Python INI文件读写的详细指南
目录
- 一、INI文件基础与python环境
- 1. INI文件简介
- 2. 典型INI文件结构
- 3. Python标准库支持
- 二、核心功能函数详解
- 1. 文件读取操作
- ConfigParser.read(filenames, encoding=None)
- ConfigParser.get(section, option, *, raw=False, vars=None, fallback)
- 2. 类型安全获取
- ConfigParser.getint(section, option, **kwargs)
- ConfigParser.getfloat(section, option, **kwargs)
- ConfigParserandroid.getboolean(section, option, **kwargs)
- 3. 文件写入操作
- ConfigParser.write(fileobject, space_around_delimiters=True)
- ConfigParser.add_section(section)
- 4. 实用工具函数
- ConfigParser.has_section(section)
- ConfigParser.has_option(section, option)
- ConfigParser.items(section, raw=False, vars=None)
- 三、高级特性与配置处理
- 1. 插值(值引用)处理
- ExtendedInterpolation()
- 2. DEFAULT 特殊节
- 全局默认值机制
- 3. 多级配置管理
- 分层配置处理
- 三、企业级最佳实践
- 1. 配置验证模式
- 2. 安全加密存储
- 3. 热重载配置
- 四、实用案例解析
- 1. 应用配置中心
- 2. 多语言国际支持
- 3. 跨平台路径处理
- 五、总结:核心方法速查表
- 1. 文件操作
- 2. 配置访问
- 3. 类型安全访问
- 4. 配置修改
一、INI文件基础与Python环境
1. INI文件简介
INI(Initialization)文件是一种经典的配置文件格式:
- 基础结构:节(Section)、键(Key)、值(Value)
- 主要特点:
- 人类可读的纯文本格式
- 简单直观的分层结构
- 广泛的应用支持(Windows系统、各类应用)
- 适用场景:
- 应用程序配置
- 系统参数设置
- 简单的数据持久化
2. 典型INI文件结构
; 这是注释行 [Database] ; 节(Section) host = localhost ; 键(Key) = 值(Value) port = 5432 user = admin password = secret123 ; 包含特殊字符的值 [Logging] level = DEBUG file = /var/log/app.log max_size = 10 ; 单位:MB [Features] enabled = true modules = core, auth, api
3. Python标准库支持
import configparser
configparser是Python标准库的一部分,无需额外编程客栈安装,支持:
- Python 2.x和3.x全版本兼容
- 丰富的类型转换
- 安全的插值(Interpolation)功能
- 灵活的读写选项
二、核心功能函数详解
1. 文件读取操作
ConfigParser.read(filenames, encoding=None)
功能:读取并解析 INI 文件
参数:
filenames:文件路径(字符串或列表)encoding:文件编码(默认为系统编码)返回:成功加载的文件列表特点:- 支持多个文件输入
- 自动跳过不存在文件
案例:
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
loaded_files = config.read(['app.ini', 'user.ini'], encoding='utf-8')
print(f"成功加载文件: {loaded_files}")
ConfigParser.get(section, option, *, raw=False, vars=None, fallback)
功能:获取配置项的值
参数:
section:配置节名称option:配置项名称fallback:未找到时的默认值raw:禁用插值处理vars:额外的变量字典返回:配置项的字符串值
案例:
# 获取数据库端口(带默认值)
db_port = config.get('Database', 'port', fallback='5432')
print(f"数据库端口: {db_port}")
# 禁用插值处理
log_file = config.get('Logging', 'file_path', raw=True)
2. 类型安全获取
ConfigParser.getint(section, option, **kwargs)
功能:获取整型配置值
参数:同 get()
返回:整数类型值
案例:
max_users = config.getint('System', 'max_users', fallback=100)
print(f"最大用户数: {max_users}")
ConfigParser.getfloat(section, option, **kwargs)
功能:获取浮点型配置值
参数:同 get()
返回:浮点数类型值
案例:
mem_limit = config.getfloat('Resources', 'memory_limit', fallback=0.75)
print(f"内存限制: {mem_limit}")
ConfigParser.getboolean(section, option, **kwargs)
功能:获取布尔型配置值
参数:同 get()
支持的值:
'1', 'yes', 'true', 'on'→True'0', 'no', 'false', 'off'→False
案例:
debug_mode = config.getboolean('Debug', 'enabled', fallback=False)
print(f"调试模式: {debug_mode}")
3. 文件写入操作
ConfigParser.write(fileobject, space_around_delimiters=True)
功能:将配置写入文件
参数:
fileobject:文件对象space_around_delimiters:是否在等号周围添加空格特点:保持原有顺序和注释(但注释会被丢弃)
案例:
# 更新配置并保存
config.set('Database', 'host', 'new.db.example.com')
with open('app.ini', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
config.write(f, space_around_delimiters=False) # 紧凑格式
ConfigParser.add_section(section)
功能:添加新的配置节
参数:section:节名称错误:如果节已存在则抛出DuplicateSectionError
案例:
编程客栈try:
config.add_section('Monitoring')
except configparser.DuplicateSectionError:
print("监控节已存在")
config.set('Monitoring', 'interval', '60')
4. 实用工具函数
ConfigParser.has_section(section)
功能:检查节是否存在
返回:布尔值案例:
if not config.has_section('Backup'):
config.add_section('Backup')
ConfigParser.has_option(section, option)
功能:检查选项是否存在
返回:布尔值
案例:
if config.has_option('Logging', 'verbosity'):
level = config.get('Logging', 'verbosity')
ConfigParser.items(section, raw=False, vars=None)
功能:获取节的所有键值对
返回:(name, value) 元组列表
案例:
print("数据库配置:")
for key, value in config.items('Database'):
print(f" {key} = {value}")
三、高级特性与配置处理
1. 插值(值引用)处理
ExtendedInterpolation()
功能:支持跨节的值引用
语法:${section:option} 或 $option(当前节)
案例:
config = configparser.ConfigParser(interpolation=configparser.ExtendedInterpolation())
config['DEFAULT'] = {'app_root': '/opt/myapp'}
config['Database'] = {
'data_dir': '/var/data',
'backup_dir': '${app_root}/backup' # 引用默认值
}
config['Logging'] = {
'log_dir': '${Database:data_dir}/logs', # 跨节引用
'file': '${log_dir}/app.log' # 当前节引用
}
# 验证引用
print(config['Logging']['file']) # 输出: /var/data/logs/app.log
2. DEFAULT 特殊节
全局默认值机制
功能:
- 所有节继承 DEFAULT 的键值
- 节内同名键值覆盖 DEFAULT
案例:
[DEFAULT] timeout = 30 retries = 3 [Database] host = localhost timeout = 60 # 覆盖默认值 [API] ; 继承默认超时30和重试3 endpoint = /api/v1
# 验证继承 print(config['API']['timeout']) # 输出: 30 print(config['Database']['retries']) # 输出: 3
3. 多级配置管理
分层配置处理
功能:实现基础配置 + 环境覆盖配置
方案:创建配置管理器类
class LayeredConfig:
def __init__(self):
self.base = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.override = configparser.ConfigParser()
def load(self, base_file, override_file=None):
self.base.read(base_file, encoding='utf-8')
if override_file:
self.override.read(override_file, encoding='utf-8')
def get(self, section, option, default=None):
# 1. 检查覆盖配置
if self.override.has_option(section, option):
return self.override.get(section, option)
# 2. 检查基础配置
if self.base.has_option(section, option):
return self.base.get(section, option)
# 3. 返回默认值
return default
# 使用示例
config = LayeredConfig()
config.load('base.ini', 'production.ini')
db_host = config.get('Database', 'host', 'localhost')
三、企业级最佳实践
1. 配置验证模式
from schema import Schema, And, Use
CONFIG_SCHEMA = Schema({
'Database': {
'host': And(str, len),
'port': And(Use(int), lambda p: 1024 < p < 65535),
'user': str,
'password': str
},
'Logging': {
'level': Or('DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARNING', 'ERROR'),
'file': str
}
})
def validate_config(config):
"""验证配置是否符合预期模式"""
# 转换为普通字典
config_dict = {}
for section in config.sections():
config_dict[section] = dict(config.items(section))
# 验证
return CONFIG_SCHEMA.validate(config_dict)
# 使用
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('app.ini')
try:
validate_config(config)
print("配置验证通过")
except Exception as e:
print(f"配置错误: {e}")
2. 安全加密存储
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
class SecureConfig:
def __init__(self, key_file='secret.key'):
self.key = self._load_key(key_file)
self.cipher_suite = Fernet(self.key)
def _load_key(self, path):
"""加载或生成密钥"""
if os.path.exists(path):
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
else:
key = Fernet.generate_key()
with open(path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(key)
return key
def save_encrypted(self, config, filepath):
"""加密保存配置"""
with StringIO() as buffer:
config.write(buffer)
encrypted = self.cipher_suite.encrypt(buffer.getvalue().encode())
with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
f.write(encrypted)
def load_encrypted(self, filepath):
"""加载并解密配置"""
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
encrypted = f.read()
decrypted = self.cipher_suite.decrypt(encrypted).decode()
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read_string(decrypted)
return config
# 使用示例
secure = SecureConfig()
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config['Database'] = {'password': 'super_secret'}
secure.save_encrypted(config, 'config.enc')
decrypted_config = secure.load_encrypted('config.enc')
3. 热重载配置
import os
import time
import threading
class HotReloadConfig:
def __init__(self, filepath):
self.filepath = filepath
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.last_mtime = 0
self._lock = threading.Lock()
self.load()
# 启动监控线程
self.watcher = threading.Thread(target=self._watch_changes, daemon=True)
self.watcher.start()
def load(self):
"""加载配置"""
with self._lock:
self.config.read(self.filepath)
self.last_mtime = os.path.getmtime(self.filepath)
def _watch_changes(self):
"""监控文件变化"""
while True:
current_mtime = os.path.getmtime(self.filepath)
if current_mtime > self.last_mtime:
print("检测到配置文件修改,重新加载")
self.load()
time.sleep(3) 编程客栈# 每3秒检查一次
def get(self, section, option, fallback=None):
"""安全获取值"""
with self._lock:
return self.config.get(section, option, fallback=fallback)
# 使用示例
if __name__ == '__main__':
config = HotReloadConfig('app.ini')
while True:
print(f"当前调试模式: {config.get('Debug', 'enabled', 'false')}")
time.sleep(5)
四、实用案例解析
1. 应用配置中心
class AppConfig:
_instance = None
def __new__(cls):
if not cls._instance:
cls._instance = super().__new__(cls)
cls._instance._init_config()
return cls._instance
def _init_config(self):
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.config.read('app.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 预加载常用配置
self.debug_mode = self.config.getboolean('General', 'debug', fallback=False)
self.db_params = {
'host': self.config['Database']['host'],
'port': self.config.getint('Database', 'port'),
'user': self.config['Database']['user']
}
def get_feature_flag(self, feature):
"""获取特性开关状态"""
return self.config.getboolean('Features', feature, fallback=False)
def update_setting(self, section, key, value):
"""更新配置"""
if not self.config.has_section(section):
self.config.add_section(section)
self.config.set(section, key, value)
self._save()
def _save(self):
"""保存配置并重新加载"""
with open('app.ini', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.config.write(f)
self._init_config() # 重新初始化
# 使用示例
config = AppConfig()
print("数据库主机:", config.db_params['host'])
# 动态更新配置
config.update_setting('Database', 'host', 'new.host.example.com')
2. 多语言国际支持
; locales.ini [DEFAULT] language = en_US [en_US] greeting = Hello! farewell = Goodbye! [zh_CN] greeting = 你好! farewell = 再见! [fr_FR] greeting = Bonjour! farewell = Au revoir!
class I18nManager:
def __init__(self, filepath='locales.ini'):
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.config.read(filepath, encoding='utf-8')
# 获取可用语言列表
self.languages = [s for s in self.config.sections() if s != 'DEFAULT']
# 设置当前语言
self.current_lang = self.config.get('DEFAULT', 'language')
def set_language(self, lang_code):
"""设置当前语言"""
if lang_code in self.languages:
self.current_lang = lang_code
return True
return False
def translate(self, key, default=None):
"""翻译文本"""
try:
return self.config.get(self.current_lang, key)
except configparser.NoOptionError:
# 尝试使用默认语言
try:
return self.config.get('en_US', key)
except configparser.NoOptionError:
return default
# 使用示例
i18n = I18nManager()
print(i18n.translate('greeting')) # Hello!
i18n.set_language('zh_CN')
print(i18n.translate('greeting')) # 你好!
3. 跨平台路径处理
import os
from pathlib import Path
def resolve_path(config, section, key, default=None):
"""解析配置中的路径并标准化"""
raw_path = config.get(section, key, fallback=default)
if raw_path is None:
return None
# 展开用户目录
expanded = os.path.expanduser(raw_patjsh)
# 跨平台路径处理
path = Path(expanded)
# 处理环境变量
if '$' in expanded:
path = Path(os.path.expandvars(expanded))
return path.resolve()
# 使用示例
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('app.ini')
log_file = resolve_path(config, 'Logging', 'file', '/var/log/app.log')
data_dir = resolve_path(config, 'Database', 'data_dir', '~/app_data')
print(f"日志文件位置: {log_file}")
print(f"数据目录: {data_dir}")
五、总结:核心方法速查表
1. 文件操作
| 方法 | 描述 | 参数 | 返回 |
|---|---|---|---|
| read(filenames) | 读取INI文件 | 文件路径/列表 | 成功加载的文件列表 |
| write(fileobject) | 写入配置 | 文件对象 | None |
| read_file(f) | Python 3.2+ 替代方法 | 文件对象 | None |
| read_dict(dictionary) | 从字典读取配置 | 字典对象 | None |
2. 配置访问
| 方法 | 描述 | 参数 | 返回 |
|---|---|---|---|
| sections() | 获取所有节 | 无 | 节列表 |
| options(section) | 获取节所有键 | 节名称 | 键列表 |
| get(section, option) | 获取配置值 | 节, 键 | 字符串 |
| items(section) | 获取所有键值对 | 节名称 | (键,值)元组列表 |
3. 类型安全访问
| 方法 | 描述 | 返回类型 |
|---|---|---|
| getint() | 获取整数值 | int |
| getfloat() | 获取浮点值 | float |
| getboolean() | 获取布尔值 | bool |
4. 配置修改
| 方法 | 描述 | 错误 |
|---|---|---|
| add_section(section) | 添加新节 | DuplicateSectionError |
| remove_section(section) | 删除节 | NoSectionError |
| set(section, option, value) | 设置配置值 | NoSectionError |
| remove_option(section, option) | 删除配置项 | NoSectionError |
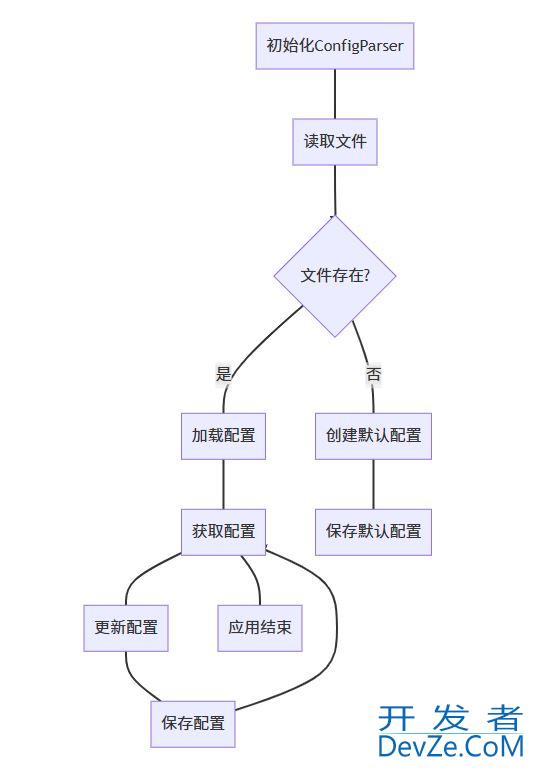
最佳实践总结:
- 使用安全访问:总是使用 get() 方法并提供 fallback 值
- 优先类型方法:使用 getint(), getboolean() 等进行类型转换
- 规范文件格式:保持统一缩进和空格风格
- 分层配置管理:使用 DEFAULT 节提供全局默认值
- 配置文件加密:生产环境敏感配置应该加密存储
- 配置版本控制:INI 文件纳入版本控制系统管理
- 环境隔离:不同环境使用不同配置文件
通过掌握这些 INI 文件处理技术,您将能够构建高效可靠的配置管理系统,满足从简单应用到企业级系统的各种需求。
以上就是Python INI文件读写的详细指南的详细内容,更多关于Python INI文件读写的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论