从基础到高级详解Python文本过滤与清理完全指南
目录
- 引言:数据质量的关键防线
- 一、基础过滤技术:字符串操作
- 1.1 核心字符串方法
- 1.2 高效批量替换
- 二、高级过滤:正则表达式应用
- 2.1 模式匹配过滤
- 2.2 敏感信息过滤
- 三、Unicode与特殊字符处理
- 3.1 Unicode规范化
- 3.2 表情符号处理
- 四、高级过滤框架:管道模式
- 4.1 可扩展过滤管道
- 4.2 上下文感知过滤
- 五、实战:社交媒体数据清洗
- 5.1 社交媒体文本净化
- 5.2 多语言社交媒体处理
- 六、日志数据过滤系统
- 6.1 日志敏感信息脱敏
- 6.2 大日志文件流式处理
- 七、最佳实践与性能优化
- 7.1 过滤方法性能对比
- 7.2 文本过滤决策树
- 7.3 黄金实践原则
- 总结:文本过滤技术全景
- 8.1 技术选型矩阵
- 8.2 核心原则总结
引言:数据质量的关键防线
在数据驱动的时代,文本过滤与清理是确保数据质量的基石。根据2023年数据工程报告,高达75%的数据质量问题源于未处理的脏数据,导致:
- 机器学习模型准确率下降30%
- 数据分析结论偏差增加45%
- 系统集成故障率上升28%
python作为数据处理的首选语言,提供了全面的文本过滤工具链。本文将系统解析Python文本过滤技术体系,结合Python Cookbook精髓,并拓展社交媒体清洗、日志处理、多语言文本等高级场景,为您提供专业的文本清理解决方案。
一、基础过滤技术:字符串操作
1.1 核心字符串方法
# 空白字符处理
text = " Hello\tWorld\n "
clean_text = text.strip() # "Hello\tWorld" - 仅移除首尾空白
full_clean = " ".join(text.split()) # "Hello World" - 移除所有空白
# 大小写转换
text = "Python is Awesome"
lower_text = text.lower() # "python is awesome"
title_text = text.title() # "Python Is Awesome"
# 字符替换
text = "data$science&analysis"
clean_text = text.replace('$', ' ').replace('&', ' ') # "data science analysis"
1.2 高效批量替换
def bulk_replace(text, replace_map):
"""批量字符替换"""
for old, new in replace_map.items():
text = text.replace(old, new)
return text
# 特殊符号清理
symbol_map = {
'$': 'USD',
'€': 'EUR',
'': 'JPY',
'&': 'and',
'@': 'at'
}
text = "Price: $100 & €85 @store"
clean_text = bulk_replace(text, symbol_map) # "Price: USD100 and EUR85 atstore"
二、高级过滤:正则表达式应用
2.1 模式匹配过滤
import re
# 移除html标签
html = "<div>Hello World</div>"
clean_text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', html) # "Hello World"
# 提取纯文本内容
def extract_text_content(html):
"""从HTML提取纯文本"""
# 移除脚本和样式
html = re.sub(r'<script.*?</script>', '', ht编程ml, flags=re.DOTALL)
html = re.sub(r'<style.*?</style>', '', html, flags=re.DOTALL)
# 移除HTML标签
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', ' ', html)
# 合并空白
return re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text).strip()
# 测试
html_content = """
<html>
<head><title>Test</title></head>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
print(extract_text_content(html_content)) # "Test Hello World!"
2.2 敏感信息过滤
def filter_sensitive_info(text):
"""过滤敏感信息"""
# 邮箱地址
text = re.sub(r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b', '[EMAIL]', text)
# 手机号码
text = re.sub(r'\b1[3-9]\d{9}\b', '[PHONE]', text)
# 身份证号
text = re.sub(r'\b\d{17}[\dXx]\b', '[ID_CARD]', text)
# 银行卡号
text = re.sub(r'\b\d{16,19}\b', '[BANK_CARD]', text)
return text
# 测试
user_input = "联系我: john@example.com, 电话13800138000, 卡号6225888888888888"
safe_text = filter_sensitive_info(user_input)
# "联系我: [EMAIL], 电话[PHONE], 卡号[BANK_CARD]"
三、Unicode与特殊字符处理
3.1 Unicode规范化
import unicodedata
def normalize_text(text):
"""Unicode规范化处理"""
# 兼容性规范化
text = unicodedata.normalize('NFKC', text)
# 移除控制字符
text = ''.join(c for c in text if unicodedata.category(c)[0] != 'C')
# 替换特殊空白
whitespace_map = {
'\u00A0': ' ', # 不换行空格
'\u200B': '', # 零宽空格
'\u2028': '\n', # 行分隔符
'\u2029': '\n' # 段落分隔符
}
return ''.join(whitespace_map.get(c, c) for c in text)
# 测试
mixed_text = "Hello\u00A0World\u200B!\u2028New\u2029Line"
clean_text = normalize_text(mixed_text) # "Hello World!\nNew\nLine"
3.2 表情符号处理
def handle_emojis(text, mode='remove'):
"""表情符号处理策略"""
# Unicode表情符号范围
emoji_pattern = re.compile(
r'[\U0001F600-\U0001F64F' # 表情符号
r'\U0001F300-\U0001F5FF' # 其他符号
r'\U0001F680-\U0001F6FF' # 交通符号
r'\U0001F700-\U0001F77F' # 炼金术符号
r']',
flags=re.UNICODE
)
if mode == 'remove':
return emoji_pattern.sub('', text)
elif mode == 'tag':
return emoji_pattern.sub('[EMOJI]', text)
elif mode == 'extract':
return emoji_pattern.findall(text)
else:
return text
# 示例
text = "Python is awesome! "
print(handle_emojis(text, 'remove')) # "Python is awesome! "
print(handle_emojis(text, 'tag')) # "Python is awesome! [EMOJI][EMOJI]"
四、高级过滤框架:管道模式
4.1 可扩展过滤管道
class TextFilterPipeline:
"""可扩展的文本过滤管道"""
def __init__(self):
self.filters = []
def add_filter(self, filter_func):
"""添加过滤函数"""
self.filters.append(filter_func)
return self
def process(self, text):
"""执行过滤"""
for filter_func in self.filters:
text = filter_func(text)
return text
# 构建过滤管道
pipeline = TextFilterPipeline()
pipeline.add_filter(str.strip) \
.add_filter(lambda s: s.lower()) \
.add_filter(lambda s: re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', s)) \
.add_filter(lambda s: re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', s))
# 使用
dirty_text = " Hello, World! \nHow are you? "
clean_text = pipeline.process(dirty_text) # "hello world how are you"
4.2 上下文感知过滤
def context_aware_filter(text, context):
"""根据上下文选择过滤策略"""
if context == 'social_media':
# 社交媒体过滤
text = remove_emojis(text)
text = expand_abbreviations(text)
return text
elif context == 'financial':
# 金融数据过滤
text = normalize_currencies(text)
text = remove_non_numeric(text)
return text
elif context == 'log_analysis':
# 日志分析过滤
text = remove_timestamps(text)
text = anonymize_ips(text)
return text
else:
return basic_clean(text)
# 社交媒体缩写扩展
abbr_map = {
'u': 'you',
'r': 'are',
'btw': 'by the way',
'lol': 'laughing out loud'
}
def expand_abbreviations(text):
words = text.split()
return ' '.join(abbr_map.get(word.lower(), word) for word in words)
五、实战:社交媒体数据清洗
5.1 社交媒体文本净化
def clean_social_media_text(text):
"""社交媒体文本综合清洗"""
# 步骤1: 基础清理
text = text.lower().strip()
# 步骤2: 处理用户提及和话题标签
text = re.sub(r'@\w+', '[USER]', text) # 用户提及
text = re.sub(r'#\w+', '[TOPIC]', text) # 话题标签
# 步骤3: 清理URL
text = re.sub(r'https?://\S+', '[URL]', text)
# 步骤4: 处理表情符号
text = handle_emojis(text, 'tag')
# 步骤5: 规范化重复字符
text = re.sub(r'(.)\1{2,}', r'\1', text) # 减少重复字符
return text
# 测试
tweet = "OMG!!! Check this out: https://example.com @john #Python is AWESOME! "
clean_tweet = clean_social_media_text(tweet)
# "omg check this out: [URL] [USER] [TOPIC] is awesome! [EMOJI]"
5.2 多语言社交媒体处理
def clean_multilingual_social_text(text):
"""多语言社交媒体清洗"""
# 语言检测 (简化版)
def detect_language(text):
if re.search(r'[\u4e00-\u9fff]', text): # 中文字符
return 'zh'
elif re.search(r'[\u3040-\u309F]', text): # 平假名
return 'ja'
elif re.search(r'[\uAC00-\uD7A3]', text): # 韩文
return 'ko'
else:
return 'en'
lang = detect_language(text)
# 语言特定处理
if lang == 'zh':
# 中文特殊处理
text = re.sub(r'【.*?】', '', text) # 移除方括号内容
text = re.sub(r'[﹒•]', '。', text) # 统一标点UdrYC
elif lang == 'ja':
# 日文特殊处理
text = re.sub(r'[ア-ン]', lambda x: chr(ord(x.group(0)) + 0x60), text) # 半角转全角
elif lang == 'ko':
# 韩文特殊处理
text = re.sub(r'[ㅋㅎ]+', 'ㅋ', text) # 减少重复字符
# 通用处理
text = clean_social_media_text(text)
return text
# 测试
weibo_post = "【热门】Python太棒了! @张三 #编程学习"
clean_post = clean_multilingual_social_text(weibo_post)
# "python太棒了! [EMOJI] [USER] [TOPIC]"
六、日志数据过滤系统
6.1 日志敏感信息脱敏
class LogAnonymizer:
"""日志敏感信息脱敏系统"""
def __init__(self):
self.rules = [
(r'\b\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}\b', '[SSN]'), # 美国社保号
(r'\b\d{17}[\dXx]\b', '[ID]'), # 身份证号
(r'\b1[3-9]\d{9}\b', '[PHONE]'), # 手机号
(r'\b\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\b', '[IP]'), # IP地址
(r'[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b', '[EMAIL]')
]
def anonymize(self, text):
"""应用所有脱敏规则"""
for pattern, replacement in self.rules:
text = re.sub(pattern, replacement, text)
return text
def add_custom_rule(self, pattern, replacement):
"""添加自定义脱敏规则"""
self.rules.append((pattern, replacement))
return self
# 使用示例
anonymizer = LogAnonymizer()
log_line = "User: john@example.com from 192.168.1.100 Accessed SSN: 123-45-6789"
safe_log = anonymizer.anonymize(log_line)
# "User: [EMAIL] from [IP] accessed SSN: [SSN]"
6.2 大日志文件流式处理
def stream_log_processing(input_file, output_file, process_func, chunk_size=65536):
"""大日志文件流式处理"""
with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fin:
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fout:
buffer = ""
while True:
编程客栈 chunk = fin.read(chunk_size)
if not chunk and not buffer:
break
buffer += chunk
lines = buffer.split('\n')
# 保留最后一行(可能不完整)
buffer = lines.pop() if lines else ""
for line in lines:
cleaned = process_func(line)
fout.write(cleaned + '\n')
# 处理剩余内容
if buffer:
cleaned = process_func(buffer)
fout.write(cleaned)
# 使用示例
def log_clUdrYCeaner(line):
"""单行日志清理函数"""
anonymizer = LogAnonymizer()
line = anonymizer.anonymize(line)
line = re.sub(r'\[DEBUG\].*', '', line) # 移除调试信息
return line.strip()
# 处理GB级日志文件
stream_log_processing('app.log', 'clean_app.log', log_cleaner)
七、最佳实践与性能优化
7.1 过滤方法性能对比
import timeit
# 测试数据
text = "a" * 10000 + "!@#$%" + "b" * 10000
# 测试函数
def test_replace():
return text.replace('!', '').replace('@', '').replace('#', '').replace('$', '').replace('%', '')
def test_re_sub():
return re.sub(r'[!@#$%]', '', text)
def test_translate():
trans = str.maketrans('', '', '!@#$%')
return text.translate(trans)
# 性能测试
methods = {
"replace": test_replace,
"re_sub": test_re_sub,
"translate": test_translate
}
results = {}
for name, func in methods.items():
time = timeit.timeit(func, number=1000)
results[name] = time
# 打印结果
print("1000次操作耗时:")
for name, time in sorted(results.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]):
print(f"{name}: {time:.4f}秒")
7.2 文本过滤决策树
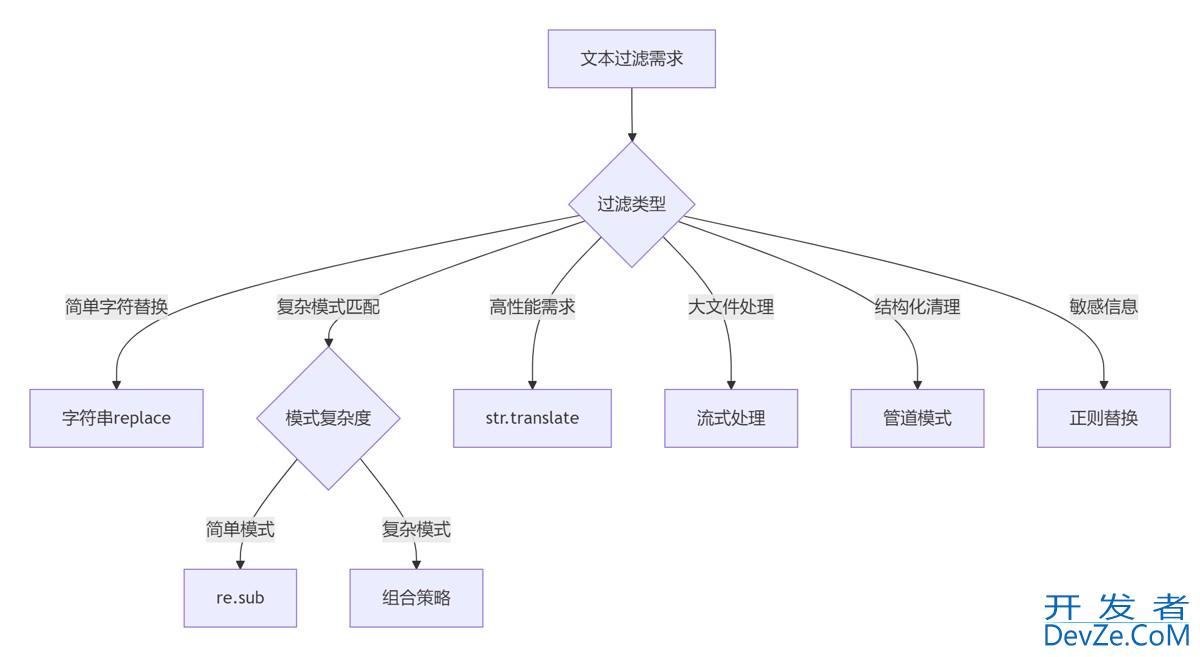
7.3 黄金实践原则
选择合适工具:
- 简单任务:字符串方法
- 复杂模式:正则表达式
- 高性能需求:str.translate
预处理规范化:
def preprocess(text):
text = unicodedata.normalize('NFKC', text)
text = text.strip()
return text
正则优化技巧:
# 预编译正则对象
EMAIL_PATTERN = re.compile(r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b')
流式处理大文件:
with open('huge.log') as f:
for line in f:
process(line)
上下文感知过滤:
def clean_text(text, contehttp://www.devze.comxt='default'):
if context == 'social':
return clean_social_media_text(text)
elif context == 'financial':
return clean_financial_text(text)
else:
return basic_clean(text)
单元测试覆盖:
import unittest
class TestTextCleaning(unittest.TestCase):
def test_email_anonymization(self):
self.assertEqual(
filter_sensitive_info("Contact: john@example.com"),
"Contact: [EMAIL]"
)
def test_html_cleaning(self):
self.assertEqual(
extract_text_content("<p>Hello</p>"),
"Hello"
)
总结:文本过滤技术全景
8.1 技术选型矩阵
| 场景 | 推荐方案 | 性能 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 简单字符替换 | str.replace() | ★★★★☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
| 复杂模式过滤 | re.sub() | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| 高性能字符移除 | str.translate() | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| 大文件处理 | 流式处理 | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| 结构化清理 | 管道模式 | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| 敏感信息过滤 | 正则替换 | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
8.2 核心原则总结
理解数据特性:分析数据特征和污染模式
分层处理策略:
- 预处理:规范化、空白处理
- 主处理:模式匹配、替换
- 后处理:格式化、验证
性能优化:
- 预编译正则表达式
- 批量化处理操作
- 避免不必要的中间结果
内存管理:
- 大文件采用流式处理
- 分块处理降低内存峰值
- 使用生成器避免内存累积
多语言支持:
- Unicode规范化
- 语言特定规则
- 字符编码处理
安全防护:
- 敏感信息脱敏
- 输入验证
- 防御性编码
文本过滤与清理是数据工程的基石。通过掌握从基础字符串操作到高级正则表达式的技术体系,结合管道模式、流式处理等工程实践,您将能够构建高效、健壮的数据清洗系统。遵循本文的最佳实践,将使您的数据处理管道更加可靠和高效,为后续的数据分析和应用奠定坚实基础。
以上就是从基础到高级详解Python文本过滤与清理完全指南的详细内容,更多关于Python文本过滤与清理的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论