java中String.matches方法使用
目录
- 一、String.matches()方法简介
- 1.1 概述
- 1.2 语法、参数、返回值
- 二、String.matches()配合正则表达式使用
- 2.1 普通字符匹配
- 2.1.1 [abc]
- 2.1.2 [^abc]
- 2.1.3 [A-Z]
- 2.1.4 [0-9]
- 2.1.5 .
- 2.2 单个符号匹配
- 2.2.1 中括号[ ]
- 2.2.2 或符号 |
- 2.2.3 ^ 符号
- 2.2.4 \S 符号
- 2.2.5 \s 符号
- 2.3 转义字符
- 2.4 匹配 ‘多种字符’ 其中的任意一个字符
- 2.4.1 \d
- 2.4.2 \w
- 2.5 匹配次数的特殊符号
- 三、其他正则表达式
一、String.matches()方法简介
1.1 概述
matches() 方法用于检测字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。
调用此方法的 str.matches(regex) 形式与以下表达式产生的结果完全相同:
Pattern.matphpches(regex, str)
1.2 语法、参数、返回值
语法
public boolean matches(String regex)参数regex -- 匹配字符串的正则表达式。返回值在字符串匹配给定的正则表达式时,返回 true。二、String.matches()配合正则表达式使用
2.1 普通字符匹配
字母、数字、汉字、下划线、以及没有特殊定义的标点符号,都是 “普通字符”。表达式中的普通字符,在匹配一个字符串的时候,匹配与之相同的
一个字符。
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [abc] | 匹配[…]中所有的字符 |
| [^abc] | 匹配除了[…]中所有的字符 |
| [A-Z] | 匹配所有区间A-Z的字符 |
| [0-9] | 表示区间,匹配0-9的数字 |
| . | 匹配除了换行符(\r、\n)之外的任何单个字符,相当于[^\r\n] |
2.1.1 [abc]
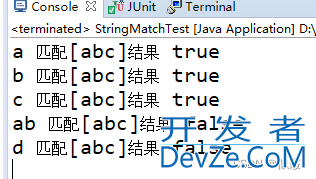
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("[abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "b";
result = s1.matches("[abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "c";
result = s1.matches("[abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches("[abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "d";
result = s1.matches("[abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[abc]结果 " + result);
}
Result:
解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配包含单个字符的字符串,该字符可以是 a、b 或 c 中的任意一个。换句话说,它会检查字符串是否只包含 a、b 或 c 中的任意一个字符。例如:“a” 会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符并且是 a。“b” 也会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符并且是 b。“c” 同样会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符并且是 c。“ab” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了多个字符。“d” 也不会匹配成功,因为它不是 a、b 或 c 中的任意一个字符。因此,如果字符串仅包含 a、b 或 c 中的任意一个字符,String.matches(“[abc]”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串包含其他字符或者包含多个字符,则返回 false。
2.1.2 [^abc]
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "b";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "c";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "d";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "e";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc]结果 " + result);
s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc]结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
在正则表达式中,^ 表示取反,[^abc] 表示匹配任意一个字符,但是不能是 a、b 或 c 中的任何一个。例如:“a” 也不会匹配成功,因为它是 a。“b” 也不会匹配成功,因为它是 b。“c” 也不会匹配成功,因为它是 c。“d” 会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符并且不是 a、b 或 c。“e” 也会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符并且不是 a、b 或 c。“ab” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了多个字符。因此,如果字符串只包含一个字符并且不是 a、b 或 c 中的任何一个,String.matches(“[^abc]”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串包含其他字符或者包含多个字符,则返回 false。
2.1.3 [A-Z]
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "A";
boolean result = s1.matches("[A-Z]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[A-Z]结果 " + result);
s1 = "B";
result = s1.matches("[A-Z]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[A-Z]结果 " + result);
s1 = "Z";
result = s1.matches("[A-Z]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[A-Z]结果 " + result);
s1 = "a";
result = s1.matches("[A-Z]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[A-Z]结果 " + result);
s1 = "AB";
result = s1.matches("[A-Z]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[A-Z]结果 " + result);
s1 = "1";
result = s1.matches("[A-Z]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[A-Z]结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配一个大写字母,即 A 到 Z 中的任意一个字母。例如:“A” 会匹配成功,因为它是大写字母 A。“B” 也会匹配成功,因为它是大写字母 B。“Z” 也会匹配成功,因为它是大写字母 Z。“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它是小写字母。“AB” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含多个字符。“1” 也不会匹配成功,因为它不是字母。因此,如果字符串只包含一个大写字母,String.matches(“[A-Z]”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串包含其他字符、小写字母或者包含多个字符,返回 false。
2.1.4 [0-9]
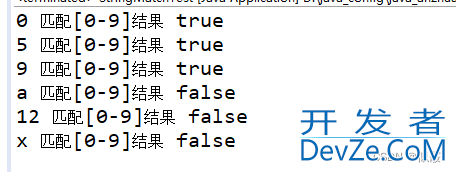
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "0";
boolean result = s1.matches("[0-9]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[0-9]结果 " + result);
s1 = "5";
result = s1.matches("[0-9]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[0-9]结果 " + result);
s1 = "9";
result = s1.matches("[0-9]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[0-9]结果 " + result);
s1 = "a";
result = s1.matches("[0-9]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[0-9]结果 " + result);
s1 = "12";
result = s1.matches("[0-9]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[0-9]结果 " + result);
s1 = "x";
result = s1.matches("[0-9]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[0-9]结果 " + result);
}
Result:
解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配一个数字字符,即 0 到 9 中的任意一个数字。例如:“0” 会匹配成功,因为它是数字 0。“5” 也会匹配成功,因为它是数字 5。“9” 也会匹配成功,因为它是数字 9。“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它不是数字。“12” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含多个字符。“x” 也不会匹配成功,因为它不是数字。因此,如果字符串只包含一个数字字符,String.matches(“[0-9]”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串包含其他字符或者包含多个字符,返回 false。
2.1.5 .
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches(".");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配.结果 " + result);
s1 = "1";
result = s1.matches(".");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配.结果 " + result);
s1 = " ";
result = s1.matches(".");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配.结果 " + result);
s1 = "\n";
result = s1.matches(".");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配.结果 " + result);
s1 = "\r";
result = s1.matches(".");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配.结果 " + result);
s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches(".");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配.结果 " + result);
System.out.println(" 斜杠r的作用 \r 斜杠n的作用 \n 都是换行 " );
}
Result:
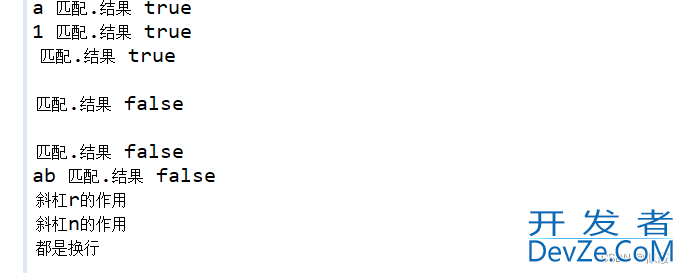
解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配任意一个字符,除了换行符以外的所有字符。例如:“a” 会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符。“1” 也会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个字符。" " 也会匹配成功,因为它只包含一个空格字符。“\n” 不会匹配成功,因为它是一个换行符。“\r” 不会匹配成功,因为它是一个换行符。“ab” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了多个字符。因此,如果字符串只包含一个字符,String.matches(“.”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串包含多个字符或者包含换行符,返回 false。
2.2 单个符号匹配
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [ ] | 只有方括号里面指定的字符才参与匹配,也只能匹配单个字符。 |
| | | 相当于“或”,可以匹配指定的字符,但是也只能选择其中一项进行匹配。 |
| ^ | 表示否,如果用在方括号内,^表示不想匹配的字符。 |
| \S | 非空字符 |
| \s | 空字符,只可以匹配一个空格、制表符、回车符、换页符,不可以匹配自己输入的多个空格。 |
2.2.1 中括号[ ]
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "ad";
result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "aad";
result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abd";
result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "acd";
result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "aod";
result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abcd";
result = s1.matches("a[abc]d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a[abc]d 结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配一个以"a"开头,然后是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符,然后是"d"结尾的字符串。例如:“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它的第二个字符不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个,且没有以d结尾。“ad” 不会匹配成功,因为它的第二个字符不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个。“aad” 会匹配成功,因为它以"a"开头,然后是"a",最后是"d"。“abd” 会匹配成功,因为它以"a"开头,然后是"b",最后是"d"。“acd” 会匹配成功,因为它以"a"开头,然后是"c",最后是"d"。“aod” 不会匹配成功,因为它的第编程客栈二个字符不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个。“abcd” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了多个字符。因此,如果字符串符合以"a"开头,然后是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符,最后是"d"结尾的模式,String.matches(“a[abc]d”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串不符合这个模式,返回 false。
2.2.2 或符号 |
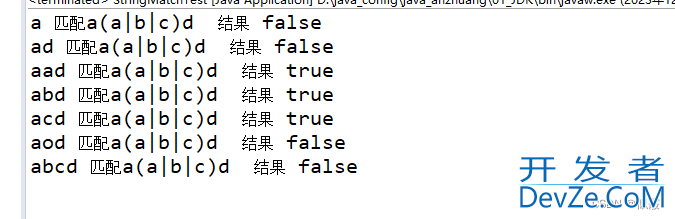
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "ad";
result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "aad";
result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abd";
result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "acd";
result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "aod";
result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abcd";
result = s1.matches("a(a|b|c)d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配a(a|b|c)d 结果 " + result);
}
Result:
解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配一个以"a"开头,然后是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符,最后是"d"结尾的字符串。在正则表达式中,(a|b|c) 表示一个分组,其中的字符"a"、“b” 或 “c"中的任意一个字符。例如:“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它的第二个字符不是"a”、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个,且没有以d结尾。“ad " 不会匹配成功,因为它的第二个字符不是"a”、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个。“aad” 会匹配成功,因为它以"a “开头,然后是"a”,最后是"d"。“abd” 会匹配成功,因为它以"a"开头,然后是"b",最后是"d"。“acd” 会匹配成功,因为它以"a"开头,然后是"c",最后是"d"。“aod” 不会匹配成功,因为它的第二个字符不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个。“abcd” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了多个字符。因此,如果字符串符合以"a"开头,然后是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符,最后是"d"结尾的模式,String.matches(“a(a|b|c)d”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串不符合这个模式,返回 false。
2.2.3 ^ 符号
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc] 结果 " + result);
s1 = "d";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc] 结果 " + result);
s1 = "e";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc] 结果 " + result);
s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches("[^abc]");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配[^abc] 结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
这个正则表达式表示匹配一个不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符的字符串。方括号内的^ 表示取反,表示匹配不在指定字符集合中的任意一个字符。例如:“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的一个字符。“d” 会匹配成功,因为它不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符。“e” 会匹配成功,因为它不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符。“ab” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了"a"和"b"两个字符。因此,如果字符串不是"a"、“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符,String.matches(“[^abc]”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串是这些字符之一,返回 false。
2.2.4 \S 符号
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("\\S");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\S 结果 " + result);
s1 = "1";
result = s1.matches("\\S");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\S 结果 " + result);
s1 = "!";
result = s1.matches("\\S");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\S 结果 " + result);
s1 = " ";
result = s1.matches("\\S");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\S 结果 " + result);
s1 = "\t";
result = s1.matches("\\S");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\S 结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
在正则表达式中,\S 表示匹配任意非空白字符。这包括字母、数字、标点符号等,只要不是空格、制表符等空白字符就可以匹配。例如:“a” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个非空白字符。“1” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个非空白字符。“!” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个非空白字符。" " 不会匹配成功,因为它是一个空白字符。“\t” 不会匹配成功,因为它是一个空白字符。因此,如果字符串是一个非空白字符,String.matches(“\S”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串是一个空白字符,返回 false。
2.2.5 \s 符号
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = " ";
boolean result www.devze.com= s1.matches("\\s");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\s 结果 " + result);
s1 = "\t";
result = s1.matches("\\s");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\s 结果 " + result);
s1 = "\n";
result = s1.matches("\\s");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\s 结果 " + result);
s1 = "a";
result = s1.matches("\\s");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\s 结果 " + result);
}
Result:
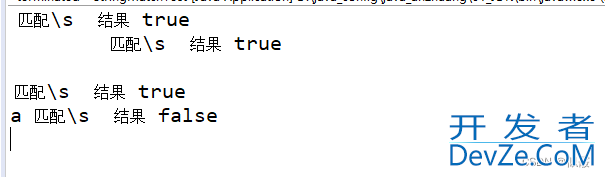
解析:
在正则表达式中,\s 表示匹配任意空白字符。这包括空格、制表符、换行符等。例如:" " 会匹配成功,因为它是一个空白字符。“\t” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个空白字符。“\n” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个空白字符。“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它不是一个空白字符。因此,如果字符串是一个空白字符,String.matches(“\s”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串不是一个空白字符,返回 false。
2.3 转义字符
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| \^ | 匹配^符号本身 |
| \$ | 匹配$符号本身 |
| \. | 匹配小数点本身 |
| \r,\n | 回车和换行符 |
| \t | 制表符 |
| \\ | 代表 ”\“ 本身 |
这个就比较简单不做代码测试了,需要注意的是对于Java中的\\理解
Java中正则表达式的\
\表示将下一字符标记为特殊字符。如\d表示数字字符匹配,等效于 [0-9]。\w表示匹配任何字类字符(字母数字下划线),注意包括下划线。与"[A-Za-z0-9_]"等效。\\中的第一个\表示java的转义字符\ 由编译器解析,第二个\是正则表达式\ 由正则表达式引擎解析。
关于Java正则和转义中\和\和\\的理解
2.4 匹配 ‘多种字符’ 其中的任意一个字符
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| \d | 任意一个数字 0-9中任意一个 |
| \w | 任意一个字母或数字或下划线,也就是A-Z,a-z,0-9,_,任意一个 |
| \s | 空格、制表符、换行符等空白字符中的任意一个 |
\s上面已经有测试例子了,看一下\d 和\w的简单测试
2.4.1 \d
\d ,但在java中需要\\d
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "1";
boolean result = s1.matches("\\d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "5";
result = s1.matches("\\d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "a";
result = s1.matches("\\d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d 结果 " + result);
s1 = "10";
result = s1.matches("\\d");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d 结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
在正则表达式中,\d 表示匹配一个数字字符。换句话说,它只匹配数字 0-9 中的任意一个字符。例如:“1” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个数字字符。“5” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个数字字符。“a” 不会匹配成功,因为它不是一个数字字符。“10” 不会匹配成功,因为它包含了两个字符。因此,如果字符串是一个数字字符,String.matches(“\\d”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串不是一个数字字符,并且返回 false。
2.4.2 \w
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
boolean result = s1.matches("\\w");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w 结果 " + result);
s1 = "5";
result = s1.matches("\\w");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w 结果 " + result);
s1 = "_";
result = s1.matches("\\w");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w 结果 " + result);
s1 = "!";
result = s1.matches("\\w");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w 结果 " + result);
}
Result:

解析:
在正则表达式中,\w 表示匹配一个单词字符,包括字母、数字和下划线。换句话说,它匹配字母数字字符以及下划线。例如:“a” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个单词字符。“5” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个单词字符。“_” 会匹配成功,因为它是一个单词字符。“!” 不会匹配成功,因为它不是一个单词字符。因此,如果字符串是一个单词字符,String.matches(“\\w”) 方法将返回 true,如果字符串不是一个单词字符,返回 false。
2.5 匹配次数的特殊符号
前面的表达式,无论是单个字符,还是多种字符其中的一个,都只能匹配一次。如果使用表达式再加上修饰匹配次数的特殊符号,那么不用重复书写表达式就可以重复多次匹配。
注:特殊符号修饰的是它前面的表达式
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| {n} | 表达式重复n次,例”\d{2}“相当于”\d\d“,可以匹配到11,12, 13 |
| {m,n} | 表达式至少重复m次,最多重复n次,例”\w{2,3}",可以匹配ac,ad,acd,但是无法匹配abcd |
| {m,} | 表达式至少重复m次,最多不设限 |
| ? | 表达式0次或1次,相当于{0,1} |
| + | 表达式至少出现1次,相当于{1,} |
| * | 表达式不出现或出现任意次,相当于{0,} |
做一个测试例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("------{n}测试-------");
String s1 = "1";
boolean result = s1.matches("\\d{2}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d{2} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "12";
result = s1.matches("\\d{2}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d{2} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "123";
result = s1.matches("\\d{2}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\d{2} 结果 " + result);
System.out.println("------{n}测试完毕-------"+"\n");
System.out.println("------{m,n}测试-------");
s1 = "1";
result = s1.matches("\\w{2,3}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{2,3} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "12";
result = s1.matches("\\w{2,3}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{2,3} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "123";
result = s1.matches("\\w{2,3}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{2,3} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "1234";
result = s1.matches("\\w{2,3}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{2,3} 结果 " + result);
System.out.println("------{m,n}测试完毕-------"+"\n");
System.out.println("------{m,}测试-------");
s1 = "1";
result = s1.matches("\\w{3,}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{3,} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "12";
result = s1.matches("\\w{3,}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{3,} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "123";
result = s1.matches("\\w{3,}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{3,} 结果 " + result);
s1 = "1234";
result = s1.matches("\\w{3,}");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配\\w{3,} 结果 " + result);
System.out.println("------{m,}测试完毕-------"+"\n");
System.out.println("------?测试-------");
s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]?e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abe";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]?e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abce";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]?e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abcde";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]?e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 " + result);
System.out.println("------?测试完毕-------"+"\n");
System.out.println("------+测试-------");
android s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]+e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abe";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]+e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abce";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]+e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abcde";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]+e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 " + result);
System.out.println("------+测试完毕-------"+"\n");
System.out.println("------*测试-------");
s1 = "ab";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]*e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abe";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]*e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abce";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]*e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 " + result);
s1 = "abcde";
result = s1.matches("ab[cd]*e");
System.out.println(s1 + " 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 " + result);
System.out.println("------*测试完毕-------"+"\n");
}
Result:
------{n}测试-------
1 匹配\d{2} 结果 false12 匹配\d{2} 结果 true123 匹配\d{2} 结果 false------{n}测试完毕-------------{m,n}测试-------
1 匹配\w{2,3} 结果 false12 匹配\w{2,3} 结果 true123 匹配\w{2,3} 结果 true1234 匹配\w{2,3} 结果 false------{m,n}测试完毕-------------{m,}测试-------
1 匹配\w{3,} 结果 false12 匹配\w{3,} 结果 false123 匹配\w{3,} 结果 true1234 匹配\w{3,} 结果 true------{m,}测试完毕-------------?测试-------
ab 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 falseabe 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 trueabce 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 trueabcde 匹配ab[cd]?e 结果 false------?测试完毕-------------+测试-------
ab 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 falseabe 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 falseabce 匹配ab[cd]+e 结果 trueabcde 匹配编程客栈ab[cd]+e 结果 true------+测试完毕-------------*测试-------
ab 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 falseabe 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 trueabce 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 trueabcde 匹配ab[cd]*e 结果 true------*测试完毕-------
三、其他正则表达式
表达式实在太多而且可以自定义无穷无尽,但是相信小白看完这篇文章后,对于java使用正则表达式已经入门了,附上一些参考链接,里面有很多正则表达式的例子。
关于Java正则和转义中\和\和\\的理解
Java 正则表达式的用法和实例Java 之正则表达式语法及常用正则表达式汇总java正则表达式大全(常用)
到此这篇关于java中String.matches方法使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java String.matches内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论