Java使用POI实现Excel文件的创建与处理
目录
- 1、背景
- 2、创建表格
- 2.1 定义表头对象
- 2.2 Excel生成器
- 2.3 创建模板
- 2.4 处理Excel表头
- 2.5 处理Excel内容单元格样式
- 2.6 处理单个表头
- 3、追加sheet
- 4、静态工具
- 5、单元测试
- 6、完整代码示例
1、背景
需求中有需要用户自定义Excel表格表头,然后生成Excel文件,使用EasyExcel更适合生成固定表头的Excel文档,所以此处采用POI原生方式进行开发。文档如下:
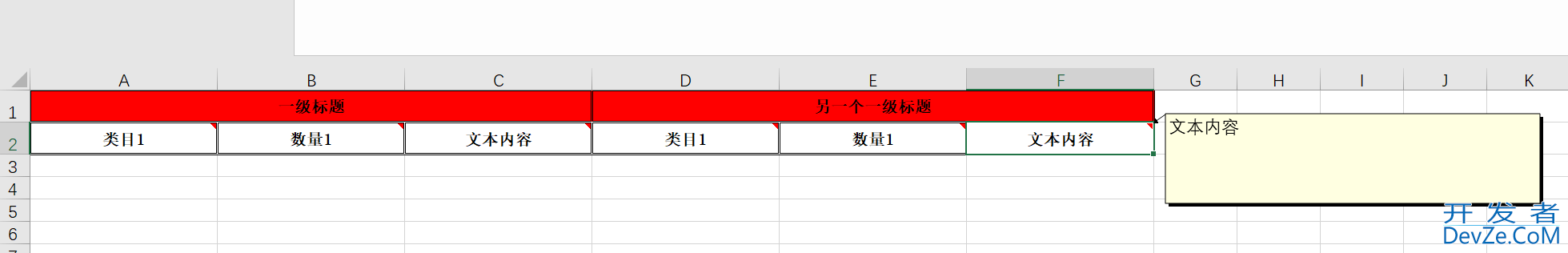
2、创建表格
主要的代码逻辑如下,非主要方法可以在完整代码中找到。
2.1 定义表头对象
根据需求,表头需要制定2级表头,我们先定义一个Excel表头对象。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ExcelModelDto {
/*** 名称 */
private String fieldName;
/*** 提示语 */
private String comment;
/*** 类型 */
private Integer type;
/*** 背景色 */
private short backgroundColor;
/*** 子标题 */
private List<Child> children;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class Child {
/*** 字段编码 */
private String fieldCode;
/*** 字段名称 */
private String fieldName;
/*** 提示语 */
private String comment;
/*** 类型 */
private Integer type;
/*** 下拉框选项 */
private String[] items;
}
}
2.2 Excel生成器
创建一个Excel文件生成对象,包含多个属性,其中包括:文件路径、文件名称、是否需要下拉框、文件后缀名、最大文本行数等。
@Slf4j
public class ExcelGenerator {
private final String localPath;
private final String sheetName;
php private final String fileName;
private final String file;
private final Boolean needItems;
private final List<ExcelModelDto> data;
/*** 字段编码集合,从data中解析 */
private final List<String> fieldCodeList;
public static final Integer FIRST_ROW = 2;
public static final Integer LAST_ROW = 65535;
public static final String FILE_SUFFIX = ".xlsx";
public static final String PATH_SUFFIX = "/";
public static final String ITEM_SHEET_NAME = "itemSheet";
public static final String END_FLAG = "*";
public static final Integer MAX_CONTENT_ROW_NUMBER = 1002;
/**
* 扩展字段sheet页行数记录key值
*/
public static final String EXTEND_PAGE_ROW_NUMBER_KEY = "extend";
public ExcelGenerator(String localPath, String fileName, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
this(localPath, fileName, sheetName, true, data);
}
public ExcelGenerator(String localPath, String fileName, String sheetName, Boolean needItems, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
this.localPath = localPath;
this.fileName = fileName;
this.sheetName = sheetName;
this.file = localPath + fileName;
this.needItems = needItems;
this.data = data;
fieldCodeList = this.parseField(data);
}
}
2.3 创建模板
/**
* 生成模板
*
* @throws IOException 异常
*/
public void createTemplate() throws IOException {
this.doCreateSheet(Paths.get(file), sheetName, data);
}
/**
* 向Excel文件新增一个新的工作表,并处理表头。
*
* @param pathForFile 新工作表将要保存的文件路径。
* @throws IOException 如果读写文件时发生异常。
*/
private void doCreateSheet(Path pathForFile, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data)
throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = this.getSheetByName(workbook, sheetName, false);
// 处理Excel表头
this.dealExcelHeadingCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 处理Excel内容单元格,默认都是有二级标题
this.dealExcelContentCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 将inputStream转换为outputStream,并重新写入文件
try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(pathForFile)) {
workbook.write(outputStream);
} finally {
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("创建Excel模板文件共耗时:{}秒。", (endTime - startTime) / 1000);
}
}
2.4 处理Excel表头
/**
* 处理 Excel 表头数据,包括第一行和第二行的标题单元格样式设置、数据填充和合并单元格。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param sheet 主表的工作表对象
* @param data 表头数据
*/
private void dealExcelHeadingCell(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
// 创建第一行和第二行表头数据,并设置行高
Row row1 = this.getRow(sheet, 0);
Row row2 = this.getRow(sheet, 1);
row1.setHeightInPoints(20);
row2.setHeightInPoints(20);
// 已经存在的列号
int lastCellNum = this.getLastCellNum(sheet, 1);
int currentCellNum = lastCellNum;
int startCellNum = lastCellNum;
int endCellNum;
for (ExcelModelDto excelModelDto : data) {
// 一级标题名称
String firstTitleName = excelModelDto.getFieldName();
// 一级标题单元格样式
CellStyle firstTitleCellStyle = this.buildFirstTitleCellStyle(workbook, excelModelDto);
// 二级标题的单元格样式
CellStyle secondTitleCellStyle = this.getCellStyle(workbook, IndexedColors.WHITE.getIndex());
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = excelModelDto.getChildren();
if (children == null || children.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
for (ExcelModelDto.Child child : children) {
// 处理表头单元格
this.dealTitleCell(workbook, sheet, child, firstTitleName, firstTitleCellStyle, secondTitleCellStyle, currentCellNum);
// 处理完后列号加一
currentCellNum++;
}
endCellNum = currentCellNum - 1;
// POI 版本升级后,合并单元格需要大于一个单元格
if (startCellNum != endCellNum) {
CellRangeAddress region = new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, startCellNum, endCellNum);
sheet.addMergedRegion(region);
}
startCellNum = endCellNum + 1;
}
}
2.5 处理Excel内容单元格样式
/**
* 格式化内容单元格。
*
* @param sheet 工作表对象。
* @param workbook 工作簿对象。
*/
private void dealExcelContentCell(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
// 获取统一的单元格样式,不用每个单元格获取一个对象,防止对象过多
CellStyle childCellStyle = this.getContentCellStyle(workbook);
// 只格式化内容单元格,且有上限
int maxContentRowNumber = MAX_CONTENT_ROW_NUMBER;
// 跳过表头,从文本行开始
for (int rowNumber = 2; rowNumber < maxContentRowNumber; rowNumber++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
// 列号从0开始
int cellNumber = 0;
for (ExcelModelDto excelModelDto : data) {
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = excelModelDto.getChildren();
for (ExcelModelDto.Child child : children) {
String[] items = child.getItems();
if (Objects.isNull(items) || items.length == 0) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellStyle(childCellStyle);
}
// 每处理完一个单元格,列号加1
cellNumber++;
}
}
}
}
2.6 处理单个表头
在处理表头过程中,如果items 不为空,则说明此列需要下拉框,数组为供用户选择的下拉内容,防止下拉框内容过大,所以将下拉内容单独生成到一个隐藏的sheet页中,并且使用表达式来表达下拉框内容,设定到单元格中。
/**
* 处理Excel表格的标题单元格。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param sheet 工作表对象
* @param child ExcelModelDto.Child 对象,包含字段名、注释和下拉框选项等信息
* @param firstTitleName 一级标题名称
* @param firstTitleCellStyle 一级标题单元格样式
* @param secondTitleCellStyle 二级标题单元格样式
* @param index 当前处理的列索引
*/
private void dealTitleCell(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet,
ExcelModelDto.Child child, String firstTitleName,
CellStyle firstTitleCellStyle, CellStyle secondTitleCellStyle,
int index) {
Row row1 = this.getRow(sheet, 0);
Row row2 = this.getRow(sheet, 1);
String secondFieldName = child.getFieldName();
String comment = child.getComment();
String[] items = child.getItems();
// 一级表头
Cell cell1 = row1.createCell(index);
cell1.setCellValue(firstTitleName);
cell1.setCellStyle(firstTitleCellStyle);
// 二级表头,标题如果以* 号结尾,则* 置为红色
Cell cell2 = row2.createCell(index);
RichTextString textString = this.parseCellValue(workbook, Font.COLOR_NORMAL, true, secondFieldName);
cell2.setCellValue(textString);
cell2.setCellStyle(secondTitleCellStyle);
// 设置下拉框
if (items != null && items.length > 0 && needItems) {
this.appendItems(workbook, sheet, secondTitleCellStyle, secondFieldName, items, index);
}
// 设置表头备注
if (!org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils.isEmpty(comment)) {
this.setComment(sheet, cell2, comment);
}
// 根据字段长度自动调整列的宽度
sheet.setColumnWidth(index, 100 * 50);
}
/**
* 在指定的工作簿和工作表中追加枚举类型的项,并设置公式引用。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param sheet 工作表对象
* @param childCellStyle 子单元格样式
* @param secondTitleName 第二级标题名称
* @param items 枚举类型的项数组
* @param index 当前项在总体中的索引位置
*/
private void appendItems(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet, CellStyle childCellStyle, String secondTitleName, String[] items, int index) {
// 如果有序列单元格,则创建一个sheet页,来保存所有的枚举类型,同时隐藏该sheet页
Sheet itemsSheet = this.getSheetByName(workbook, ITEM_SHEET_NAME, true);
// 追加sheet的时候,需要看隐藏sheet的列已经到哪一列了,避免追加时将原有隐藏列覆盖掉
int existItemCell = this.getLastCellNum(itemsSheet, 0);
// 将枚举数组写入到独立的sheet页中,同时设置表头格式
String formula = this.writeItems(itemsSheet, childCellStyle, secondTitleName, existItemCell, items);
// 设置公式到模板的sheet页中,格式化后的最终公式为
// =itemSheet!$B$1:$B$88
// 表明该单元格引用的是 itemSheet sheet页中 B1~B88的数据
formula = String.format("=%s!%s", ITEM_SHEET_NAME, formula);
this.setItems(sheet, formula, FIRST_ROW, LAST_ROW, index, index);
}
3、追加sheet
有些需要在已有的Excel文档中追加新的sheet表格内容,效果如下:

/**
* 在指定的 Excel 文件中添加一个新的工作表,并填充数据。
*
* @param sheetName 新工作表的名称
* @param data 要填充的数据列表
* @throws IOException 如果在操作文件时发生了 I/O 错误
*/
public void appendSheet(String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data) throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 路径不存在则创建,保证路径是存在的
Path pathForLocalPath = Paths.get(localPath);
boolean existPath = Files.exists(pathForLocalPath);
if (!existPath) {
Files.createDirectories(pathForLocalPath);
}
// 如果文件不存在,则走创建sheet逻辑
Path pathForFile = Paths.get(file);
if (!Files.exists(pathForFile)) {
this.doCreateSheet(pathForFile, sheetName, data);
return;
}
// 如果文件存在则走追加sheet逻辑
try (InputStream inputStream = Files.newInputStream(pathForFile)) {
this.doAppendSheet(inputStream, pathForFile, sheetName, data);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("追加Excel模板文件共耗时:{}秒。", (endTime - startTime) / 1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("追加Excel模板文件失败!", e);
throw new BizException(e);
}
}
/**
* 向Excel文件追加一个新的工作表,并处理表头。
*
* @param inputStream Excel文件的输入流。
* @param pathForFile 新工作表将要保存的文件路径。
* @throws IOException 如果读写文件时发生异常。
*/
private void doAppendSheet(InputStream inputStream, Path pathForFile, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data)
throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
Sheet sheet = this.getSheetByName(workbook, sheetName, false);
// 处理Excel表头
this.dealExcelHeadingCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 处理Excel内容单元格,默认都是有二级标题
this.dealExcelContentCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 将inputStream转换为outputStream,并重新写入文件
try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(pathForFile)) {
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
workbook.write(outputStream);
}
}
4、静态工具
每次使用都需要new一个对象来创建Excel文件,所以创建一个静态工具类,来通过静态方法实现文档的创建与追加。
public class ExcelGeneratorExecutors {
/**
* 创建 Excel 模板文件。
*
* @param localPath 本地路径
* @param fileName 文件名
* @param sheetName 工作表名称
* @param data 数据列表
* @throws IOException 如果创建模板文件失败
*/
public static void createTemplate(String localPath, String fileName, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data) throws IOException {
ExcelGenerator excelGenerator = new ExcelGenerator(localPath, fileName, sheetName, data);
excelGenerator.createTemplate();
}
/**
* 在指定路径的Excel文件中追加一个新的工作表,并填充数据。
*
* @param localPath Excel文件的本地路径。
* @param fileName Excel文件的名称。
* @param sheetName 新增工作表的名称。
* @param data 填充到新增工作表的数据。
* @throws IOException 如果在追加工作表或填充数据时发生I/O错误。
*/
public static void appendSheet(String localPath, String fileName, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data) throws IOException {
ExcelGenerator excelGenerator = new ExcelGenerator(localPath, fileName, sheetName, data);
excelGenerator.appendSheet(sheetName, data);
}
}
5、单元测试
@Test
public void testGenerate() {
String localPath = "D:\\mytmp\\template\\";
String dateTime = DateUtils.format(new Date(), DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_COMMENT_2);
String fileName = String.format("生成模板-%s.xlsx", dateTime);
String sheetName = "测试";
List<ExcelModelDto> data = this.buildExcelModelDtoList();
ExcelGenerator excelGenerator = new ExcelGenerator(localPath, fileName, sheetName, data);
try {
excelGenerator.createTemplate();
List<ExcelModelDto> data2 = this.buildExcelModelDtoList2();
excelGenerator.appendSheet("自定义sheet", data);
excelGenerator.appendSheet("自定义sheet2", data2);
excelGenerator.appendSheet("自定义sheet3", data2);
log.info("模板文件生成,名称为:{}", fileName);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void testGenerate2() {
String localPath = "D:\\mytmp\\template\\";
String dateTime = DateUtils.format(new Date(), DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_COMMENT_2);
String fileName = String.format("生成模板-%s.xlsx", dateTime);
String sheetName = "测试";
List<ExcelModelDto> data = this.buildExcelModelDtoList();
try {
ExcelGeneratorExecutors.createTemplate(localPath, fileName, sheetName, data);
ExcelGeneratorExecutors.appendSheet(localPath, fileName, sheetName, data);
ExcelGeneratorExecutors.appendSheet(localPath, fileName, "自定义sheet3", data);
log.info("模板文件生成,名称为:{}", fileName);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public List<ExcelModelDto> buildExcelModelDtoList() {
List<ExcelModelDto> data = new ArrayList<>();
ExcelModelDto excelModelDto = new ExcelModelDto();
excelModelDto.setFieldName("电器");
excelModelDto.setComment("song");
excelModelDto.setType(2);
excelModelDto.setBackgroundColor((short) 2);
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = new ArrayList<>();
ExcelModelDto.Child child1 = new ExcelModelDto.Child();
child1.setComment("类目1");
child1.setFieldCode("category");
child1.setFieldName("类目1");
List<String> list1 = Lists.newArrayList("冰箱", "洗衣机", "空调");
child1.setItems(list1.toArray(new String[0]));
ExcelModelDto.Child child2 = new ExcelModelDto.Child();
child2.setComment("数量1");
child2.setFieldCode("qty");
child2.setFieldName("数量1");
List<String> list2 = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "3");
child2.setItems(list2.toArray(new String[0]));
ExcelModelDto.Child child3 = new ExcelModelDto.Child();
child3.setComment("文本内容");
child3.setFieldCode("textValue");
child3.setFieldName("文本内容");
children.add(child1);
children.add(child2);
children.add(child3);
excelModelDto.setChildren(children);
data.add(excelModelDto);
return data;
}
public List<ExcelModelDto> buildExcelModelDtoList2() {
List<ExcelModelDto> data = new ArrayList<>();
ExcelModelDto excelModelDto0 = new ExcelModelDto();
excelModelDto0.setFieldName("商家运单号");
excelModelDto0.setComment("商家运单号");
excelModelDto0.setType((int) IndexedColors.TURQUOISE1.getIndex());
excelModelDto0.setBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.TURQUOISE1.getIndex());
ExcelModelDto.Child child0 = new ExcelModelDto.Child();
child0.setComment("关联第一个sheet页的商家运单号");
child0.setFieldCode("orderNo");
child0.setFieldName("商家运单号*");
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children0 = new ArrayList<>();
children0.add(child0);
excelModelDto0.setChildren(children0);
ExcelModelDto excelModelDto = new ExcelModelDto();
excelModelDto.setFieldName("购买电器");
excelModelDto.setComment("song");
excelModelDto.setType((int) IndexedColors.TURQUOISE1.getIndex());
excelModelDto.setBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.TURQUOISE1.getIndex());
ExcelModelDto.Child child1 = new ExcelModelDto.Child();
child1.setComment("类目");
child1.setFieldCode("category");
child1.setFieldName("类目");
List<String> list1 = Lists.newArrayList("冰箱", "洗衣机", "空调");
child1.setItems(list1.toArray(new String[0]));
ExcelModelDto.Child child2 = new ExcelModelDto.Child();
child2.setComment("数量");
child2.setFieldCode("qty");
child2.setFieldName("数量");
//List<String> list2 = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "3");
//child2.setItems(list2.toArray(new String[0]));
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = new ArrayList<>();
children.add(child1);
children.add(child2);
excelModelDto.setChildren(children);
data.add(excelModelDto0);
data.add(excelModelDto);
return data;
}
6、完整代码示例
@Slf4j
public class ExcelGenerator {
private final String localPath;
private final String sheetName;
private final String fileName;
private final String file;
private final Boolean needItems;
private final List<ExcelModelDto> data;
/*** 字段编码集合,从data中解析 */
private final List<String> fieldCodeList;
public static final Integer FIRST_ROW = 2;
public static final Integer LAST_ROW = 65535;
public static final String FILE_SUFFIX = ".xlsx";
public static final String PATH_SUFFIX = "/";
public static final String ITEM_SHEET_NAME = "itemSheet";
public static final String END_FLAG = "*";
public static final Integer MAX_CONTENT_ROW_NUMBER = 1002;
/**
* 扩展字段sheet页行数记录key值
*/
public static final String EXTEND_PAGE_ROW_NUMBER_KEY = "extend";
public ExcelGenerator(String localPath, String fileName, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
this(localPath, fileName, sheetName, true, data);
}
public ExcelGenerator(String localPath, String fileName, String sheetName, Boolean needItems, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
this.localPath = localPath;
this.fileName = fileName;
this.sheetName = sheetName;
this.file = localPath + fileName;
this.needItems = needItems;
this.data = data;
fieldCodeList = this.parseField(data);
}
/**
* 创建对象时,将ExcelModel中的字段按顺序排好,保存到List中
*
* @param data 入参
* @return 返回值
*/
public List<String> parseField(List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
List<String> fieldCodeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (ExcelModelDto modelDto : data) {
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = modelDto.getChildren();
for (ExcelModelDto.Child child : children) {
String fieldCode = child.getFieldCode();
fieldCodeList.add(fieldCode);
}
}
return fieldCodeList;
}
/**
* 生成模板
*
* @throws IOException 异常
*/
public void createTemplate() throws IOException {
this.doCreateSheet(Paths.get(file), sheetName, data);
}
/**
* 在指定的 Excel 文件中添加一个新的工作表,并填充数据。
*
* @param sheetName 新工作表的名称
* @param data 要填充的数据列表
* @throws IOException 如果在操作文件时发生了 I/O 错误
*/
public void appendSheet(String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data) throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 路径不存在则创建,保证路径是存在的
Path pathForLocalPath = Paths.get(localPath);
boolean existPath = Files.exists(pathForLocalPath);
if (!existPath) {
Files.createDirectories(pathForLocalPath);
}
php // 如果文件不存在,则走创建sheet逻辑
Path pathForFile = Paths.get(file);
if (!Files.exists(pathForFile)) {
this.doCreateSheet(pathForFile, sheetName, data);
return;
}
// 如果文件存在则走追加sheet逻辑
try (InputStream inputStream = Files.newInputStream(pathForFile)) {
this.doAppendSheet(inputStream, pathForFile, sheetName, data);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("追加Excel模板文件共耗时:{}秒。", (endTime - startTime) / 1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("追加Excel模板文件失败!", e);
throw new BizException(e);
}
}
/**
* 向Excel文件新增一个新的工作表,并处理表头。
*
* @param pathForFile 新工作表将要保存的文件路径。
* @throws IOException 如果读写文件时发生异常。
*/
private void doCreateSheet(Path pathForFile, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data)
throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = this.getSheetByName(workbook, sheetName, false);
// 处理Excel表头
this.dealExcelHeadingCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 处理Excel内容单元格,默认都是有二级标题
this.dealExcelContentCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 将inputStream转换为outputStream,并重新写入文件
try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(pathForFile)) {
workbook.write(outputStream);
} finally {
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("创建Excel模板文件共耗时:{}秒。", (endTime - startTime) / 1000);
}
}
/**
* 向Excel文件追加一个新的工作表,并处理表头。
*
* @param inputStream Excel文件的输入流。
* @param pathForFile 新工作表将要保存的文件路径。
* @throws IOException 如果读写文件时发生异常。
*/
private void doAppendSheet(InputStream inputStream, Path pathForFile, String sheetName, List<ExcelModelDto> data)
throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
Sheet sheet = this.getSheetByName(workbook, sheetName, false);
// 处理Excel表头
this.dealExcelHeadingCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 处理Excel内容单元格,默认都是有二级标题
this.dealExcelContentCell(workbook, sheet, data);
// 将inputStream转换为outputStream,并重新写入文件
try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(pathForFile)) {
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
workbook.write(outputStream);
}
}
/**
* 处理 Excel 表头数据,包括第一行和第二行的标题单元格样式设置、数据填充和合并单元格。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param sheet 主表的工作表对象
* @param data 表头数据
*/
private void dealExcelHeadingCell(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
// 创建第一行和第二行表头数据,并设置行高
Row row1 = this.getRow(sheet, 0);
Row row2 = this.getRow(sheet, 1);
row1.setHeightInPoints(20);
row2.setHeightInPoints(20);
// 已经存在的列号
int lastCellNum = this.getLastCellNum(sheet, 1);
int currentCellNum = lastCellNum;
int startCellNum = lastCellNum;
int endCellNum;
for (ExcelModelDto excelModelDto : data) {
// 一级标题名称
String firstTitleName = excelModelDto.getFieldName();
// 一级标题单元格样式
CellStyle firstTitleCellStyle = this.buildFirstTitleCellStyle(workbook, excelModelDto);
// 二级标题的单元格样式
CellStyle secondTitleCellStyle = this.getCellStyle(workbook, IndexedColors.WHITE.getIndex());
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = excelModelDto.getChildren();
if (children == null || children.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
for (ExcelModelDto.Child child : children) {
// 处理表头单元格
this.dealTitleCell(workbook, sheet, child, firstTitleName, firstTitleCellStyle, secondTitleCellStyle, currentCellNum);
// 处理完后列号加一
currentCellNum++;
}
endCellNum = currentCellNum - 1;
// POI 版本升级后,合并单元格需要大于一个单元格
if (startCellNum != endCellNum) {
CellRangeAddress region = new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, startCellNum, endCellNum);
sheet.addMergedRegion(region);
}
startCellNum = endCellNum + 1;
}
}
/**
* 格式化内容单元格。
*
* @param sheet 工作表对象。
* @param workbook 工作簿对象。
*/
private void dealExcelContentCell(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet, List<ExcelModelDto> data) {
// 获取统一的单元格样式,不用每个单元格获取一个对象,防止对象过多
CellStyle childCellStyle = this.getContentCellStyle(workbook);
// 只格式化内容单元格,且有上限
int maxContentRowNumber = MAX_CONTENT_ROW_NUMBER;
// 跳过表头,从文本行开始
for (int rowNumber = 2; rowNumber < maxContentRowNumber; rowNumber++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
// 列号从0开始
int cellNumber = 0;
for (ExcelModelDto excelModelDto : data) {
List<ExcelModelDto.Child> children = excelModelDto.getChildren();
for (ExcelModelDto.Child child : children) {
String[] items = child.getItems();
if (Objects.isNull(items) || items.length == 0) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellStyle(childCellStyle);
}
// 每处理完一个单元格,列号加1
cellNumber++;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 处理Excel表格的标题单元格。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param sheet 工作表对象
* @param child ExcelModelDto.Child 对象,包含字段名、注释和下拉框选项等信息
* @param firstTitleName 一级标题名称
* @param firstTitleCellStyle 一级标题单元格样式
* @param secondTitleCellStyle 二级标题单元格样式
* @param index 当前处理的列索引
*/
private void dealTitleCell(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet,
ExcelModelDto.Child child, String firstTitleName,
CellStyle firstTitleCellStyle, CellStyle secondTitleCellStyle,
int index) {
Row row1 = this.getRow(sheet, 0);
Row row2 = this.getRow(sheet, 1);
String secondFieldName = child.getFieldName();
String comment = child.getComment();
String[] items = child.getItems();
// 一级表头
Cell cell1 = row1.createCell(index);
cell1.setCellValue(firstTitleName);
cell1.setCellStyle(firstTitleCellStyle);
// 二级表头,标题如果以* 号结尾,则* 置为红色
Cell cell2 = row2.createCell(index);
RichTextString textString = this.parseCellValue(workbook, Font.COLOR_NORMAL, true, secondFieldName);
cell2.setCellValue(textString);
cell2.setCellStyle(secondTitleCellStyle);
// 设置下拉框
if (items != null && items.length > 0 && needItems) {
this.appendItems(workbook, sheet, secondTitleCellStyle, secondFieldName, items, index);
}
// 设置表头备注
if (!org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils.isEmpty(comment)) {
this.setComment(sheet, cell2, comment);
}
// 根据字段长度自动调整列的宽度
sheet.setColumnWidth(index, 100 * 50);
}
/**
* 设置单元格下拉框
* 下拉框引用单独一个sheet页中的数据
*
* @param sheet sheet
* @param formula 公式
* @param firstRow 起始行
* @param lastRow 结束行
* @param firstCol 起始列
* @param lastCol 结束列
*/
public void setItems(Sheet sheet, String formula, int firstRow, int lastRow, int firstCol, int lastCol) {
CellRangeAddressList addressList = new CellRangeAddressList(firstRow, lastRow, firstCol, lastCol);
DataValidationHelper helper = sheet.getDataValidationHelper();
DataValidationConstraint constraint = helper.createFormulaListConstraint(formula);
DataValidation validation = helper.createValidation(constraint, addressList);
validation.setShowErrorBox(true);
sheet.addValidationData(validation);
}
/**
* 设置单元格备注信息
*
* @param sheet sheet
* @param cell 单元格
* @param textString 提示信息
*/
public void setComment(Sheet sheet, Cell cell, String textString) {
Drawing<?> drawing = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
CreationHelper factory = sheet.getWorkbook().getCreationHelper();
// 设置提示框大小,默认根据 提示信息的大小来确认提示框高度
/// ClientAnchor anchor = factory.createClientAnchor();
textString = StringUtils.defaultIfBlank(textString, "");
int length = textString.length();
int row2 = length / 25 + 6;
// (int dx1, int dy1, int dx2, int dy2, short col1, int row1, short col2, int row2)
// 前四个参数是坐标点,后四个参数是编辑和显示批注时的大小.
ClientAnchor anchor = new XSSFClientAnchor(0, 0, 0, 0, (short) 4, 2, (short) 6, row2);
Comment comment = drawing.createCellComment(anchor);
RichTextString str = factory.createRichTextString(textString);
comment.setString(str);
comment.setAuthor("Auto+");
// 以上参数不设置时会有默认值,当一个被重复设置批注时会报错
// Multiple cell comments in one cell are not allowed
// 故在设置批注前检查锚点位置有无批注,有的话移除
if (cell.getCellComment() != null) {
cell.removeCellComment();
}
cell.setCellComment(comment);
}
/**
* 获取单元格样式对象
*
* @param workbook 工作簿
* @param backGroundColor 背景色
* @return 返回样式对象
*/
public CellStyle getCellStyle(Workbook workbook, short backGroundColor) {
CellStyle cellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
CreationHelper createHelper = workbook.getCreationHelper();
cellStyle.setDataFormat(createHelper.createDataFormat().getFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
// IndexedColors.YELLOW.getIndex()
cellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(backGroundColor);
cellStyle.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
// 水平居中
cellStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
// 垂直居中
cellStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
// 设置边框及颜色
cellStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.DOUBLE);
cellStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.DOUBLE);
cellStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.DOUBLE);
cellStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.DOUBLE);
cellStyle.setTopBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
cellStyle.setBottomBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
cellStyle.setLeftBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
cellStyle.setRightBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
return cellStyle;
}
/**
* 向sheet中写入 序列内容
*
* @param sheet sheet
* @param cellStyle 单元格格式,表头格式
* @param itemsType 序列类型
*编程 @param col 列号
* @param items 序列数组
* @return 返回坐标
*/
protected String writeItems(Sheet sheet, CellStyle cellStyle, String itemsType, 编程int col, String[] items) {
// 第一行为表头数据
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
if (row == null) {
row = sheet.createRow(0);
}
Cell cell = row.createCell(col);
// 获取单元格列所对应的字母,即 0=A,1=B ...
String columnLetter = CellReference.convertNumToColString(col);
cell.setCellValue(itemsType);
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
int length = items.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Row itemRow = sheet.getRow(i + 1);
if (itemRow == null) {
itemRow = sheet.createRow(i + 1);
}
Cell itemRowCell = itemRow.createCell(col);
itemRowCell.setCellValue(items[i]);
}
// 格式化后的公式坐标为 $B$1:$B$88
return String.format("$%s$%s:$%s$%s", columnLetter, 2, columnLetter, items.length + 1);
}
/**
* 格式化单元格字体样式
*
* @param workbook 工作簿
* @param fontColor 字体颜色
* @param isBold 是否加粗http://www.devze.com
* @param value 单元格值
*/
public RichTextString parseCellValue(Workbook workbook, short fontColor, boolean isBold, String value) {
value = StringUtils.defaultIfBlank(value, "");
XSSFRichTextString textString = new XSSFRichTextString(value);
Font font1 = getFontStyle(workbook, fontColor, isBold);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(value)) {
int length = value.length();
// 如果内容是以 * 号结尾的,则将 * 号置为红色,默认黑色
if (value.endsWith(END_FLAG)) {
int point = length - 1;
textString.applyFont(0, point, font1);
Font font2 = getFontStyle(workbook, Font.COLOR_RED, isBold);
textString.applyFont(point, length, font2);
} else {
textString.applyFont(0, length, font1);
}
}
return textString;
}
/**
* 获取字体样式
*
* @param workbook 工作簿
* @param fontColor 字体颜色
* @param isBold 是否加粗
* @return 返回值
*/
public Font getFontStyle(Workbook workbook, short fontColor, boolean isBold) {
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setColor(fontColor);
if (isBold) {
font.setBold(true);
}
font.setFontName("宋体");
// 字体大小
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 10);
return font;
}
/**
* 获取指定行在给定工作表中的最后一个单元格的索引。
*
* @param sheet 工作表对象
* @param rowNum 行号(从0开始计数)
* @return 最后一个单元格的索引,若行不存在则返回0
*/
private int getLastCellNum(Sheet sheet, int rowNum) {
int existCell = 0;
// 指定sheet页不为空,则获取已经有多少列
Row row = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if (Objects.nonNull(row)) {
existCell = row.getLastCellNum();
// 如果不存在返回的是-1,业务上从0开始计算
if (existCell < 0) {
existCell = 0;
}
}
return existCell;
}
/**
* 获取或创建指定名称的工作表并将其隐藏。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @return 指定名称的工作表对象
*/
private Sheet getSheetByName(Workbook workbook, String sheetName, boolean hide) {
Sheet itemsSheet = workbook.getSheet(sheetName);
// 指定sheet页为空则创建
if (Objects.isNull(itemsSheet)) {
itemsSheet = workbook.createSheet(sheetName);
int sheetIndex = workbook.getSheetIndex(sheetName);
workbook.setSheetHidden(sheetIndex, hide);
}
return itemsSheet;
}
/**
* 根据行号获取或创建指定Sheet中的Row对象。
*
* @param sheet 要操作的Sheet对象。
* @param rowNum 需要获取或创建的行号。
* @return 指定行号的Row对象。
*/
private Row getRow(Sheet sheet, int rowNum) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if (Objects.isNull(row)) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
}
return row;
}
/**
* 构建第一行标题单元格样式。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象。
* @param excelModelDto Excel模型数据传输对象。
* @return 第一行标题单元格样式。
*/
private CellStyle buildFirstTitleCellStyle(Workbook workbook, ExcelModelDto excelModelDto) {
// 根据字段类型来获取背景色
short backGroundColor = excelModelDto.getBackgroundColor();
CellStyle cellStyle = this.getCellStyle(workbook, backGroundColor);
Font font = this.getFontStyle(workbook, Font.COLOR_NORMAL, true);
cellStyle.setFont(font);
return cellStyle;
}
/**
* 在指定的工作簿和工作表中追加枚举类型的项,并设置公式引用。
*
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @param sheet 工作表对象
* @param childCellStyle 子单元格样式
* @param secondTitleName 第二级标题名称
* @param items 枚举类型的项数组
* @param index 当前项在总体中的索引位置
*/
private void appendItems(Workbook workbook, Sheet sheet, CellStyle childCellStyle, String secondTitleName, String[] items, int index) {
// 如果有序列单元格,则创建一个sheet页,来保存所有的枚举类型,同时隐藏该sheet页
Sheet itemsSheet = this.getSheetByName(workbook, ITEM_SHEET_NAME, true);
// 追加sheet的时候,需要看隐藏sheet的列已经到哪一列了,避免追加时将原有隐藏列覆盖掉
int existItemCell = this.getLastCellNum(itemsSheet, 0);
// 将枚举数组写入到独立的sheet页中,同时设置表头格式
String formula = this.writeItems(itemsSheet, childCellStyle, secondTitleName, existItemCell, items);
// 设置公式到模板的sheet页中,格式化后的最终公式为
// =itemSheet!$B$1:$B$88
// 表明该单元格引用的是 itemSheet sheet页中 B1~B88的数据
formula = String.format("=%s!%s", ITEM_SHEET_NAME, formula);
this.setItems(sheet, formula, FIRST_ROW, LAST_ROW, index, index);
}
/**
* 获取单元格样式对象
*
* @param workbook 工作簿
* @return 返回样式对象
*/
public CellStyle getContentCellStyle(Workbook workbook) {
CellStyle cellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
CreationHelper createHelper = workbook.getCreationHelper();
cellStyle.setDataFormat(createHelper.createDataFormat().getFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
// 背景色为纯色
cellStyle.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.NO_FILL);
// 设置单元格格式为文本格式
DataFormat format = workbook.createDataFormat();
cellStyle.setDataFormat(format.getFormat("@"));
return cellStyle;
}
}
到此这篇关于Java使用POI实现Excel文件的创建与处理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java POI创建Excel内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论