SpringBoot main方法结束程序不停止的原因分析及解决方法
目录
- 前言
- 原因
- debug源码
- 技巧
- 流程
- await方法
- 非daemon线程的意义
- setDaemon介绍
- 例子
- -1的原因
- 调用链
- 技巧
- 具体内容
前言
对于Java开发来说,天天都在用SpringBoot,每次启动都执行了main方法,该方法应该是最容易让人忽视的地方之一,不过几行代码,为什么执行完后JVM不结束呢?
本文以内嵌tomcat为例进行说明,并分享一些debug和画图的技巧。
原因
先说结论,是因为main方法启动了一个线程,这个线程是非daemon的,并且run方法执行的任务是TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();(死循环),即非daemon线程+任务不停止=程序不退出。
debug源码
技巧
在debug时,有的源码是抽象方法,我们可以用快捷键F7跳转到具体正在执行的实现类方法,另外Alt+F9可以强制到达光标的位置。
流程
下面将debug对应的源码,有兴趣的朋友可以跟着动手试试。
SpringBoot启动入口,调用静态run方法。
/** 一般demo
* @date 2021/9/12 9:09
* @author www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class CommonDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CommonDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
调用重载的run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
创建SpringApplication对象调用run方法
public static ConfigurableApplijscationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
由于该run方法很长,这里只贴到与本文main方法结束为何程序不退出的代码,对整个启动流程有兴趣的可以去看这篇:Springboot启动原理和自动配置原理解析 这里我们注意refreshContext。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArgumAsQNMyYLJFents = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
……
refreshContext调用了一个抽象方法,我们在debug模式使用F7进入具体的实现类。
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
这里就初始化一些资源(placeholder,beanFactory,BeanPostProcessor,MessageSource,ApplicationEventMulticaster),注意onRefresh方法。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
……
进入onRefresh,这里会创建WebServer:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
这里是具体创建webServer的步骤,注意getTomcatWebServer。
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
创建TomcatWebServer对象。
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0, getShutdown());
}
设置一些属性,并执行initialize方法。
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null;
initialize();
}
初始化并启动tomcat容器,然后就开起非daemon await线程。
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unablhttp://www.devze.come to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
创建非daemon线程设置线程名等参数并启动。
private void startDaemonAwaitThread() {
Thread awaitThread = new Thread("container-" + (containerCounter.get())) {
@Override
public void run() {
TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();
}
};
awaitThread.setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader());
awaitThread.setDaemon(false);
awaitThread.start();
}
至此由于awaitThread.setDaemon(false);和TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();,启动该线程awaitThread后,main方法后续虽然执行完毕,但是程序不会退出。
await方法
这里单独看一下TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();。
该方法的Java doc:
/** * Wait until a proper shutdown command is received, then return. * This keeps the main thread alive - the thread pool listening for http * connections is daemon threads. */
指的是通过等候关闭命令这个动作来保持main线程存活,而HTTP线程作为daemon线程会在main线程结束时终止。
任务一直运行的原因:源码如下,debug会进入getPortWithOffset()的值是-1的分支(注意这里不是server.port端口号),然后会不断循环Thread.sleep( 10000 )直到发出关机指令修改stopAwait的值为true。
@Override
public void await() {
// Negative values - don't wait on port - tomcat is embedded or we just don't like ports
if (getPortWithOffset() == -2) {
// undocumented yet - for embedding apps that are around, alive.
return;
}
if (getPortWithOffset() == -1) {
try {
awaitThread = Thread.currentThread();
while(!stopAwait) {
try {
Thread.sleep( 10000 );
} catch( InterruptedException ex ) {
// continue and check the flag
}
}
} finally {
awaitThread = null;
}
return;
}
……
stopAwait的值只会在org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#stopAwait中被修改,源码如下:
public void stopAwait() {
stopAwait=true;
Thread t = awaitThread;
if (t != null) {
ServerSocket s = awaitSocket;
if (s != null) {
awaitSocket = null;
try {
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignored
}
}
t.interrupt();
try {
t.join(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignored
}
}
}
而该方法会在容器生命周期结束方法org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#stopInternal中被调用。
非daemon线程的意义
setDaemon介绍
上面将线程设置为非daemon线程:awaitThread.setDaemon(false)。
java.lang.Thread#setDaemon源码如下:
/**
* Marks this thread as either a {@linkplain #isDaemon daemon} thread
* or a user thread. The Java Virtual MAChine exits when the only
* threads running are all daemon threads.
*
* <p> This method must be invoked before the thread is started.
*
* @param on
* if {@code true}, marks this thread as a daemon thread
*
* @throws IllegalThreadStateException
* if this thread is {@linkplain #isAlive alive}
*
* @throws SecurityException
* if {@link #checkAccess} determines that the current
* thread cannot modify this thread
*/
public final void setDaemon(boolean on) {
checkAccess();
if (isAlive()) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
}
daemon = on;
}
根据上面的Java doc注释可知:标记该线程是否是daemon线程,而JVM退出仅当只剩下daemon线程。
所以非daemon线程存活,JVM是不会退出的。
例子
如下代码,我们在main方法中启动了一个非daemon线程,并且调用了阻塞方法java.io.InputStream#read()。
// https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": start");
Thread awaitThread =
new Thread("non-daemon") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": start");
System.in.read();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": end");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
awaitThread.setDaemon(false);
awaitThread.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": end");
}
启动程序后,再不进行键盘输入的情况下,程序不会停止,运行结果如下:
main: start
main: endnon-daemon: start
main线程结束,但是程序不退出。
-1的原因
上面留了个问题,为什么getPortWithOffset()的返回值是-1。
如下getPort()的值为-1,此时相当于直接调用了getPort()方法。
https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
@Override
public int getPortWithOffset() {
// Non-positive port values have special meanings and the offset should
// not apply.
int port = getPort();
if (port > 0) {
return port + getPortOffset();
} else {
return port;
}
}
而getPort直接取的是port属性。
@Override
public int getPort() {
return this.port;
}
注意这里的port不是我们指定的server.port这个属性,而是关闭命令监听的端口。
/**
* The port number on which we wait for shutdown commands.
*/
private int port = 8005;
为什么是8005而不是-1呢?那是在哪被修改了呢?
port属性提供的修改方式是setPort(),而使用Alt+F7找到在getServer中被修改为-1。
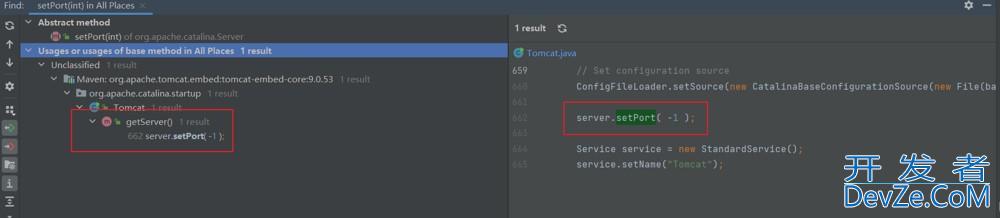
在server.setPort( -1 );打一个断点,重新debug,可以知道具体修改的时机。
之前我们debug过方法createWebServer,是具体创建webServer的步骤,但是我们这里要进入getWebServer。
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
……
配置tomca实例参数,但是要注意这里的tomcat.getService()方法。
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
内部调用getServer()。
public Service getService() {
return getServer().findServices()[0];
}
至此,就是这里就将server.setPort( -1 );。
public Server getServer() {
if (server != null) {
return server;
}
System.setProperty("catalina.useNaming", "false");
server = new StandardServer();
initBaseDir();
// Set configuration source
ConfigFileLoader.setSource(new CatalinaBaseConfigurationSource(new File(basedir), null));
// https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
server.setPort( -1 );
Service service = new StandardService();
service.setName("Tomcat");
server.addService(service);
rjavascripteturn server;
}
调用链
技巧
如果我们想画一个方法本次被调用(线程内部)的流程图,那么我们可以debug进入该方法,Alt+F8执行如下代码,打印出方法调用栈对应的mermaid js 内容,然后使用文本绘图工具进行渲染。
// https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
List<String> methodChain = Arrays.stream(stackTrace)
.filter(e -> !e.getClassName().startsWith("java.") && !e.getClassName().startsWith("jdk.") && !e.getMethodName().contains("<"))
.map(e -> e.getClassName() + "." + e.getMethodName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
StringBuilder mermaidCode = new StringBuilder("graph TD\n");
for (int i = methodChain.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
mermaidCode.append(String.format(" %s --> %s\n",
methodChain.get(i),
methodChain.get(i-1)));
}
System.out.println(mermaidCode);
这种方式比较适合线程内部展示具体方法的被调用关系,可以自定义根据包名等条件过滤掉不想要展示的类,但是对于跨线程的调用却不起作用,因为原理是线程自身的调用栈。
具体内容
如图,debug到org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer#startDaemonAwaitThread内部,执行上面的代码。
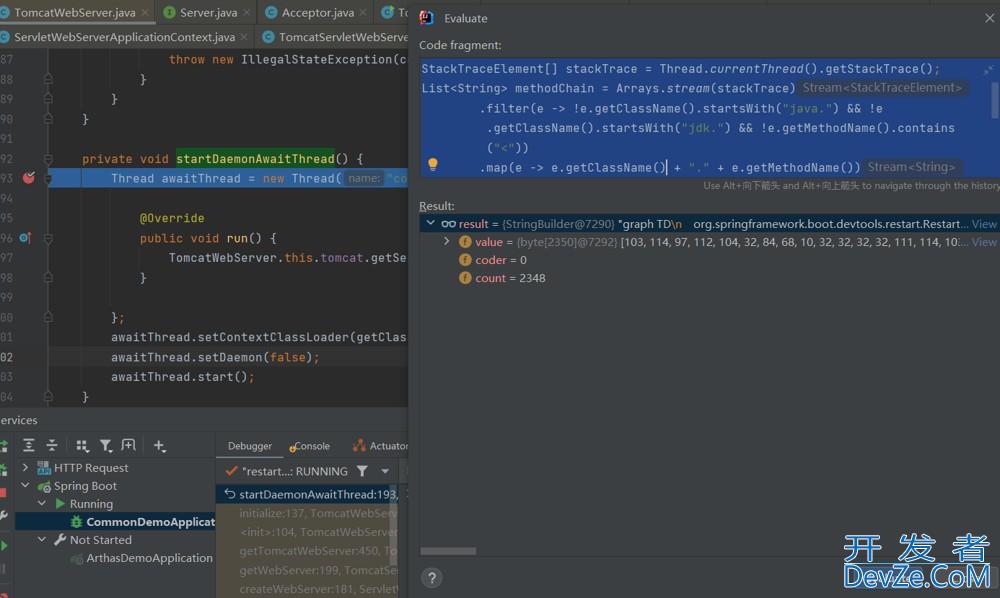
输出内容:
graph TD
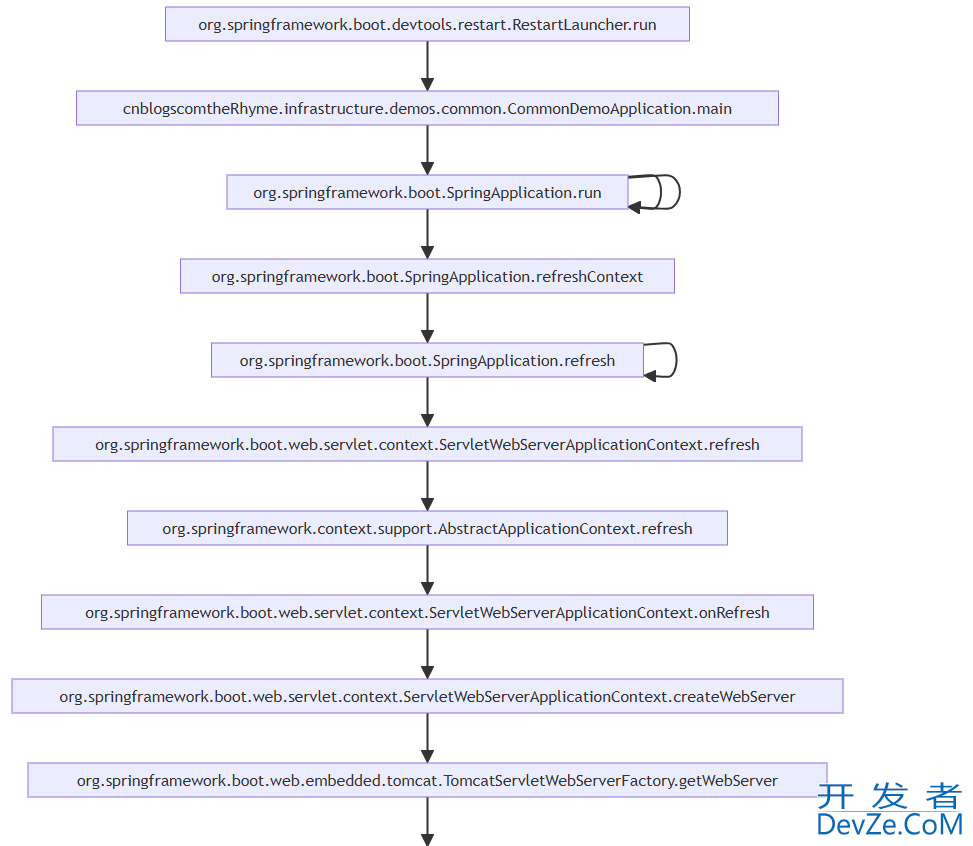
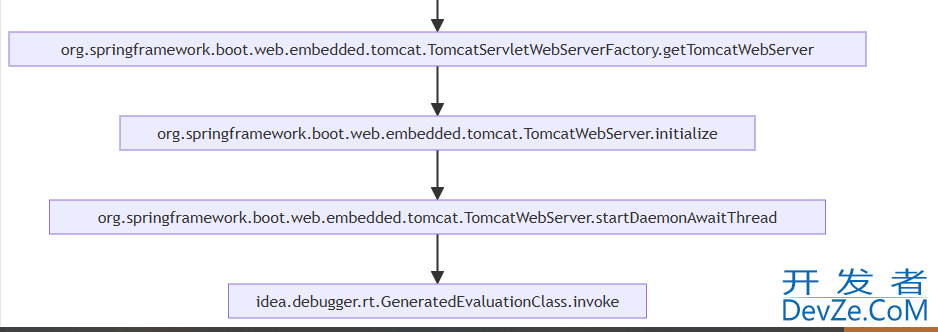
org.springframework.boot.devtools.restart.RestartLauncher.run --> cnblogscomtheRhyme.infrastructure.demos.common.CommonDemoApplication.main cnblogscomtheRhyme.infrastructure.demos.common.CommonDemoApplication.main --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh --> org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh orAsQNMyYLJFg.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh --> org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh --> org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh --> org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.createWebServer org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.createWebServer --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getTomcatWebServer org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getTomcatWebServer --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.initialize org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.initialize --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.startDaemonAwaitThread org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.startDaemonAwaitThread --> idea.debugger.rt.GeneratedEvaLuationClass.invoke
把内容放入文本绘图中,即可得到如下流程图:
到此这篇关于SpringBoot main方法结束程序不停止的原因分析及解决方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot main方法结束程序不停止内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论