Spring Security常用配置的使用解读
目录
- 初体验
- 自定义用户名密码
- 使用配置文件配置
- 使用 Java 代码配置
- 自定义拦截规则
- 登录注销配置
- 方法安全
- 总结
Spring Security 是 Spring 家族为我们提供的一款安全管理的框架,它是一个功能强大并且可以灵活定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。Spring Security 侧重于为 Java 应用程序提供身份验证和授权。与所有 Spring 项目一样,Spring Security 的真正强大之处在于它非常容易扩展来满足我们的不同需求。
在 SSM 时代,Spring Security 因为繁琐的配置而不被人们常用,但是在 Spring Boot 中为提供了自动化配置方案,可以零配置使用 Spring Security。
初体验
在 pom.XML 中导入 maven 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency>
只要在项目中加入 Spring Security 的依赖,项目中的所有接口都会被保护起来了。
当我们访问我们的项目的时候,就会先来到 Spring Security 默认的登录页面,
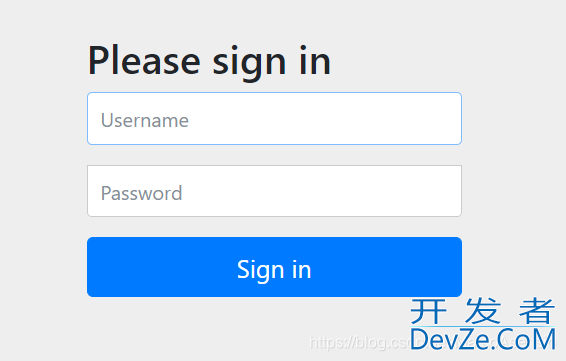
默认的用户名是 user,密码会在控制台打印,

登录后就可以正常访问项目了。
自定义用户名密码
因为密码是随机生成的一段密钥,不方便记忆,所以我们可以自己配置用户名和密码。
配置用户名和密码的方式有三种,我们可以在配置文件中配置,也可以在 Java 代码中配置,还可以在数据库中配置,我们先看如何在配置文件中配置。
使用配置文件配置
使用配置文件配置比较简单,直接在 application.yml 中配置即可。
spring:
security:
user:
name: user
password: 1234
使用 Java 代码配置
使用 Java 代码配置也比较简单,我们只需要编写一个 SecurityConfig 配置类,重写一个 configure() 方法即可。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("user").password("$2a$10$zwUhw4cAEv1AH6auayRPbePJAKk87peABiKegNMp4mqKXWxJZyDQS").roles("user")
.and()
.withUser("admin").password("$2a$10$mDQiCHTt3RLV.pLozBKOBOVIe7kaa3vYUCqZUu.957mpomdztOr0y").roles("admin");
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
使用 Java 代码配置比较灵活,我们可以用 and() 方法来配置多个用户。
在 Spring 5 以后要求我们配置的密码必须是加密的,我们可以配置一个 BCryptPasswordEncoder 密码编码器来帮助我们加密密码,我们只需要在单元测试中创建一个 BCryptPasswordEncoder 密码编码器,调用它的 encode()方法来加密,把得到的值复制到代码中,然后再将这个密码编码器配置到容器中,这个密码编码器的的好处是即使是相同的字段也可以得到不同的结果。
自定义拦截规则
因为 Spring Security 默认拦截所有的请求,但我们实际项目中肯定不能这样,所以我们应该自定义拦截规则,针对不同的请求,制定不同的处理方式。
这就需要用到 HttpSecurity 的配置,我们只需要在配置类中实现重载的 configure() 方法
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests() // 验证请求
// 路径匹配,参数是要处理的 url
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin") // 要具有某种权限
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAnyRole("admin", "user")// 要具有某种权限中的一种
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
登录注销配置
Spring Security 为我们提供的绝不止上面的那么简单,我们通过配置 HttpSecurity 还可以定制登录接口,登录成功后的响应,登录失败后的响应以及注销的相关操作。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.formLogin()
// 登录处理接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
// 定义登录页面,未登录时,访问一个需要登录之后才能访问的接口,会自动跳转到该页面
.loginPage("/login")
// 定义登录时,用户名的 key,默认为 username
.usernameParameter("uname")
// 定义登录时,用户密码的 key,默认为 password
.passwordParameter("passwd")
// 登录成功的处理器
.successHandler(new AuthenticationSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = httpServletResponse.getWriter();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 200);
map.put("msg", authentication.getPrincipal());
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
})
// 登录失败的处理器
.failureHandler(new AuthenticationFailureHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFail编程客栈ure(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWrvUIvPiOvKiter out = httpServletResponse.getWriter();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 401);
php if (e instanceof LockedException) {
map.put("msg", "账户被锁定,登录失败!");
} else if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
map.put("msg", "用户名或密码输入错误,登录失败!");
} else if (e instanceof DisabledException) {
map.put("msg", "账户被禁用,登录失败!");
} else if (e instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
map.put("msg", "账户过期,登录失败!");
} else if (e instanceof CredentialsExpiredException) {
map.put("msg", "密码过期,登录失败!");
} else {
map.put("msg", "登录失败!");
}
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
})
// 和表单登录相关的接口统统都直接通过
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
// 注销成功的处理器
.logoutSuccessHandler(new LogoutSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
httpServletResponse.setContentType("applihttp://www.devze.comcation/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = httpServletResponse.getWriter();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 200);
map.put("msg", "注销登录成功!");
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
});
}
}
方法安全
Spring Security 还为我们提供了方法级别安全的配置,什么是方法安全呢?就是在调用方法的时候来进行验证和授权。怎么实现方法安全呢?
首先我们要在配置类上加一个注解 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity,
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
并将 prePostEnabled 和 securepythondEnabled 两个属性值设置为 true,接下来就可以在方法上加注解来进行权限控制了。
我们先写一个 MethodService
@Service
public class MethodService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('admin')")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin";
}
@Secured("ROLE_user")
public String user() {
return "hello user";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin', 'user')")
public String hello() {
return "hello hello";
}
}
用@PreAuthorize 注解和@Secured 注解来控制方法的访问权限,再写一个 HelloController
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
MethodService methodService;
@GetMapping("hello1")
public String hello1() {
return methodService.admin();
}
@GetMapping("hello2")
public String hello2() {
return methodService.user();
}
@GetMapping("hello3")
public String hello3() {
return methodService.hello();
}
}
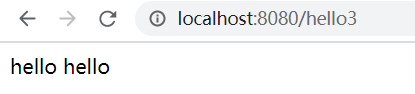
此时启动项目,我们用 admin 登录,分别发送 hello1,hello2,hello3 请求
hello1 请求能够访问
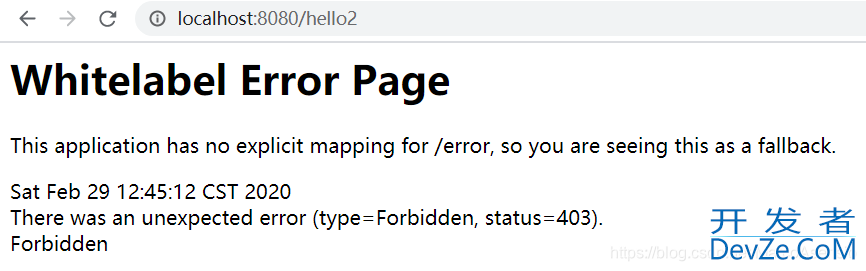
因为配置了 user() 方法要具有 user 权限才能访问,所以报 403 错误
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论