cur == parent.left){
parent.left = cur.right;
}else{
parent.right = cur.right;
}
}else if(cur.right == null){
if(cur == root){
root = cur.left;
}else if(cur == parent.left){
parent.left = cur.left;
}else{
parent.right = cur.left;
}
}else{
// cur.left != null && cur.right != null
TreeNode parentTarget = cur;
TreeNode target = cur.right;
// 在右树中找最小值
while(target.left != null){
parentTarget = target;
target = target.left;
}
// 直到找到右树中的最左边的树
cur.val = target.val;
// 删除target
if(parentTarget.left == target) {
parentTarget.left = target.right;
}else{
// parentTarget.right == target
parentTarget.right = target.right;
}
}
}
Map
- map是一种(k,v)结构的数据结构
- map可以进行去重,TreeMap不可以插入null的key,HashMap可以插入null的key,因为红黑树是要进行比较的,哈希表是不进行比较的
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();// 底层是红黑树,查找的时间复杂度O(N*logN) Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();// 底层是哈希表,查找的时间复杂度O(1) // 哈希表 = 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
Map的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();// 底层是红黑树,查找的时间复杂度O(N*logN)
// 插入元素
map.put("push",3);// push出现了3次
// 获取元素,给定一个key值可以获取它的value值
Integer val = map.get("push");
Integer val1 = map.get("aaa");// null
// 获取val值,如果没有这个值,返回一个默认值
Integer val2 = map.getOrDefault("bbb",99999);
System.out.println(val);
// 删除key值
// map.remove("push");
// 把所有的key放入一个集合中
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
System.out.println(set);
// 获取values中的所有值
ArrayList<Integer> value = new ArrayList(map.values());
System.out.println(value);
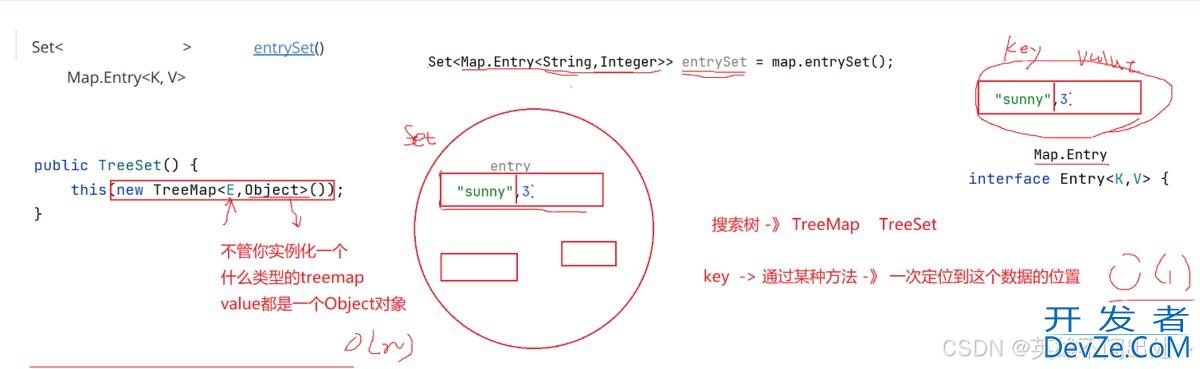
// 把Map.Entry<String,Integer>当做Set中的一个节点
// map.entrySet()用于获取这种节点
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entrySet){
System.out.println("key: " + entry.getKey() + " value: " + entry.getValue());
}
// boolean map.containsKey("push"); 判断是否含有key
// boolean map.containsValue(3); 判断是否含有value
Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();// 底层是哈希表,查找的时间复杂度O(1)
// 哈希表 = 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
}
Set
- set是一种只有key的模型
Set的使用
- Set是要进行去重的
- TreeSet不可以插入null的key,HashSet可以插入null的key,因为红黑树是要进行比较的,哈希表是不进行比较的
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("push");
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
// set是无序的
System.out.println(set);
Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
哈希表
- 查找可以一次定位到该元素,时间复杂度为O(1)
哈希冲突(碰撞):不同的key通过相同的哈希函数得到相同的值
哈希冲突是必然产生的,我们要做的是降低冲突的概率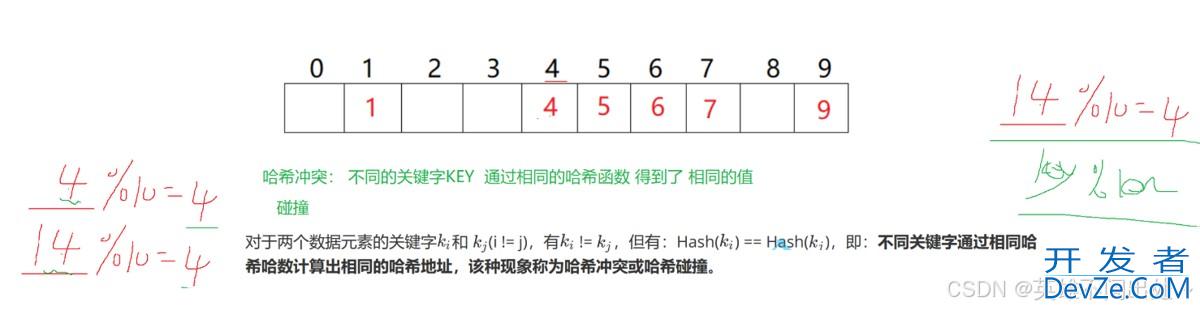
解决哈希冲突:哈希函数的设计要合理
哈希函数要简单哈希表中要均匀分到数组中去哈希表的范围要合理,比如有m个地址,存储位置就是[0,m-1]
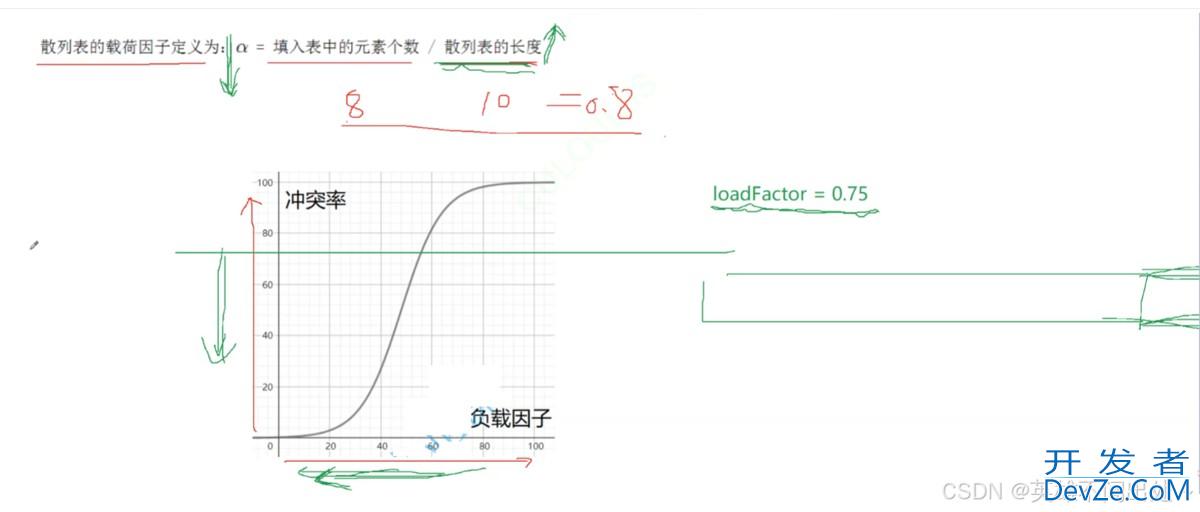
负载因子的调节(重点)
- 负载因子影响了哈希冲突,负载因子越大冲突率越高
- 哈希表中的负载因子定义为:a = 填入表中的元素个数 / 哈希表的长度比如:a = 8 / 10 = 0.8
如果降低冲突率就要降低负载因子,因此要扩容哈希表的大小,不增加插入的元素是不现实的,给定一个阈值,如果超过了就扩大哈希表的容量
闭散列
- 开放定址法,如果没有达到js阈值,但是冲突了,就放到冲突的下一个空的位置上,这个也叫线性探测
- 线性探测的缺点:把冲突的元素都集中放到了一起
- 二次探测:为了解决线性探测的缺点,通过公式进行处理,H0是当前冲突的位置,i是出现冲突的次数,m是哈希表的大小,Hi表示冲突后,下一次要放的位置

4. 线性探测对于空间的利用率不高
开散列
- 开散列:又叫链地址法,为了解决空间利用率不高的问题,开散列是数组 + 链表 + 红黑树的模式
- 把冲突的元素挂到同一个空间下的链表上
- Java是采用开散列的方式实现的

4. 扩容之后需要重新哈希,因为数组长度变了,要重新计算节点存放的位置
5. 遍历哈希数组中每个数组元素,都要重新计算节点位置
package Demo1;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HashBuck {
// 链表数组,数组中的每一个元素都时链表的头结点
public class Node{
public int key;
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize;
public static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
public HashBuck(){
array = new Node[10];
}www.devze.com
public void put(int key,int value){
int index = key % array.length;
// 遍历index下标的链表 是否存在key 存在就更新value 不存在就头插这个节点
Node node = new Node(key,value);
// 该链表的头结点
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur != null){
if(cur.key == key){
// 如果插入的这个key相同就替换这个key
cur.val = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 没有找到这个节点就头插
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
// 负载因子大于阈值
if(doLoadFactor() > DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR){
// 扩容
// array = Arrays.copyOf(array,2*array.length);
resize();
}
}
private void resize(){
// 建一个新的数组
Node[] newArray = new Node[2*array.length];
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
Node cur = array[i];
while(cur != null){
Node tmp = cur.next;
// 每次都要算新数组的下标因为是一个链表有很多个节点
int newIndex = cur.key % newArray.length;
// 头插法
cur.next = newArray[newIndex];
newArray[newIndex] = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
// 计算负载因子
private float doLoadFactor(){
return usedSize * 1.0f / array.length;
}
// 获取对应key的value值
public int get(int key){
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur != null){
if(cur.key == key){
// 如果插入的这个key相同就替换这个key
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
}
HashMap是线程不安全的,因为采用了头插法,后面采用了尾插法变得安全了,ConcurrentHashMap是线程安全的,之后学到了线程就可以理解了
如果key是String,Person类型就不能除以数组的长度了,该怎么找到对应的下标呢?
可以用hashcode来将自定义类型转化为整形类型
hashCode和equals

HashMap和HashSet
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("hello",2);
hashMap.put("abcde",10);
hashMap.put("abc",11);
Integer val = hashMap.get("hello");
System.out.println(val);
// 遍历map
System.out.println(hashMap);
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : hashMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println("key:" + entry.getKey() + " value:" + entry.getValue());
}
// Map不支持迭代器遍历,Set支持迭代器遍历
// 可以将Map转化为Set进行迭代器遍历
HashMap<Student,Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<>();
hashMap1.put(new Student(),2);
hashMap1.put(new Student(),2);
hashMap1.put(null,2);
// TreeMap<Student,Integer> hashMap2 = new TreeMap<>();
// hashMap2.put(new Student(),3);
// hashMap2.put(new Student(),3);
// Sutdent不能进行比较
// set可以去重,Set的底层是HashMap
// 每次存储元素的时候,默认的value都是一个Object对象
HashjavascriptSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("hello");
System.out.println(set);
}
面试题
只出现一次的数字
宝石与石头旧键盘随机链表的复制
统计6个数中数字出现的次数
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1,1,2,2,3,3};
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
if(!map.containsKey(array[i])){
map.put(array[i],1);
}else{
int k = map.get(array[i]);
k++;
map.put(array[i],k);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
前k个高频单词

如果频率相同放入堆中要使用大根堆,要让love排在i的前面
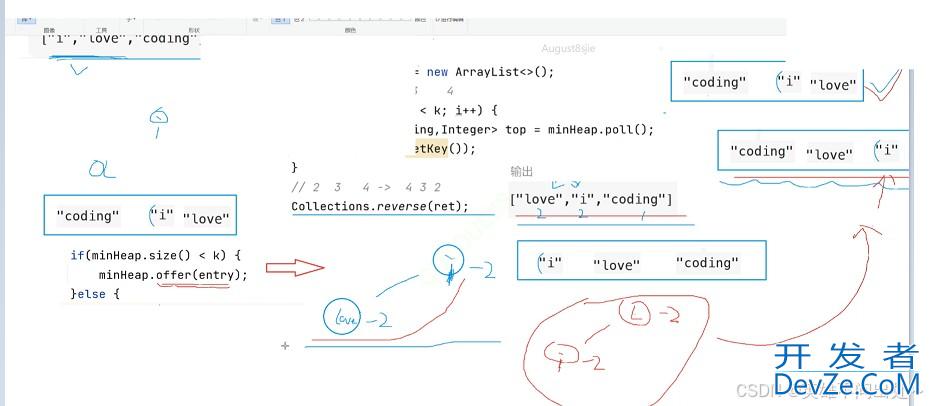
class Solution {
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
// 1. 统计单词出现的次数
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(String s : words){
if(!map.containsKey(s)){
map.put(s,1);
}else{
int val = map.get(s);
map.put(s,val+1);
}
}
// 2. 把单词和出现的次数当做一个整体放入小根堆中
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(
new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>>(){
public int compare(Map.Entry<String,Integer> o1,Map.Entry<String,Integer> o2){
// 放元素的时候,如果频率相同,我们转变为大根堆 -> 按照单词的字典序进行排序
if(o1.cuoWlgetValue().compareTo(o2.getValue()) == 0){
return o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey());
}
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){
if(minHeap.size() < k){
// 没有放满小根堆
minHeap.add(entry);
}else{
// 放满了和堆顶元素比较大小
// 如果比堆顶元素还大,就入堆
int v = minHeap.peek().getValue();
if(v < entry.getValue()){
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(entry);
}else{
// 出现频率相同,比较字典序大小
if(v == entry.getValue()){
if(minHeap.peek().getKey().compareTo(entry.getKey()) > 0){
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(entry);
}
}
}
}
}
// 2 3 4 -> 4 3 2
List<String> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0;i < k;i++){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> top = minHeap.poll();
arr.add(top.getKey());
}
// 逆置
Collections.reverse(arr);
return arr;
}
}
HashMap的源码
如果达到一定条件会把哈希表编程红黑树:如果链表的长度大于8并且数组的长度大于64就会进行树化


到此这篇关于Java Map和Set的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java Map和Set内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论