SpringBoot集成Easy-Es全过程
目录
- SpringBoot集成Easy-Es
- 一、集成demo
- 二、索引CRUD
- 三、数据CURD
- 总结
SpringBoot集成Easy-Es
Easy-Es(简称EE)是一款基于ElasticSearch(简称Es)官方提供的RestHighLevelClient打造的ORM开发框架,在 RestHighLevelClient 的基础上,只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生
一、集成demo
1、添加依赖
<!-- 排除springboot中内置的es依赖,以防和easy-es中的依赖冲突-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入es的坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>7.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javascriptorg.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.easy-es</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-es-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
2、配置信息
# 默认为true,若为false时,则认为不启用本框架 easy-es.enable: true #填你的es连接地址 easy-es.address : 127.0.0.1:9200 # username: 有设置才填写,非必须 easy-es.username : elastic # password: 有设置才填写,非必须 easy-es.password : 123456
3、启动类中添加 @EsMapperScan 注解,扫描 Mapper 文件夹
@SpringBootApplication
@EsMapperScan("com.example.elasticsearch.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void maiBejCdHon(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
4、实体类和mapper
@Data
public class Document {
/**
* es中的唯一id,当您字段命名为id且类型为String时,且不需要http://www.devze.com采用UUID及自定义ID类型时,可省略此注解
*/
@IndexId(type = IdType.NONE)
private String id;
/**
* 文档标题,不指定类型默认被创建为keyword类型,可进行精确查询
*/
private String title;
/**
* 文档内容,指定了类型及存储/查询分词器
*/
@IndexField(fieldType = FieldType.TEXT, analyzer = Analyzer.IK_SMART, searchAnalyzer = Analyzer.IK_MAX_WORD)
private String content;
}
public interface DocumentMapper extends BaseEsMapper<Document> {
}
5、测试
@RestController
public class EasyEsController {
@Autowired
private DocumentMapper documentMapper;
@GetMapping("/insert")
http://www.devze.com public Integer insert() {
// 初始化-> 新增数据
Document document = new Document();
document.setTitle("老汉");
document.setContent("推*技术过硬");
return documentMapper.insert(document);
}
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<Document> search() {
// 查询出所有标题为老汉的文档列表
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(Document::getTitle, "老汉");
return documentMapper.selectList(wrapper);
}
}
http://localhost:8080/insert(插入数据)
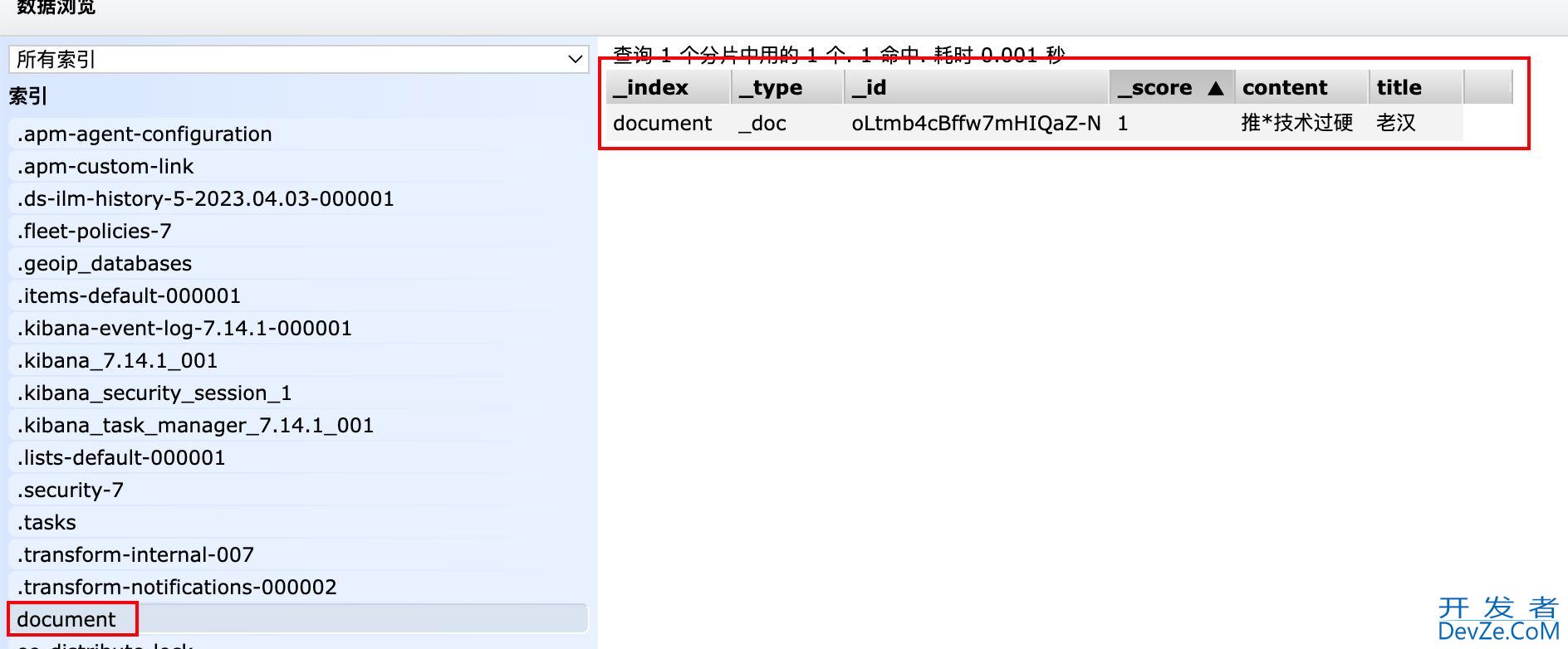
http://localhost:8080/search(查询数据)
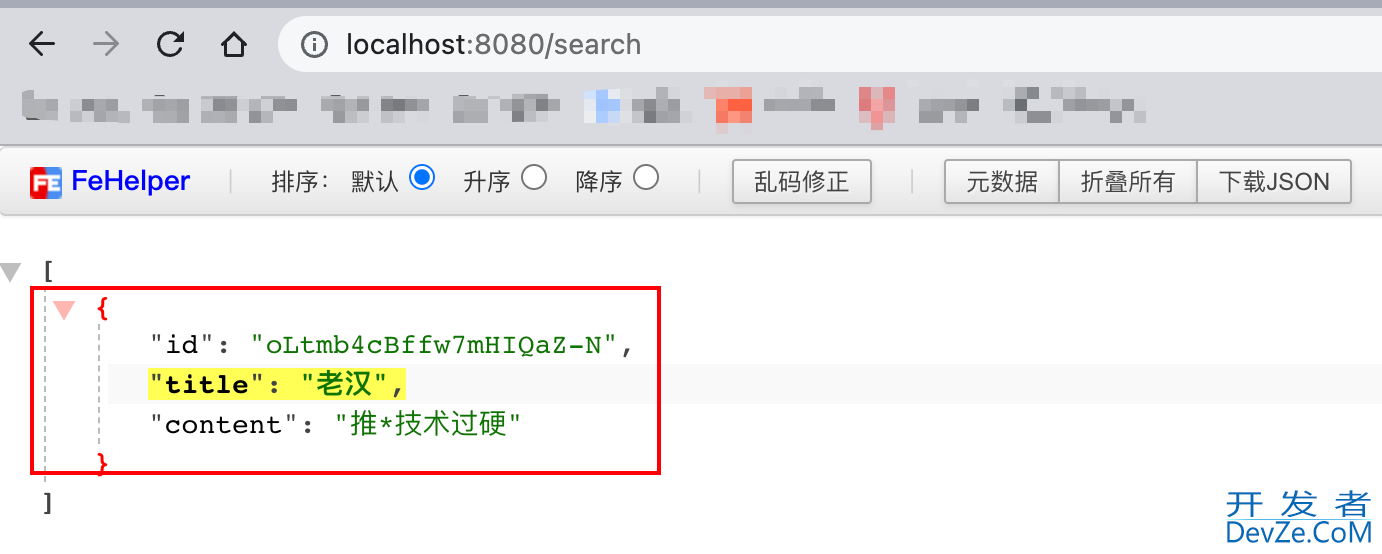
二、索引CRUD
首先说一下索引的托管模式,EE这里有三种托管模式
- 自动托管之平滑模式(默认):在此模式下,索引的创建更新数据迁移等全生命周期用户均不需要任何操作即可完成
- 自动托管之非平滑模式:在此模式下,索引额创建及更新由EE全自动异步完成,但不处理数据迁移工作
- 手动模式:在此模式下,索引的所有维护工作EE框架均不介入,由用户自行处理,EE提供了开箱即用的索引CRUD相关API
前置条件
索引CRUD相关的API都属于手动挡范畴,因此我们执行下述所有API前必须先配置开启手动挡,以免和自动挡冲突
easy-es:
global-config:
process_index_mode: manul # 手动挡模式
创建索引
@Test
void createIndex01(){
// 绝大多数场景推荐使用
documentMapper.createIndex();
}
@Test
void createIndex02(){
// 适用于定时任务按日期创建索引场景
String indexName = LocalDate.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd"));
documentMapper.createIndex(indexName);
}
@Test
void createIndex03() {
// 复杂场景使用
LambdaEsIndexWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsIndexWrapper<>();
// 此处简单起见 索引名称须保持和实体类名称一致,字母小写 后面章节会教大家更如何灵活配置和使用索引
wrapper.indexName(Document.class.getSimpleName().toLowerCase());
// 此处将文章标题映射为keyword类型(不支持分词),文档内容映射为text类型(支持分词查询)
wrapper.mapping(Document::getTitle, FieldType.KEYWORD, 2.0f)
.mapping(Document::getContent, FieldType.TEXT, Analyzer.IK_SMART, Analyzer.IK_MAX_WORD);
// 设置分片及副本信息,可缺省
wrapper.settings(3, 2);
// 创建索引
boolean isOk = documentMapper.createIndex(wrapper);
}
查询索引
@Test
public void testExistsIndex() {
// 测试是否存在指定名称的索引
String indexName = Document.class.getSimpleName().toLowerCase();
boolean existsIndex = documentMapper.existsIndex(indexName);
Assertions.assertTrue(existsIndex);
}
@Test
public void testGetIndex() {
GetIndexResponse indexResponse = documentMapper.getIndex();
// 这里打印下索引结构信息 其它分片等信息皆可从indexResponse中取
indexResponse.getMappings().forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(v.getSourceAsMap()));
}
更新索引
/**
* 更新索引
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateIndex() {
// 测试更新索引
LambdaEsIndexWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsIndexWrapper<>();
// 指定要更新哪个索引
String indexName = Document.class.getSimpleName().toLowerCase();
wrapper.indexName(indexName);
wrapper.mapping(Document::getTitle, FieldType.KEYWORD);
wrapper.mapping(Document::getContent, FieldType.TEXT, Analyzer.IK_SMART, Analyzer.IK_MAX_WORD);
wrapper.mapping(Document::getInfo, FieldType.TEXT, Analyzer.IK_SMART, Analyzer.IK_MAX_WORD);
boolean isOk = documentMapper.updateIndex(wrapper);
Assertions.assertTrue(isOk);
}
删除索引
@Test
public void testDeleteIndex() {
// 指定要删除哪个索引
String indexName = Document.class.getSimpleName().toLowerCase();
boolean isOk = documentMapper.deleteIndex(indexName);
Assertions.assertTrue(isOk);
}
三、数据CURD
// 插入一条记录,默认插入至当前mapper对应的索引
Integer insert(T entity);
// 插入一条记录 可指定具体插入的索引,多个用逗号隔开
Integer insert(T entity, String... indexNames);
// 批量插入多条记录
Integer insertBATch(Collection<T> entityList)
// 批量插入多条记录 可指定具体插入的索引,多个用逗号隔开
Integer insertBatch(Collection<T> entityList, String... indexNames);
// 根据 ID 删除
Integer deleteById(Serializable id);
// 根据 ID 删除 可指定具体的索引,多个用逗号隔开
Integer deleteById(Serializable id, String... indexNames);
// 根据 entity 条件,删除记录
Integer delete(LambdaEsQueryWrapper<T> wrapper);
// 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
Integer deleteBatchIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
// 删除(根据ID 批量删除)可指定具体的索引,多个用逗号隔开
Integer deleteBatchIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList, String... indexNames);
//根据 ID 更新
Integer updateById(T entity);
//根据 ID 更新 可指定具体的索引,多个用逗号隔开
Integer updateById(T entity, String... indexNames);
// 根据ID 批量更新
Integer updateBatchByIds(Collection<T> entityList);
//根据 ID 批量更新 可指定具体的索引,多个用逗号隔开
Integer upwww.devze.comdateBatchByIds(Collection<T> entityList, String... indexNames);
// 根据动态条件 更新记录
Integer update(T entity, LambdaEsUpdateWrapper<T> updateWrapper);
// 获取总数
Long selectCount(LambdaEsQueryWrapper<T> wrapper);
// 获取总数 distinct为是否去重 若为ture则必须在wrapper中指定去重字段
Long selectCount(Wrapper<T> wrapper, boolean distinct);
// 根据 ID 查询
T selectById(Serializable id);
// 根据 ID 查询 可指定具体的索引,多个用逗号隔开
T selectById(Serializable id, String... indexNames);
// 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
List<T> selectBatchIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
// 查询(根据ID 批量查询)可指定具体的索引,多个用逗号隔开
List<T> selectBatchIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList, String... indexNames);
// 根据动态查询条件,查询一条记录 若存在多条记录 会报错
T selectOne(LambdaEsQueryWrapper<T> wrapper);
// 根据动态查询条件,查询全部记录
List<T> selectList(LambdaEsQueryWrapper<T> wrapper);
参数文档:Easy-Es文档
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论