Python实现文件下载的方法汇总与适用场景介绍
目录
- 1. 使用urllib.request(python标准库)
- 2. 使用requests库(最常用)
- 3. 使用wget库
- 4. 使用http.client(底层HTTP客户端)
- 5. 使用aiohttp(异步下载)
- 6. 使用pycurl(libcurl绑定)
- 7. 使用urllib3(requests底层库)
- 8. 使用socket原始下载(仅限高级用户)
- 9. 使用multiprocessing多进程下载
- 10. 使用scrapy(网页爬虫下载)
- 高级技巧:断点续传实现
- 方法对比与选择指南
- 安全注意事项
- 总结
在Python开发中,文件下载是常见需求。本文将全面介绍10种Python下载文件的方法,涵盖标准库、第三方库以及高级技巧,每种方法都配有完整代码示例和适用场景分析。
1. 使用urllib.request(Python标准库)
适用场景:简单下载需求,无需额外安装库
import urllib.request
url = "https://example.com/file.zip"
filename = "downloaded_file.zip"
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
print(f"文件已保存为: {filename}")
# 进阶:添加请求头
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0"}
req = urllib.request.Request(url, headers=headers)
with urllib.request.urlopen(req) as response:
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.read())
2. 使用requests库(最常用)
适用场景:需要更友好API和高级功能
import requests
url = "https://example.com/large_file.iso"
filename = "large_file.iso"
# 简单下载
response = requests.get(url)
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
# 流式下载大文件
with requests.get(url, stream=True) as r:
r.raise_for_status()
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=8192):
f.write(chunk)
3. 使用wget库
适用场景:模拟linux wget命令行为
import wget
url = "https://example.com/image.jpg"
filename = wget.download(url)
print(f"\n下载完成: {filename}")
# 指定保存路径
wget.download(url, out="/path/to/save/image.jpg")
4. 使用http.client(底层HTTP客户端)
适用场景:需要底层控制或学习HTTP协议
import http.client
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("example.com")
conn.request("GET", "/file.pdf")
response = conn.getresponse()
with open("document.pdf", 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.read())
conn.close()
5. 使用aiohttp(异步下载)
适用场景:高性能异步下载,I/O密集型任务
import aiohttp
import asyncio
async def download_file(url, filename):
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(url) as response:
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
while True:
chunk = await response.content.read(8192)
if not chunk:
break
f.write(chunk)
print(f"异步下载完成: {filename}")
urls = [
("https://example.com/file1.zip", "file1.zip"),
("https://example.com/file2.zip", "file2.zip")
]
async def main():
tasks = [download_file(url, name) for url, name in urls]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
asyncio.run(main())
6. 使用pycurl(libcurl绑定)
适用场景:需要C级别性能或复杂传输选项
import pycurl
from io import BytesIO
buffer = BytesIO()
c = pycurl.Curl()
c.setopt(c.URL, "https://example.com/data.json")
c.setopt(c.WRITEDATA, buffer)
c.perform()
c.close()
body = buffer.getvalue()
with open("data.json", 'wb') as f:
f.write(body)
7. 使用urllib3(requests底层库)
适用场景:需要比requests更底层的控制
import urllib3
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
url = "https://example.com/video.mp4"
response = http.request("GET", url, preload_content=False)
with open("video.mp4", 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.stream(1024):
f.write(chunk)
response.release_conn()
8. 使用socket原始下载(仅限高级用户)
适用场景:学习网络原理或特殊协议需求
import socket
def download_via_socket(url, port=80, filename="output.bin"):
# 解析URL(简化版,实际应使用urllib.parse)
host = url.split('/')[2]
path = '/' + '/'.join(url.split('/')[3:])
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((host, port))
request = f"GET {path} HTTP/1.1\r\nH编程客栈ost: {host}\r\n\r\n"
s.send(request.encode())
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
while True:
data = s.recv(1024)
if not data:
break
f.write(data)
s.close()
download_via_socket("http://example.com/file")
9. 使用multiprocessing多进程下载
适用场景:CPU密集型下载任务(如需要解压/加密)
import requests
from multiprocessing import Pool
def download(args):
url, filename = args
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.iter_content(8192):
f.write(chunk)
return filename
urls = [
("https://example.com/file1.zip", "file1.zip"),
("https://example.com/file2.zip", "file2.zip")
]
with Pool(4) as p: # 4个进程
results = p.map(download, urls)
print(f"下载完成: {results}")
10. 使用scrapy(网页爬虫下载)js
适用场景:需要从网页中批量下载资源
import scrapy
from scrapy.crawler import CrawlerProcess
class FileDownloadSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "filedownload"
start_urls = ["https://example.com/downloads"]
def parse(self, response):
for href in response.css('a.download-link::attr(href)').getall():
yield scrapy.Request(
response.urljoin(href),
callback=self.save_file
)
def save_file(self, response):
path = response.url.split('/')[-1]
with open(path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.body)
self.log(f"保存文件: {path}")
process = CrawlerProcess()
process.crawl(FileDownloadSpider)
process.start()
高级技巧:断点续传实现
import requests
import os
def download_with_resume(url, filename):
headers = {}
if os.path.exists(filename):
downloaded = os.path.getsize(filename)
headers = {'Range': f'bytes={downloaded}-'}
with requests.get(url, headers=headers, stream=True) as r:
mode = 'ab' i编程客栈f headers else 'wb'
with open(filename, mode) as f:
for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=8192):
f.write(chunk)
download_with_resume("https://example.com/large_file.iso", "large_file.iso")
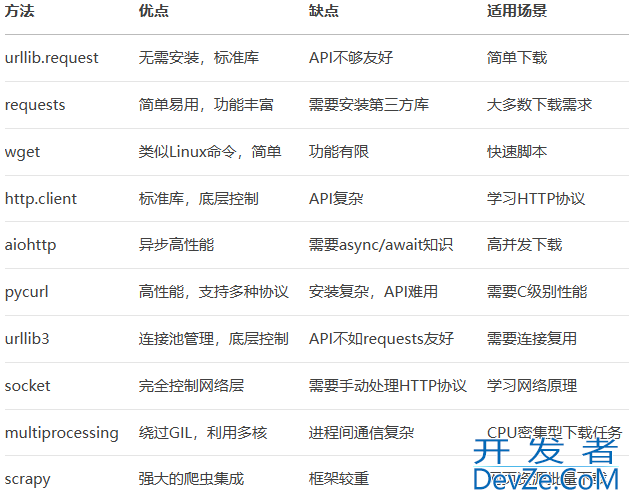
方法对比与选择指南
安全注意事项
验证HTTPS证书:
# requests示例(默认验证证书)
requests.get("https://example.com", verify=True)
限制下载大小防止DOS攻击:
max_size = 1024 * 1024 * 100 # 100MB
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
downloaded = 0
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.iter_content(8192):
downloaded += len(chunk)
if downloaded > max_size:
raise ValueError("文件超过最大限制")
f.write(chunk)
清理文件名防止路径遍历:
import re
def sanitize_filename(filename):
return re.sub(r'[\\/*?:"<>|]', "", filename)
总javascript结
本文介绍了Python下载文件的10种方法,从标准库到第三方库,从同步到异步,涵盖了各种应用场景。选择哪种方法取决于你的具体需求:
简单需求:urllib.request或requests
高性能需求:aiohttp或pycurl
特殊场景:multiprocessing或scrapy
到此这篇关于Python实现文件下载的方法汇总与适用场景介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python文件下载内容请搜索编程编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论