通过C++获取CPU占用率的代码示例(windows、linux、macOS)
目录
- 获取CPU占用率
- Windows平台
- 一、获取系统整体CPU占用率
- 二、获取特定进程CPU占用率
- 三、常见问题
- linux平台
- 一、核心原理
- 二、实现步骤
- 三、扩展说明
- 四、优化与替代方案
- MACOS平台
- 一、核心实现原理
- 二、代码实现示例
- 三、关键点说明
- 四、扩展功能
- 五、编译注意事项
获取CPU占用率
windows平台
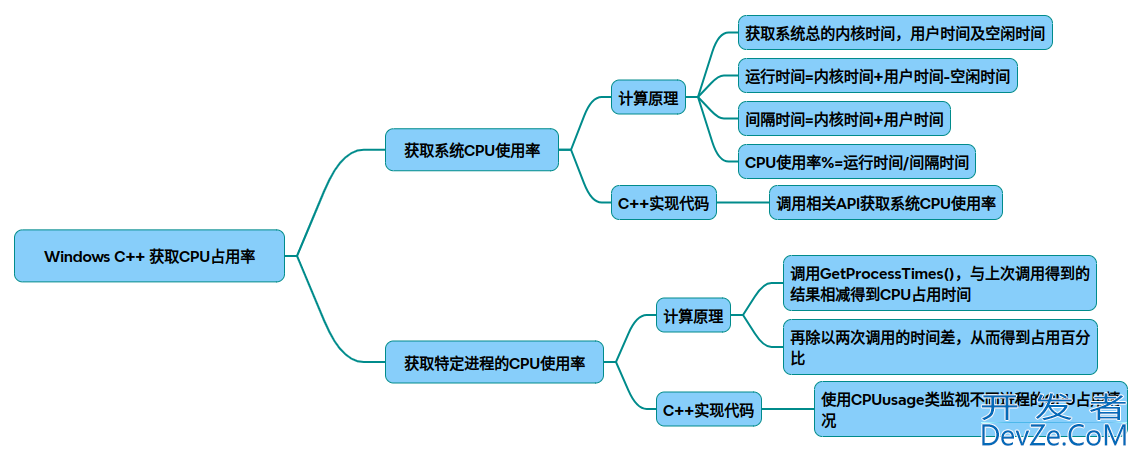
在Windows系统下使用C++获取CPU占用率,常见方法可分为系统整体占用率和特定进程占用率两类。以下是具体实现方法及核心代码示例:
一、获取系统整体CPU占用率
方法1:基于GetSystemTimandroides函数
原理:通过计算两次采样的系统空闲时间、内核时间和用户时间差值,结合公式得出整体CPU使用率。
#include <windows.h>
#include <IOStream>
double GetCpuUsage() {
FILETIME idleTime, kernelTime, userTime;
static FILETIME preIdleTime, preKernelTime, preUserTime;
GetSystemTimes(&idleTime, &kernelTime, &userTime);
// 转换为64位整型
ULONGLONG i编程客栈dle = (*(ULONGLONG*)&idleTime) - (*(ULONGLONG*)&preIdleTime);
ULONGLONG kernel = (*(ULONGLONG*)&kernelTime) - (*(ULONGLONG*)&preKernelTime);
ULONGLONG user = (*(ULONGLONG*)&userTime) - (*(ULONGLONG*)&preUserTime);
preIdleTime = idleTime;
preKernelTime = kernelTime;
preUserTime = userTime;
if (kernel + user == 0) return 0.0;
return ((kernel + user - idle) * 100.0) / (kernel + user);
}
// 调用示例
int main() {
while (true) {
Sleep(1000); // 间隔1秒采样
std::cout << "CPU Usage: " << GetCpuUsage() << "%" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
- 关键点:需间隔一定时间(如1秒)采样两次数据。公式:(内核时间 + 用户时间 - 空闲时间) / (内核时间 + 用户时间)。
方法2:使用性能计数器(PDH库)
适用场景:需要高精度或实时监控多个计数器。
#include <windows.h>
#include <pdh.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "pdh.lib")
double GetCpuUsageByPdh() {
static PDH_HQUERY query;
static PDH_HCOUNTER counter;
static bool initialized = false;
if (!initialized) {
PdhOpenQuery(nullptr, 0, &query);
PdhAddCounter(query, L"\\Processor(_Total)\\% Processor Time", 0, &counter);
initialized = true;
}
PDH_FMT_COUNTERVALUE value;
PdhCollectQueryData(query);
PdhGetFormattedCounterValue(counter, PDH_FMT_DOUBLE, nullptr, &value);
return value.doubleValue;
}
- 优点:与任务管理器数据一致,支持多核统计。
二、获取特定进程CPU占用率
原理:通过GetProcessTimes获取进程的内核和用户时间,计算两次采样的时间差占比。
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream>
class ProcessCpuMonitor {
public:
ProcessCpuMonitor(dwORD pid) : pid_(pid) {
hProcess_ = OpenProcess(PROCESS_QUERY_LIMITED_INFORMATION, FALSE, pid_);
}
~ProcessCpuMonitor() {
if (hProcess_) CloseHandle(hProcess_);
}
float GetUsage() {
FILETIME createTime, exitTime, kernelTime, userTime;
if (!GetProcessTimes(hProcess_, &createTime, &exitTime, &kernelTime, &userTime))
return -1;
ULONGLONG currentKernel = *(ULONGLONG*)&kernelTime;
ULONGLONG currentUser = *(ULONGLONG*)&userTime;
ULONGLONG delta = (currentKernel + currentUser) - (lastKernel_ + lastUser_);
// 计算时间差(单位:100纳秒)
ULONGLONG timePassed = GetTickCount64() - lastTick_;
lastTick_ = GetTickCount64();
lastKernel_ = currentKernel;
lastUser_ = currentUser;
if (timePassed == 0) return 0.0f;
return (delta / 10000.0f) / timePassed * 100.0f; // 转换为百分比
}
private:
DWORD pid_;
HANDLE hProcess_ = nullptr;
ULONGLONG lastKernel_ = 0, lastUser_ = 0;
ULONGLONG lastTick_ = 0;
};
// 调用示例
int main() {
DWORD pid = 1234; // 目标进程ID
ProcessCpuMonitor monitor(pid);
while (true) {
Sleep(1000);
std::cout << "Process CPU Usage: " << monitor.GetUsage() << "%" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
注意事项:
需以PROCESS_QUERY_LIMITED_INFORMATION权限打开进程。
公式:(进程时间差 / 系统时间差) * 100%。三、常见问题
- 与任务管理器数据不一致:因采样间隔和计算方式差异,结果可能有轻微偏差。
- 多核CPU:上述方法返回的是整体利用率,如需单核数据,需遍历每个逻辑处理器。
- 权限问题:获取系统级数据需管理员权限,进程级数据则不需要。
linux平台
在Linux系统下使用C++获取CPU占用率,主要通过解析/proc/stat文件实现。以下是具体实现方法和原理说明:
一、核心原理
Linux内核通过/proc/stat文件提供CPU活动的统计信息。文件中记录了从系统启动到当前时刻,CPU在不同状态下的累计时间(单位:时钟周期),包括:
- user:用户态执行时间
- nice:低优先级用户态时间
- system:内核态执行时间
- idle:空闲时间
- iowait:I/O等待时间
- irq:硬件中断时间
- softirq:软件中断时间
通过两次采样这些数值,计算时间差并分析CPU占用率。
二、实现步骤
读取 /proc/stat 文件
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
struct CpuTime {
unsigned long user, nice, system, idle, iowait, irq, softirq;
};
CpuTime readCpuStats() {
std::ifstream file("/proc/stat");
std::string cpu_label;
CpuTime time;
file >> cpu_label >> time.user >> time.nice >> time.system >> time.idle
>> time.iowait >> time.irq >> time.softirq;
return time;
}
- 计算CPU使用率通过两次采样时间差计算CPU利用率:
double calculateCpuUsage(const CpuTime& prev, const CpuTime& curr) {
const unsigned long prev_total = prev.user + prev.nice + prev.system + prev.idle
+ prev.iowait + prev.irq + prev.softirq;
const unsigned long curr_total = curr.user + curr.nice + curr.system + curr.idle
+ curr.iowait + curr.irq + curr.softirq;
const unsigned long total_di编程客栈ff = curr_total - prev_total;
const unsigned long idle_diff = curr.idle - prev.idle;
return (total_diff - idle_diff) * 100.0 / total_diff;
}
- 完整示例
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
CpuTime prev = readCpuStats();
sleep(1); // 采样间隔1秒
CpuTime curr = readCpuStats();
double usage = calculateCpuUsage(prev, curr);
std::cout << "CPU Usage: " << usage << "%" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
三、扩展说明
多核CPU处理
/proc/stat中每行对应一个CPU核心(如cpu0, cpu1),需分别解析。进程级CPU占用率
通过读取/proc/[pid]/stat获取进程的utime(用户态时间)和stime(内核态时间),结合系统总时间计算。注意事项
采样间隔建议≥1秒,避免瞬时波动。需处理/proc文件读取失败的情况。高精度场景可使用clock_gettime替代sleep。四、优化与替代方案
使用 sysinfo 系统调用
获取粗略的系统负载信息,但精度较低。调用 getrusage 函数
适用于统计进程自身的CPU使用情况。第三方库
如libstatgrab或procps-ng提供封装接口。macOS平台
在 macOS 系统下通过 C++ 获取 CPU 占用率,需要调用 Mach 内核 API 实现。以下是基于 、、 等资料的实现方案:
一、核心实现原理
Mach API 调用
macOS 基于 Darwin 内核,通过 <mach/mach_host.h> 提供的 host_statistics 函数获取 CPU 时间统计信息。CPU 占用率计算
需两次采样间隔内的 CPU 使用时间差,公式:CPU 占用率 = (用户态时间 + 内核态时间) / (总时间差) * 100%二、代码实现示例
#include <mach/mach_host.h>
#include <mach/processor_info.h>
#include <unistd.h>
编程客栈
double get_cpu_usage() {
host_cpu_load_info_data_t cpuinfo;
mach_msg_type_number_t count = HOST_CPU_LOAD_INFO_COUNT;
kern_return_t kr = host_statistics(mach_host_self(),
HOST_CPU_LOAD_INFO,
(host_info_t)&cpuinfo,
&count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) return -1.0;
// 第一次采样
uint64_t total_user_prev = cpuinfo.cpu_ticks[CPU_STATE_USER];
uint64_t total_sys_prev = cwww.devze.compuinfo.cpu_ticks[CPU_STATE_SYSTEM];
uint64_t total_idle_prev = cpuinfo.cpu_ticks[CPU_STATE_IDLE];
uint64_t total_used_prev = total_user_prev + total_sys_prev;
// 等待 1 秒后再次采样
sleep(1);
kr = host_statistics(mach_host_self(),
HOST_CPU_LOAD_INFO,
(host_info_t)&cpuinfo,
&count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) return -1.0;
uint64_t total_user = cpuinfo.cpu_ticks[CPU_STATE_USER];
uint64_t total_sys = cpuinfo.cpu_ticks[CPU_STATE_SYSTEM];
uint64_t total_idle = cpuinfo.cpu_ticks[CPU_STATE_IDLE];
uint64_t total_used = total_user + total_sys;
// 计算差值
uint64_t used_diff = total_used - total_used_prev;
uint64_t idle_diff = total_idle - total_idle_prev;
uint64_t total_diff = used_diff + idle_diff;
return (total_diff == 0) ? 0 : (used_diff * 100.0) / total_diff;
}
三、关键点说明
多核 CPU 处理
上述代码返回的是 所有 CPU 核心的平均占用率。若需获取单核数据,需通过 host_processor_info 函数遍历每个核心 。时间间隔选择
两次采样间隔建议 1 秒(sleep(1)),间隔过短会导致误差增大。错误处理
检查 host_statistics 返回值是否为 KERN_SUCCESS,避免因权限问题或 API 调用失败导致崩溃。四、扩展功能
获取单进程 CPU 占用
结合 proc_pidinfo 函数和 PROC_PIDTASKINFO 参数,可获取指定进程的 CPU 时间 。实时监控
通过多线程循环调用上述函数,实现动态曲线绘制(参考 中的 ImGui 方案)。五、编译注意事项
头文件依赖:需包含 <mach/mach.h> 和 <mach/mach_host.h>
链接框架:添加 -framework IOKit 编译选项
示例:clang++ -framework IOKit cpu_usage.cpp -o cpu_usage
以上就是通过C++获取CPU占用率的代码示例(windows、linux、macOS)的详细内容,更多关于C++获取CPU占用率的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论