Springboot使用异步方法优化Service逻辑,提高接口响应速度方式
目录
- 使用异步方法优化Service逻辑,提高接口响应速度
- 一、业务场景
- 二、异步任务在springboot的使用
- 三、自定义线程池执行异步方法
- 四、捕获(无返回值的)异步方法中的异常
- 五、捕获(有返回值)异步方法中的异常
- 总结
使用异步方法优化Service逻辑,提高接口响应速度
一、业务场景
例如生成验证码和发送验证码组成的业务,其实无需等到真正发送成功验证码才对客户端进行响应,可以让短信发送者一个耗时操作转为异步执行
二、异步任务在springboot的使用
@RestController
public class AsyncArticleController {
@Autowired
private ArticleService articleService;
/**
* 模拟获取文章后阅读量+1
*/
@PostMapping("/article")
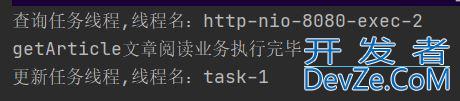
public String getArticle() {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
articleService.updateReadCount();
System.out.println("getArticle文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article;
}
}
@Service
public class ArticleService {
// 查询文章
public String selectArticle() {
// TODO 模拟文章查询操作
System.out.println("查询任务线程,线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "文章详情";
}
// 文章阅读量+1
@Async
public void updateReadCount() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新任务线程,线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class SpringbootRunnerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootRunnerApplication.class, args);
}
}
注意:
@EnableAsync // 使用异步方法时需要提前开启(在启动类上或配置类上) @Async // 被async注解修饰的方法由SpringBoot默认线程池(SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor)执行
三、自定义线程池执行异步方法
第一步配置自定义线程池
package com.hl.springbootrunner.asyncdemo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
@EnableAsync // 开启多线程, 项目启动时自动创建
@Configuratihttp://www.devze.comon
public class AsyncConfig {
@Bean("readCountExecutor") //指定自定义线程池名称
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncOperationExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(8);
// 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 设置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliv编程客栈eSeconds(60);
// 设置线程名前缀+分组名称
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("AsyncOperationThread-");
executor.setThreadGroupName("AsyncOperationGroup");
// 所有任务结束后关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
第二步, 在@Async注解上指定执行的线程池,ArticleService中指定执行的线程池
// 文章阅读量+1,指定线程池
@Async("readCountExecutor")
public void updateReadCountByExecutor() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
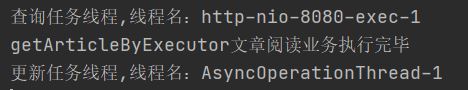
System.out.println("更新任务线程,线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
第三步,在AsyncArcicleController中
/**
* 模拟获取文章后阅读量+1,指定线程池
*/
@PostMapping("/articleByExecutor")
public String getArticleByExecutor() {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
articleService.updateReadCountByExecutor();
编程客栈 System.out.println("getArticleByExecutor文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article;
}
四、捕获(无返回值的)异步方法中的异常
自定义异常处理类CustomAsyncExceptionHandler
@Component
phppublic class CustomAsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... obj) {
System.out.println("异常捕获---------------------------------");
System.out.println("Exception message - " + throwable.getMessage());
System.out.println("Method name - " + method.getName());
for (Object param : obj) {
System.out.println("Parameter value - " + param);
}
System.out.println("异常捕获---------------------------------");
}
}
@Async("readCountExecutor")
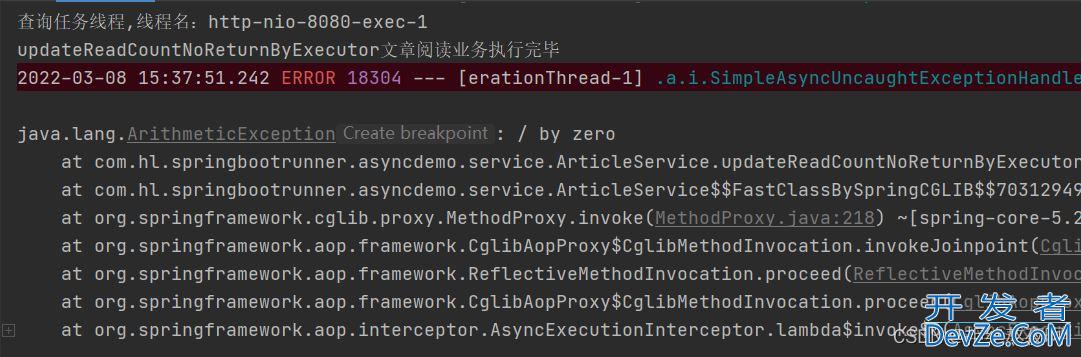
public void updateReadCountNoReturnByExecutor() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
int i = 1/0;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新任务线程,线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
五、捕获(有返回值)异步方法中的异常
使用Future类及其子类来接收异步方法返回值
// 文章阅读量+1
@Async("readCountExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<Integer> updateReadCountHasResult() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
www.devze.com try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
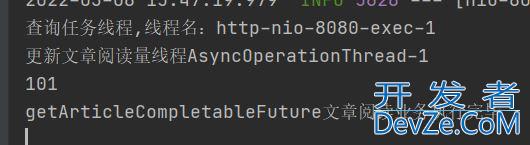
System.out.println("更新文章阅读量线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(100 + 1);
}
@GetMapping("/articleCompletableFuture")
public String getArticleCompletableFuture() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = articleService.updateReadCountHasResult();
//无返回值的异步方法抛出异常不会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
//有返回值的异步方法抛出异常会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
int count = 0;
// 循环等待异步请求结果
while (true) {
if(future.isCancelled()) {
System.out.println("异步任务取消");
break;
}
if (future.isDone()) {
count = future.get();
System.out.println(count);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("getArticleCompletableFuture文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article + count;
}
注意:
- 无返回值的异步方法抛出异常不会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
- 有返回值的异步方法抛出异常会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论