本地缓存在Java中的实现过程
目录
- 1、介绍
- 2、实现方式
- 2.1www.devze.com、HashMap
- 2.2、LinkedHashMap
- 2.3、Guava Cache
- 2.4、Caffeine Cache
- 2.5、Ehcache
- 2.6、使用Spring Cache注解
- 3、性能对比
- 4、使用建议
- 总结
本地缓存是Java应用中常用的性能优化手段。如下图所示:
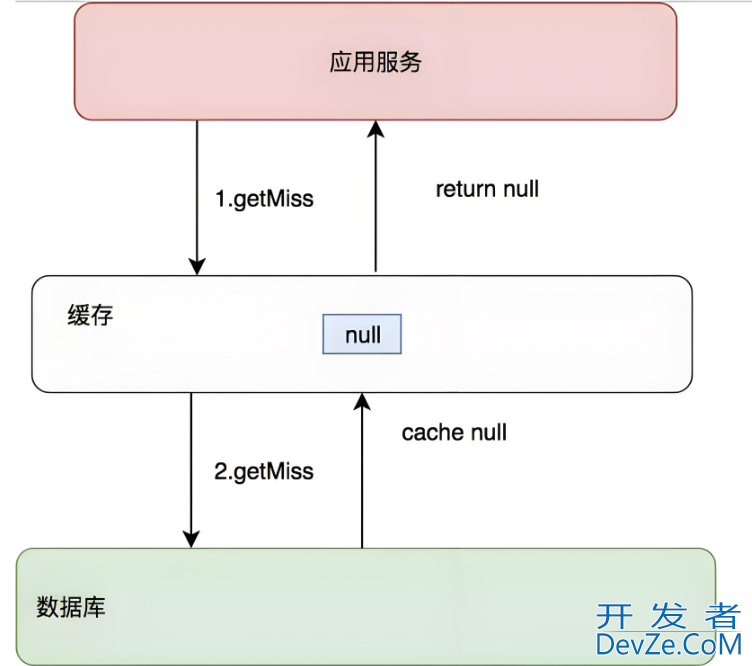
在分布式系统中,同一个应用部署有多个,这些应用的本地缓存仅限于本地应用内部,是互不相通的,在负载均衡中,分配到处理的各个应用读取本地缓存的结果可能会存在不一致。
注意:本地缓存是jvm层面的缓存,一旦该应用重启或停止了,缓存也消失了。
1、介绍
引入缓存,主要用于实现系统的高性能,高并发。如下图所示:
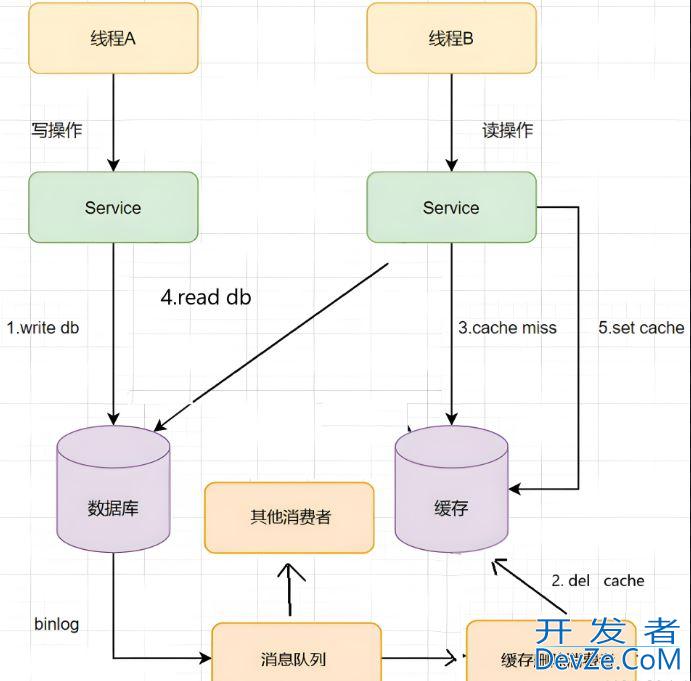
将数据库查询出来的数据放入缓存服务中,因为缓存是存储在内存中的,内存的读写性能远超磁盘的读写性能,所以访问的速度非常快。
注意:
但是电脑重启后,内存中的数据会全部清除,而磁盘中的数据虽然读写性能很差,但是数据不会丢失。
2、实现方式
2.1、HashMap
最简单的方式是使用ConcurrentHashMap实现线程安全的缓存。
代码示例如下:
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class SimpleCache<K, V> {
private final ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void put(K key, V value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
public V get(K key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
public void remove(K key) {
cache.remove(key);
}
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
}
适用场景:
- 简单的内存缓存需求
- 缓存数据量很小(几百条以内)
- 不需要过期策略或淘汰机制
- 快速原型开发
优点:
- 零依赖
- 实现简单直接
- 性能极高
缺点:
- 缺乏过期、淘汰等高级功能
- 需要手动实现线程安全(使用ConcurrentHashMap除外)
如下所示:
// 简单的配置项缓存
private static final Map<String, String> CONFIG_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public String getConfig(String key) {
return CONFIG_CACHE.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> loadConfigFromDB(k));
}
2.2、LinkedHashMap
利用LinkedHashMap的访问顺序特性实现LRU(最近最少使用)缓存。
如下图所示:
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private final int maxSize;
public LRUCache(int maxSize) {
super(maxSize, 0.75f, true);
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return size() > maxSize;
}
}
适用场景:
- 需要简单的LRU淘汰策略
- 缓存数量固定且不大
- 不想引入第三方库
优点:
- JDK内置,无额外依赖
- 实现LRU策略简单
缺点:
- 功能有限
- 并发性能一般
如下所示:
// 最近访问的用户基本信息缓存
private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 1000;
private static final Map<Long, UserInfo> USER_CACHE =
Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap<Long, UserInfo>(MAX_ENTRIES, 0.75f, true) {
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > MAX_ENTRIES;
}
});
2.3、Guava Cache
Guava Cache是JVM层面的缓存,服务停掉或重启便消失了,在分布式环境中也有其局限性。
因此,比较好的缓存方案是Guava Cache+Redis双管齐下。先查询Guava Cache,命中即返回,未命中再查redis。
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>32.1.2-jre</version> <!-- 使用最新版本 -->
</dependency>
代码如下所示:
import com.google.common.cache.Cache;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
public class GuavaCacheExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//建造者模式
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100) // 最大缓存数量
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 写入后10分钟过期
.build();
// 放入缓存
cache.put("key1", "value1");
// 获取缓存
String value = cache.getIfPresent("key1");
System.out.println(value);
// 移除缓存
cache.invalidate("key1");
}
}
适用场景:
- 需要丰富的缓存特性(过期、淘汰、刷新等)
- 中等规模缓存(几千到几十万条目)
- 需要良好的并发性能
- 项目已经使用Guava库
优点:
- 功能全面(权重、刷新、统计等)
- 良好的API设计
- 中等规模的优秀性能
缺点:
- 不如Caffeine性能高
- 大型缓存时内存效率一般
示例如下:
// 商品详情缓存,30分钟自动过期,最大10000条
LoadingCache<Long, Product> productCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.expireAfterWrite(30, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.recordStats()
.build(new CacheLoaderjavascript<Long, Product>() {
@Override
public Product load(Long id) {
return productDao.findById(id);
}
});
// 使用
Product product = productCache.get(123L);
2.4、Caffeine Cache
Caffeine是Guava Cache的现代替代品,性能更好。
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
<version>3.1.8</version> <!-- 使用最新版本 -->
</dependency>
代码示例如下:
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
public class CaffeineCacheExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String, String&androidgt; cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
String value = cache.getIfPresent("key1");
System.out.println(value);
}
}
适用场景:
- 高性能要求的应用
- 大规模缓存(几十万以上条目)
- 需要最优的读写性能
- 现代Java项目(JDK8+)
优点:
- 目前性能最好的Java缓存库
- 内存效率高
- 丰富的特性(异步加载、权重等)
- 优秀的并发性能
缺点:
- 较新的库,老项目可能不适用
- API与Guava不完全兼容
示例如下:
// 高性能的秒杀商品库存缓存
Cache<Long, AtomicInteger> stockCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100_000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 库存信息短期有效
.refreshAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 1秒后访问自动刷新
.build(id -> new AtomicInteger(queryStockFromDB(id)));
// 使用
int remaining = stockCache.get(productId).decrementAndGet();
2.5、Ehcache
Ehcache是一个成熟的Java缓存框架:功能更强大,支持磁盘持久化、分布式缓存等。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>3.10.8</version>
</dependency>
import org.ehcache.Cache;
import org.ehcache.config.builders.CacheConfigurationBuilder;
import org.ehcache.config.builders.ResourcePoolsBuilder;
import org.ehcache.config.units.MemoryUnit;
import org.ehcache.core.config.DefaultConfiguration;
import org.ehcache.core.spi.service.LocalPersistenceService;
import org.ehcache.impl.config.persistence.DefaultPersistenceConfiguration;
import org.ehcache.impl.persistence.DefaultLocalPersistenceService;
public class EhcacheExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 配置持久化到磁盘
LocalPersistenceService persistenceService = new DefaultLocalPersistenceService(
new DefaultPersistenceConfiguration(new File("cache-data")));
// 创建缓存管理器
DefaultConfiguration config = new DefaultConfiguration(
persistenceService, ResourcePoolsBuilder.heap(100).build());
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheConfigurationBuilder.newCacheConfigurationBuilder(
String.class, String.class,
ResourcePoolsBuilder.newResourcePoolsBuilder()
.heap(100, MemoryUnit.MB) // 堆内内存
.disk(1, MemoryUnit.GB) // 磁盘持久化
).buildConfig(String.class);
// 写入数据
cache.put("key1", "value1");
// 读取数据
String value = cache.get("key1");
System.out.println("Value: " + value); // 输出 Value: value1
// 关闭资源
persistenceService.close();
}
}
适用场景:
- 企业级应用
- 需要持久化到磁盘
- 需要分布式缓存支持
- 复杂的缓存拓扑需求
优点:
- 功能最全面(堆外、磁盘、集群等)
- 成熟的监控和管理
- 良好的Spring集成
缺点:
- 性能不如Caffeine
- 配置较复杂
- 内存效率一般
示例如下:
<!-- ehcache.XML -->
<cache name="financialDataCache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000"
timeToLiveSeconds="3600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</cache>
// 金融数据缓存,需要持久化
@Cacheable(value = "financialDataCache",
key = "#symbol + '_' + #date.format(yyyyMMdd)")
public FinancialData getFinancialData(String symbol, LocalDate date) {
// 从外部API获取数据
}
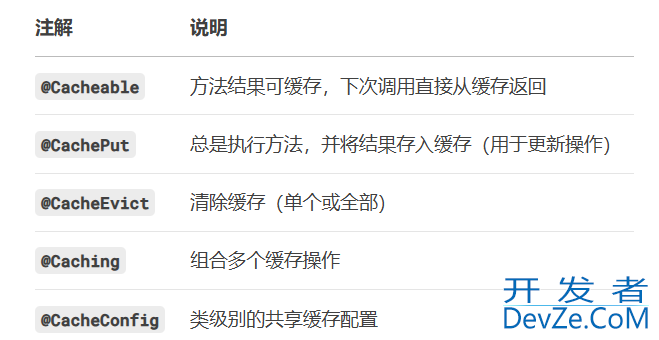
2.6、使用Spring Cache注解
Spring框架提供了缓存抽象。关于cache的常用注解如下:
1、引入依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Cache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用Caffeine作为缓存实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、使用缓存配置类
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnabljavascripteCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
import org.springframework.cache.caffeine.CaffeineCacheManager;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager() {
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(100)
.maximumSize(500)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.recordStats());
return cacheManager;
}
@Bean
@Primary
public CacheManager productCacheManager() {
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager("products");
cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.HOURS));
return cacheManager;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager userCacheManager() {
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager("users");
cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(500)
.expireAfterAccess(30, TimeUnit.MINUTES));
return cacheManager;
}
}
注意:在设置缓存配置类的时候,可以配置多个。
然后在服务类中指定使用哪个缓存管理器:
@Service
public class UserService {
@Cacheable(value = "users", cacheManager = "userCacheManager")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
// ...
}
}
3、服务类使用缓存
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ProductService {
// 根据ID获取产品,如果缓存中有则直接返回
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id")
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
// 模拟数据库查询
System.out.println("查询数据库获取产品: " + id);
return findProductInDB(id);
}
// 更新产品信息,并更新缓存
@CachePut(value = "products", key = "#product.id")
public Product updateProduct(Product product) {
// 模拟数据库更新
System.out.println("更新数据库中的产品: " + product.getId());
return updateProductInDB(product);
}
// 删除产品,并清除缓存
@CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "#id")
public void deleteProduct(Long id) {
// 模拟数据库删除
System.out.println("从数据库删除产品: " + id);
}
// 清除所有产品缓存
@CacheEvict(value = "products", allEntries = true)
public void clearAllCache() {
System.out.println("清除所有产品缓存");
}
// 模拟数据库查询方法
private Product findProductInDB(Long id) {
// 实际项目中这里应该是数据库操作
return new Product(id, "产品" + id, 100.0);
}
// 模拟数据库更新方法
private Product updateProductInDB(Product product) {
// 实际项目中这里应该是数据库操作
return product;
}
}
4、实体类
public class Product {
private Long id;
private String name;
private double price;
// 构造方法、getter和setter省略
// 实际项目中应该包含这些方法
}
5、控制器示例:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/products")
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
public ProductController(ProductService productService) {
this.productService = productService;
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Product getProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
return productService.getProductById(id);
}
@PutMapping
public Product updateProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
return productService.updateProduct(product);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
productService.deleteProduct(id);
}
@PostMapping("/clear-cache")
public void clearCache() {
productService.clearAllCache();
}
}
适用场景:
- Spring/Spring Boot项目
- 需要声明式缓存
- 可能切换缓存实现
- 需要与Spring生态深度集成
优点:
- 统一的缓存抽象
- 注解驱动,使用简单
- 轻松切换实现(Caffeine/Ehcache/Redis等)
缺点:
- 性能取决于底层实现
- 高级功能需要了解底层实现
如下所示:
// 多级缓存配置:本地缓存+Redis
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
// 本地一级缓存
@Bean
@Primary
public CacheManager localCacheManager() {
CaffeineCacheManager manager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
manager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(30, TimeUnit.MINUTES));
return manager;
}
// Redis二级缓存
@Bean
public CacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(2))
.disableCachingNullValues())
.build();
}
}
// 服务层使用
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "products",
cacheManager = "localCacheManager") // 先用本地缓存
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "products",
cacheManager = "redisCacheManager",
unless = "#result == null") // 再用Redis缓存
public Product getProduct(Long id) {
return productRepository.findById(id);
}
}
3、性能对比

1.合理设置缓存大小:
根据可用内存设置上限。使用weigher对大型对象特殊处理。
2.选择合适的过期策略:
// 根据业务场景选择 .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 写入后固定时间过期 .expir编程eAfterAccess(30, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 访问后延长有效期 .refreshAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 写入后定时刷新
3.监控缓存命中率:
CacheStats stats = cache.stats(); double hitRate = stats.hitRate(); // 命中率 long evictionCount = stats.evictionCount(); // 淘汰数量
4.避免缓存污染:
// 不缓存null或空值
.build(key -> {
Value value = queryFromDB(key);
return value == null ? Optional.empty() : value;
});
@Cacheable(unless = "#result == null || #result.isEmpty()")
5.考虑使用软引用(内存敏感场景):
.softValues() // 内存不足时自动回收
根据您的具体业务需求、数据规模和性能要求,选择最适合的缓存方案,并持续监控和优化缓存效果。
4、使用建议
简单小规模缓存:ConcurrentHashMap或LinkedHashMap
- 适用于配置项、简单查询结果缓存
- 无外部依赖,实现简单
中等规模通用缓存:Guava Cache或Caffeine
- 适用于大多数业务数据缓存
- Guava适合已有Guava依赖的项目
- Caffeine性能更好,推荐新项目使用
高性能大规模缓存:Caffeine
- 适用于高并发、高性能要求的场景
- 如秒杀系统、高频交易系统
企业级复杂需求:Ehcache
- 需要持久化、集群等高级功能
- 已有Ehcache使用经验的项目
Spring项目:Spring Cache + Caffeine
- 利用Spring抽象层,方便后续扩展
- 推荐Caffeine作为底层实现
多级缓存架构:Caffeine + Redis
- 本地缓存作为一级缓存
- Redis作为二级分布式缓存
- 通过Spring Cache抽象统一管理
总结
内存管理:设置合理的 maximumSize 或 expireAfterWrite,避免内存溢出(OOM)。
并发安全:Guava/Caffeine/Ehcache 均为线程安全,直接使用即可。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论