SpringBoot快速搭建RESTful应用的流程步骤
目录
- Spring Boot Web 入门指南:零基础构建 RESTful 应用
- 一、Spring Boot 核心优势
- 二、5 分钟创建第一个 Web 应用
- 步骤 1:使用 Spring Initializr 创建项目
- 步骤 2:项目结构解析
- 步骤 3:编写第一个 REST 控制器
- 步骤 4:启动应用
- 步骤 5:测试javascript接口
- 三、核心注解详解
- 四、实现 CRUD 接口示例
- 1. 创建用户模型
- 2. 实现控制器
- 3. 使用 Postman 测试
- 五、关键配置技巧
- 1. 修改端口号
- 2. 自定义返回 jsON 格式
- 3. 开启热部署(实时生效)
- 六、调试与问题排查
- 1. 查看自动配置报告
- 2. 常用端点监控
- 七、下一步学习建议
Spring Boot Web 入门指南:零基础构建 RESTful 应用
Spring Boot 彻底简化了 Java Web 开发流程,让你能在 5 分钟内创建一个可运行的 Web 应用。以下是新手必学核心内容:
一、Spring Boot 核心优势
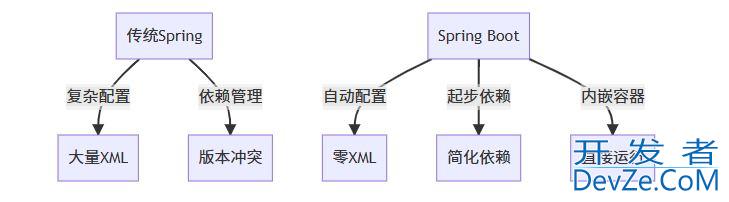
二、5 分钟创建第一个 Web 应用
步骤 1:使用 Spring Initializr 创建项目
访问 start.spring.io 配置:
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 3.2.x
- Dependencies:
Spring Web - Packaging: Jar
点击 “Generate” 下载项目压缩包
步骤 2:项目结构解析
src/ ├── main/ │ ├── java/ │ │ └── com/example/demo/ │ │ ├── DemoApplication.java // 启动类 │ │ └── controller/ // 控制器目录 │ └─编程客栈─ resources/ │ ├── static/ // 静态资源(css/JS) │ ├── templates/ // 模板文件(Thymeleaf) │ └── application.properties // 配置文件 └── test/ // 测试代码
步骤 3:编写第一个 REST 控制器
创建 HelloController.java:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController // 标记为 REST 控制器
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello") // 处理 GET 请求
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello Spring Boot Web!";
}
@GetMapping("/user")
public User getUser() {
return new User(1, "Alice"); // 自动转为 JSON
}
// 内部用户类
static class User {
private int id;
private String name;
// 构造器 + Getter 省略(实www.devze.com际开发需加上)
}
}
步骤 4:启动应用
在 DemoApplication.java 右键选择:
- Run As → Spring Boot App
- 或使用命令:
mvn spring-boot:run
控制台出现 Tomcat started on port 8080 表示成功
步骤 5:测试接口
打开浏览器访问:
- http://localhost:8080/hello → 显示文本
- http://localhost:8080/user → 返回 JSON:
{"id":1, "name":"Alice"}
三、核心注解详解
| 注解 | 作用 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| @RestController | 定义 REST 控制python器 | 类注解 |
| @GetMapping | 处理 GET 请求 | @GetMapping("/path") |
| @PostMapping | 处理 POST 请求 | @PostMapping("/users") |
| @RequestMapping | 通用请求映射 | @RequestMapping("/api") |
| @RequestParam | 获取 URL 参数 | @RequestParam String name |
| @PathVariable | 获取路径变量 | @PathVariable int id |
| @RequestBody | 获取请求体 JSON 数据 | @RequestBody User user |
| @ResponseBody | 返回数据而非视图 | 方法或类注解 |
四、实现 CRUD 接口示例
1. 创建用户模型
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
// 构造器 + Getter/Setter 省略
}
2. 实现控制器
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
// 临时存储(实际应连接数据库)
private final List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
private int nextId = 1;
// 创建用户
@PostMapping
public User createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
user.setId(nextId++);
users.add(user);
return user;
}
// 获取所有用户
@GetMapping
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return users;
}
// 获取单个用户
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return users.stream()
.filter(u -> u.getId().equals(id))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null); // 实际应返回404
}
}
3. 使用 Postman 测试
POST http://localhost:8080/api/users
Body (JSON):{"name": "Bob", "email": "bob@example.com"}
GET http://localhost:8080/api/users
返回:[{"id":1, "name":"Bob", "email":"bob@example.com"}]
五、关键配置技巧
1. 修改端口号
src/resources/application.properties:
server.port=9090 # 修改为9090端口
2. 自定义返回 JSON 格式
spring.jackson.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss spring.jackson.time-zone=GMT+8
3. 开启热部署(实时生效)
添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
六、调试与问题排查
1. 查看自动配置报告
启动时添加参数:
java -jar demo.jar --debug
在日志中搜索 CONDITIONS EVALuaTION REPORT
2. 常用端点监控
# application.properties management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator
七、下一步学习建议
连接数据库
- 添加
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa+ 数据库驱动
实现登录认证
- 学习
spring-boot-starter-security
前端整合
- 使用 Thymeleaf 或 vue.js 整合
部署实战
- 打包:
mvn clean package - 运行:
java -jar target/demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
新手避坑提示:遇到问题时先检查:
- 注解是否遗漏(如 @RestController)
- 包结构是否正确(控制器要在启动python类同级或子目录)
- 依赖是否完整(检查 pom.XML)
以上就是SpringBoot快速搭建RESTful应用的流程步骤的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot搭建RESTful应用的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论