使用Python打造一个强大的文件分析工具
目录
- 完整代码
- 工具功能概览
- 技术栈
- 代码结构分析
- 1. 图形界面设计
- 2. 文件分析逻辑
- 3. 命令执行功能
- 4. 辅助功能
- 使用方法
- 示例输出
- 运行结果
在日常工作中,我们经常需要分析文件夹中的文件分布情况,例如文件类型、文件大小分布以及文件的修改时间等。手动统计这些信息费时费力,因此开发一个自动化工具可以大大提高效率。本文将介绍一个基于 python 和 wxPython 开发的图形化文件分析工具,能够快速分析文件夹并生成详细的统计报告。
完整代码
import wx
import os
import csv
import datetime
import subprocess
import sys
from collections import defaultdict
import uuid
class FileAnalyzerFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(None, title="使用Python打造一个强大的文件分析工具", size=(800, 600))
# Create main panel
self.panel = wx.Panel(self)
main_sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
# Folder selection section
folder_sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)
self.folder_text = wx.TextCtrl(self.panel, size=(400, -1))
browse_button = wx.Button(self.panel, label="Browse...")
analyze_button = wx.Button(self.panel, label="Analyze")
folder_sizer.Add(wx.StaticText(self.panel, label="Folder: "), 0, wx.ALIGN_CENTER_VERTICAL, 5)
folder_sizer.Add(self.folder_text, 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
folder_sizer.Add(browse_button, 0, wx.ALL, 5)
folder_sizer.Add(analyze_button, 0, wx.ALL, 5)
# Output file section
output_sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)
self.output_text = wx.TextCtrl(self.panel, size=(400, -1))
self.output_text.SetValue("analysis_results")
output_sizer.Add(wx.StaticText(self.panel, label="Output Base Name: "), 0, wx.ALIGN_CENTER_VERTICAL, 5)
output_sizer.Add(self.output_text, 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
# Analysis results
results_label = wx.StaticText(self.panel, label="Analysis Results:")
self.results_text = wx.TextCtrl(self.panel, style=wx.TE_MULTILINE | wx.TE_READONLY, size=(-1, 200))
# Command execution section
cmd_label = wx.StaticText(self.panel, label="Command Editor:")
self.cmd_text = wx.TextCtrl(self.panel, size=(-1, 100), style=wx.TE_MULTILINE)
execute_button = wx.Button(self.panel, label="Execute Command")
# Command output
cmd_output_label = wx.StaticText(self.panel, label="Command Output:")
self.cmd_output = wx.TextCtrl(self.panel, style=wx.TE_MULTILINE | wx.TE_READONLY, size=(-1, 100))
# Add components to main sizer
main_sizer.Add(folder_sizer, 0, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(output_sizer, 0, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(results_label, 0, wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(self.results_text, 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(cmd_label, 0, wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(self.cmd_text, 0, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(execute_button, 0, wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(cmd_output_label, 0, wx.ALL, 5)
main_sizer.Add(self.cmd_output, 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 5)
python
self.panel.SetSizer(main_sizer)
# Bind events
browse_button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.on_browse)
analyze_button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.on_analyze)
execute_button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.on_execute_command)
# Set default properties
self.folder_path = ""
# Show window
self.Centre()
self.Show()
def on_browse(self, event):
"""Open folder browser dialog"""
dialog = wx.DirDialog(self, "Choose a directory:", style=wx.DD_DEFAULT_STYLE)
if dialog.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
self.folder_path = dialog.GetPath()
self.folder_text.SetValue(self.folder_path)
dialog.Destroy()
def on_analyze(self, event):
"""Analyze the selected folder and generate three CSV files"""
folder_path = self.folder_编程客栈text.GetValue()
output_base = self.output_text.GetValue()
if not folder_path or not os.path.isdir(folder_path):
wx.MessageBox("Please select a valid folder.", "Error", wx.OK | wx.ICON_ERROR)
return
# Generate output file paths
file_types_path = f"{output_base}_file_types.csv"
size_dist_path = f"{output_base}_size_distribution.csv"
month_stats_path = f"{output_base}_year_month.csv"
try:
# Initialize statistics dictionaries
file_type_stats = defaultdict(int)
file_size_stats = {
"0-10KB": 0,
"10KB-100KB": 0,
"100KB-1MB": 0,
"1MB-10MB": 0,
"10MB-100MB": 0,
"100MB+": 0
}
file_month_stats = defaultdict(int)
total_count = 0
total_size = 0
# Create result message
result_msg = f"Analyzing folder: {folder_path}\n\n"
# Walk through the directory
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(folder_path):
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
try:
# Get file extension
_, extension = os.path.splitext(file)
extension = extension.lower()
if not extension:
extension = "(no extension)"
# Get file size
javascript size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
total_size += size
# Categorize by size
if size < 10 * 1024: # < 10KB
file_size_stats["0-10KB"] += 1
elif size < 100 * 1024: # < 100KB
file_size_stats["10KB-100KB"] += 1
elif size < 1024 * 1024: # < 1MB
file_size_stats["100KB-1MB"] += 1
elif size < 10 * 1024 * 1024: # < 10MB
file_size_stats["1MB-10MB"] += 1
elif size < 100 * 1024 * 1024: # < 100MB
file_size_stats["10MB-100MB"] += 1
else: # >= 100MB
file_size_stats["100MB+"] += 1
# Get file modification date
mod_time = os.path.getmtime(file_path)
dt = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(mod_time)
month_year = dt.strftime("%Y-%m")
# Update statistics
file_type_stats[extension] += 1
file_month_stats[month_year] += 1
total_count += 1
except (IOError, OSError) as e:
# Skip files that can't be Accessed
continue
# Generate report
result_msg += f"Total files: {total_count}\n"
result_msg += f"Total size: {self.format_size(total_size)}\n\n"
# Write to separate CSV files
# 1. File Types CSV
with open(file_types_path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
csv_writer.writerow(["Statistics by File Type"])
csv_writer.writerow(["Extension", "Count"])
sorted_types = sorted(file_type_stats.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for ext, count in sorted_types:
csv_writer.writerow([ext, count])
# 2. Size Distribution CSV
with open(size_dist_path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
csv_writer.writerow(["Statistics by File Size"])
csv_writer.writerow(["Size Range", "Count"])
for size_range, count in file_size_stats.items():
csv_writer.writerow([size_range, count])
# 3. Year-Month Statistics CSV
with open(month_stats_path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
csv_writer.writerow(["Statistics by Month"])
csv_writer.writerow(["Month", "Count"])
sorted_months = sorted(file_month_stats.items())
for month, count in sorted_months:
csv_writer.writerow([month, count])
# Show file types in result
result_msg += "File types (Top 10):\n"
for ext, count in sorted_types[:10]:
result_msg += f"{ext}: {count} files\n"
result_msg += "\nSize distribution:\n"
for size_range, count in file_size_stats.items():
result_msg += f"{size_range}: {count} files\n"
result_msg += "\nAnalysis completed successfully!\n"
result_msg += f"CSV reports saved to:\n"
result_msg += f"- {file_types_path}\n"
result_msg += f"- {size_dist_path}\n"
result_msg += f"- {month_stats_path}"
# Update results text
self.results_text.SetValue(result_msg)
except Exception as e:
wx.MessageBox(f"An error occurred: {str(e)}", "Error", wx.OK | wx.ICON_ERROR)
def on_execute_command(self, event):
"""Execute the command in the command editor"""
command = self.cmd_text.GetValue().strip()
if not command:
wx.MessageBox("Please enter a command to execute.", "Error", wx.OK | wx.ICON_ERROR)
return
try:
# Create a new process, capture output
process = subprocess.Popen(
command,
shell=True,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
universal_newlines=True
)
# Get the output
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
# Display output
output = ""
if stdout:
output += stdout
if stderr:
output += "\nErrors:\n" + stderr
self.cmd_output.SetValue(output)
except Exception as e:
self.cmd_output.SetValue(f"Error executing command: {str(e)}")
def format_size(self, size_in_bytes):
"""Format file size to human-readable format"""
for unit in ['B', 'KB', 'MB', 'GB', 'TB']:
if size_in_bytes < 1024.0 or unit == 'TB':
return f"{size_in_bytes:.2f} {unit}"
size_in_bytes /= 1024.0
def main():
app = wx.App()
frame = FileAnalyzerFrame()
app.MainLoop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
工具功能概览
这个文件分析工具提供以下核心功能:
1.文件夹选择:通过图形界面选择需要分析的文件夹。
2.文件统计分析:
- 按文件扩展名统计文件数量。
- 按文件大小区间(如 0-10KB、10KB-100KB 等)统计文件分布。
- 按文件修改时间的年月统计文件数量。
3.CSV 报告生成:将分析结果保存为三个独立的 CSV 文件,分别记录文件类型、大小分布和年月统计。
4.命令执行器:提供一个简单的命令行界面,允许用户在工具中执行系统命令并查看输出。
5.人性化界面:通过 wxPython 构建直观的图形界面,方便用户操作。
技术栈
Python:核心编程语言,用于文件操作和数据处理。
wxPython:用于构建跨平台的图形用户界面。
os 和 datetime:用于文件系统操作和时间处理。
csv:用于生成 CSV 格式的报告。
subprocess:用于执行系统命令。
collections.defaultdict:简化统计数据结构的处理。
uuid:用于生成唯一标识符(本例中未直接使用,但代码中引入)。
代码结构分析
以下是工具的核心代码结构和功能解析:
1. 图形界面设计
工具使用 wxPython 构建了一个直观的窗口,包含以下组件:
- 文件夹选择区域:包含文本框和“浏览”按钮,用于选择分析的文件夹。
- 输出文件名设置:允许用户指定输出 CSV 文件的基础名称。
- 分析结果显示:一个多行只读文本框,用于显示分析结果摘要。
- 命令编辑器:允许用户输入系统命令并执行,执行结果显示在另一个只读文本框中。
界面通过 wx.BoxSizer 进行布局,确保组件排列整齐且自适应窗口大小调整。
2. 文件分析逻辑
文件分析功能由 on_analyze 方法实现,具体步骤如下:
1.输入验证:检查用户是否选择了有效文件夹。
2.统计初始化:
- 使用 defaultdict 记录文件类型统计。
- 定义文件大小区间字典(如 0-10KB、10KB-100KB 等)。
- 使用 defaultdict 记录按年月统计的文件数量。
3.文件夹遍历:通过 os.walk 递归遍历文件夹,获取每个文件的扩展名、大小和修改时间。
4.数据处理:
- 文件扩展名统计:提取文件扩展名并计数。
- 文件大小分类:根据文件大小归类到对应区间。
- 修改时间统计:将文件修改时间格式化为“年-月”并计数。
5.报python告生成:
- 生成三个 CSV 文件,分别记录文件类型、大小分布和年月统计。
- 在界面上显示分析摘要,包括文件总数、总大小、文件类型前十、文件大小分布等。
3. 命令执行功能
命令执行功能由 on_execute_command 方法实现,允许用户输入系统命令(如 dir 或 ls)并查看输出:
- 使用 subprocess.Popen 执行命令,捕获标准输出和错误输出。
- 将执行结果显示在界面上的命令输出文本框中。
- 包含错误处理,确保命令执行失败时显示友好提示。
4. 辅助功能
文件大小格式化:format_size 方法将字节大小转换为人类可读的格式(如 KB、MB、GB)。
错误处理:工具在文件访问、分析和命令执行过程中都包含了异常捕获,确保程序稳定性。
使用方法
运行程序:
- 确保安装了 Python 和 wxPython(pip install wxPython)。
- 保存代码为 file_analyzer.py 并运行。
选择文件夹:
点击“Browse”按钮选择需要分析的文件夹。
设置输出文件名:
在“Output Base Name”文本框中输入 CSV 文件的基础名称(默认为 analysis_results)。
执行分析:
点击“Analyze”按钮,工具将分析文件夹并生成三个 CSV 文件,同时在界面上显示结果摘要。
执行命令:
在命令编辑器中输入系统命令,点击“Execute Command”查看输出。
示例输出
假设分析一个包含多种文件的文件夹,工具将生成以下 CSV 文件:
analysis_results_file_types.csv:
Statistics by File Type
Extensio编程客栈n,Count.txt,50.jpg,30.pdf,20(no extension),10...
analysis_results_size_distribution.csv:
Statistics by File Size
Size Range,Count0-10KB,6010KB-100KB,30100KB-1MB,151MB-10MB,510MB-100MB,0100MB+,0
analysis_results_year_month.csv:
Statistics by Month
Month,Count2023-01,202023-02,302024-01,40...
界面上的结果摘要可能如下:
Analyzing folder: /path/to/folder
Total files: 110Total size: 1.23 GB File types (Top 10):.txt: 50 files.jpg: 30 files.pdf: 20 files(no extension): 10 files... Size distribution:0-10KB: 60 files10KB-100KB: 30 files... Analysis completed successfully!CSV reports saved to:- analysis_results_file_types.csv- analysis_results_size_distribution.csv- analysis_results_year_month.csv
运行结果

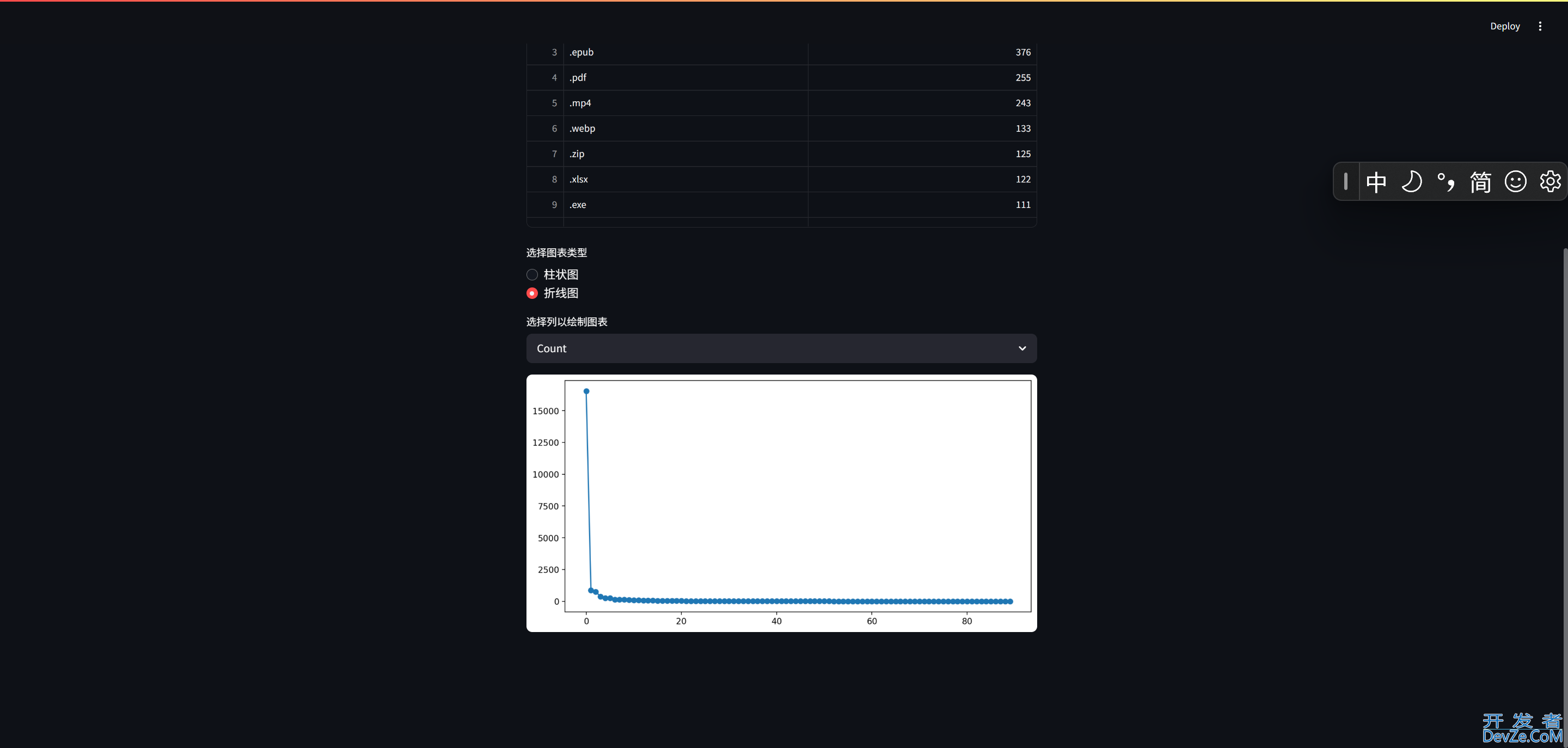
到此这篇关于使用Python打造一个强大的文件分析工具的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python文件分析内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论