Java中@RequiredArgsConstructor注解的基本用法
目录
- 前言
- 1. 基本知识
- 2. 源码解读
- 3. Demo
- 3.1 简易Demo
- 3.2 staticName属性
- 3.3 onConstructor属性
- 3.4 Access属性
- 4. @AllArgsConstructor比较
- 总结
前言
从源码中学习,事因是看到项目代码中有所引用
@RequiredArgsConstructor 是 Lombok 提供的一个注解,用于自动生成一个包含所有 final 字段和带有 @NonNull 注解字段的构造函数
这可以减少样板代码,尤其是在需要依赖注入时
1. 基本知识
Lombok 是一个 Java 库,通过注解简化代码
常用注解包括 @Getter, @Setter, @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, 和 @Data 等
针对@RequiredArgsConstructor 注解会生成一个包含所有 final 字段和带有 @NonNull 注解字段的构造函数
这对于构造必须初始化这些字段的对象非常有用
基本的语法如下:
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MyClass {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private String address;
@NonNull
private String phoneNumber;
}
对应生成的构造函数如下:
public MyClass(String name, int age, String phoneNumber) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
对应需要注意的事项如下:
字段的顺序:生成的构造函数中的参数顺序是按照字段在类中定义的顺序@NonNull注解:如果某个字段带有 @NonNull 注解,它也会包含在构造函数中,即使它不是 final 的。
与其他构造函数冲突:如果手动定义了构造函数,@RequiredArgsConstructor 生成的构造函数可能会与其冲突
与其他注解比较:
@NoArgsConstructor:生成一个无参构造函数。@AllArgsConstructor:生成一个包含所有字段(包括非 final 字段)的构造函数
2. 源码解读
先看源码的对应属性
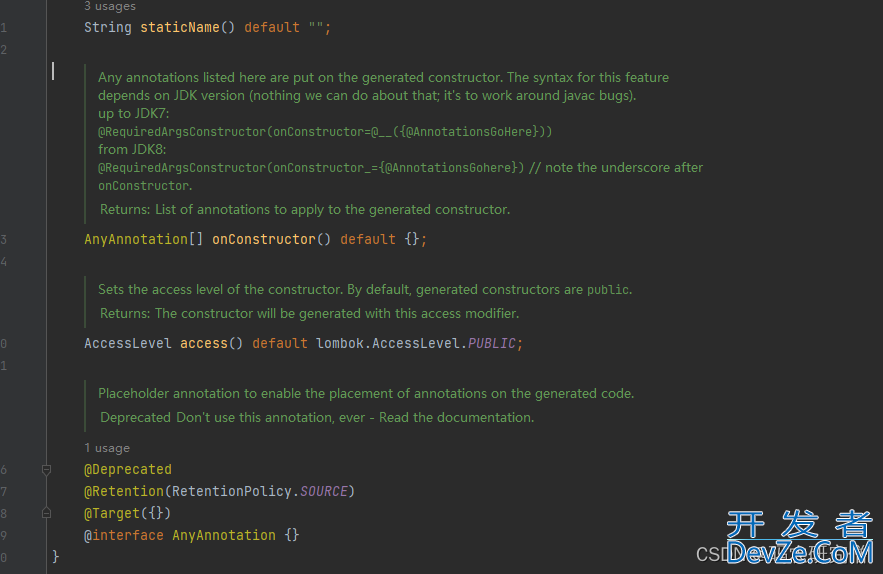
对应的属性分析如下:
staticName:
- 设置了这个属性,会生成一个静态方法,该方法调用私有构造函数
- 这个静态方法主要用于推断类型参数
onConstructor:
- 允许在生成的构造函数上添加指定的注解
- JDK 7 和 JDK 8 的语法稍有不同。
access:
- 设置构造函数的访问级别
- 默认是 public,可以设置为 private, protected 或 package
针对源码结合以下Demo进行展示
3. Demo
3.1 简易Demo
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class test {
private final String firstName;
private final String lastName;
@NonNull
private String email;
private int age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 正确使用示例
test person = new test("码农", "研究僧", "https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288");
Systewww.devze.comm.out.println("Person created: " + person);
// 错误使用示例(会导致编译错误)
// Person person2 = new Person("Jane", "Doe");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
明确需要3个属性,不可超过4个
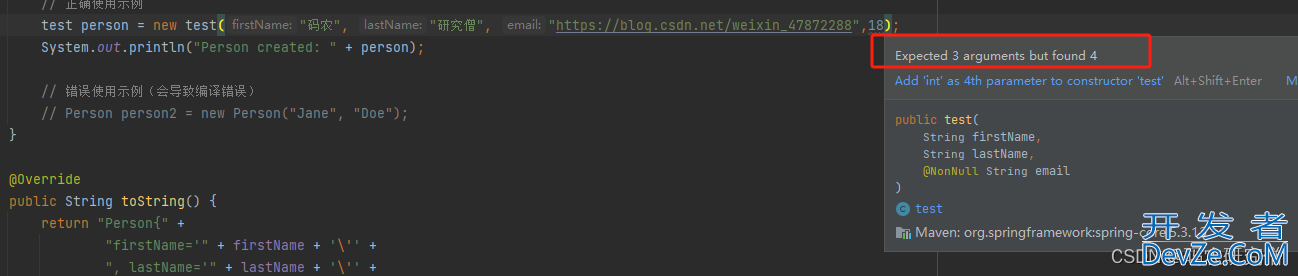
再者对应的字段属性是按照顺序的,如果更换顺序会出现如下场景:
test person = new test("码农","https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288","研究僧");
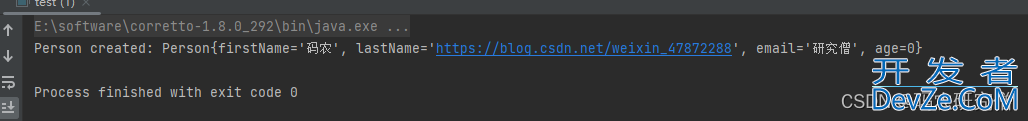
3.2 staticName属性
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
会生成一个静态方法 of 来实例化对象,而不是直接调用构造函数
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
public class test {
private final String firstName;
private final String lastName;
private final String email;
public static void main(String[] args) {
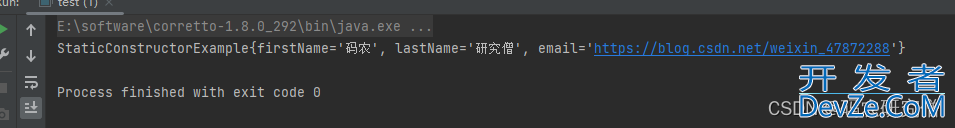
test example = test.of("码农","研究僧","https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288");
androidSystem.out.println(example);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StaticConstructorExample{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
截图如下:
3.3 onConstructor属性
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor_ = @__(@CustomAnnotation("Custom Constructor")))
会在生成的构造函数上添加 @CustomAnnotation
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface CustomAnnotation {
Strihttp://www.devze.comng value();
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor_ = @__(@CustomAnnotation("Custom Constructor")))
public class test {
private final String firstName;
private final String lastName;
private final String email;
public static void main(String[] args) {
test example = new test("码农","研究僧","https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288");
System.out.println(example);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StaticConstructorExample{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
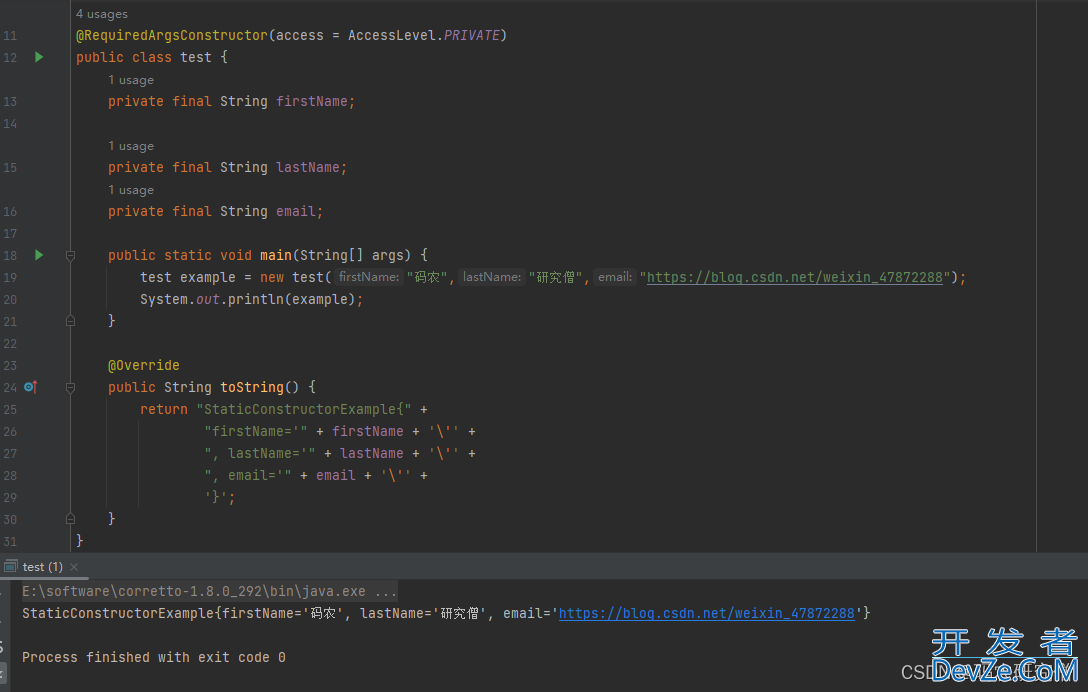
3.4 access属性
@RequiredArgsConstructor(jsaccess = AccessLevel.PRIVATE, staticName = "of")
public class test {
private final String firstName;
private final String lastName;
private final String email;
public static void main(String[] args) {
test example = test.of("码农", "研究僧", "https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288");
System.out.println(example);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StaticConstructorExample{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
不需要构造函数是私有的,可以将构造函数的访问级别设置为 public 或 protected,直接进行new
但是我的private它竟然可以new(神奇=-=)
4. @AllArgsConstructor比较
使用 @RequiredArgsConstructor 时,只有 final 字段和 @NonNull 字段会被初始化
但是@AllArgsConstructor 生成一个构造函数,该构造函数包含类中所有字段,无论它们是否为 final 或带有 @NonNull 注解
@AllArgsConstructor
public class test {
private final String firstName;
private String lastName;
@NonNull
private String email;
private int age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 正确使用示例
test person = new test("码农","研究僧","https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288",18);
System.out.println("Person created: " + person);
// 错误使用示例(会导致编译错误)
// Person person2 = new Person("Jane", "Doe");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
截图如下:(必须要有四个参数)
www.devze.com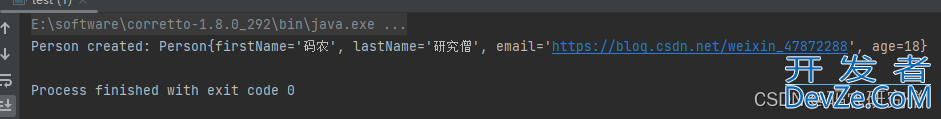
这两者都可以实用构造函数注入,但推荐使用@RequiredArgsConstructor,因为它只会初始化那些在创建对象时必需的字段
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论