详解如何用C++写一个日期计算器
目录
- 前言
- 代码的布局
- 设计数据
- 方法声明
- 方法的实现
- 获取某年某月的天数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值运算符重载
- 析构函数
- 日期+=天数
- 日期+天数
- 日期-天数
- 日期-=天数
- 前置++
- 后置++
- 后置--
- 前置--
- >运算符重载
- 实现比较大小运算符重载思路
- ==运算符重载
- *> = 运算符复用实现其他比较运算符重载
- >=运算符重载
- <运算符重载
- <=运算符重载
- !=运算符重载
- 日期-日期
- 代码错误和bug分享
前言
写一个日期计算器对学习的意义也很大。初学C++,接触了类和对象的概念,又认识了默认成员函数,然后又学习了运算符的重载。而日期计算器就很好的涵盖了这些知识。能很好的帮助我们复习学过的知识。
代码的布局
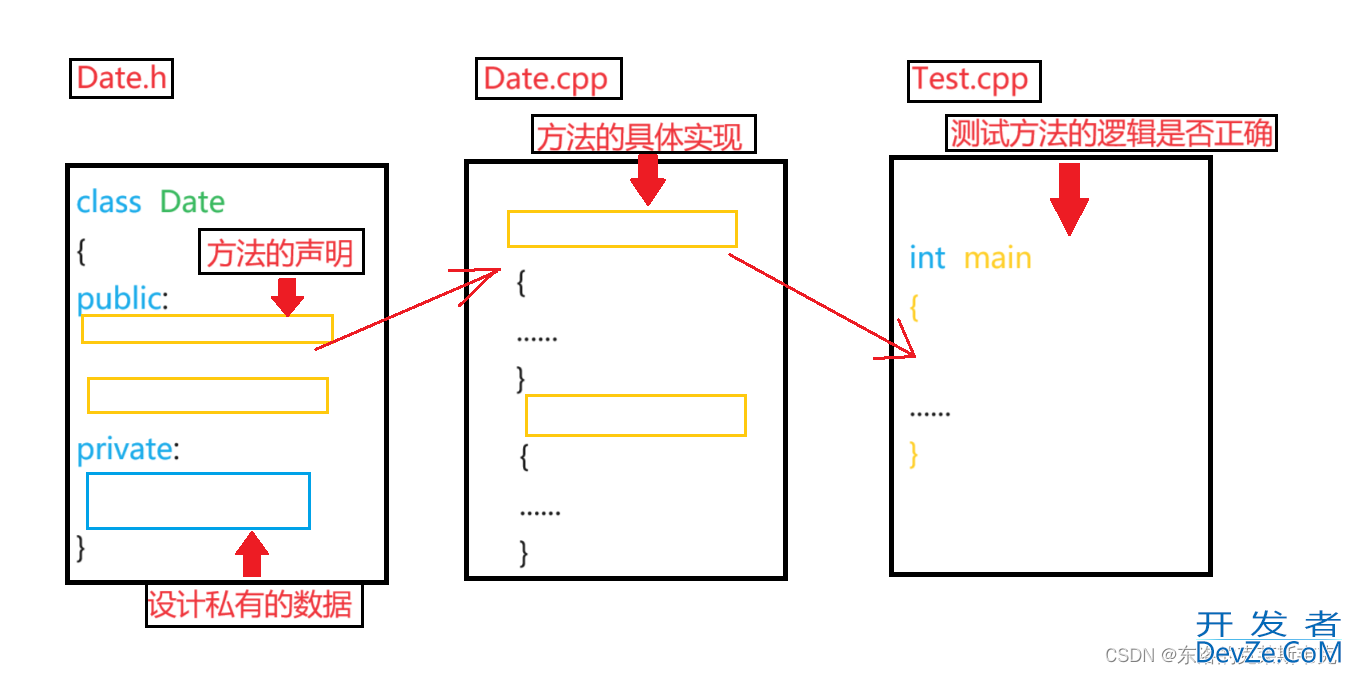
建两个 .cpp文件:Date.cpp Test.cpp
建一个 .h文件 :Date.h
作用:Date.h声明一个类 , Date.cpp类的方法的具体实现, Test.cpp测试方法的逻辑
设计数据
年:_year 月:_month 日:_day
变量名前面加“ _ ”符号,是为了和普通的数据或一些参数做区分。增加代码可读性。
方法声明
// 获取某年某月的天数 int GetMonthDay(int year, int month); // 全缺省的构造函数 Date(int year = 2024, int month = 4, int day = 18); // 拷贝构造函数 Date(const Date& d); // 赋值运算符重载 Date& operator=(const Date& d); // 析构函数 ~Date(); // 日期+=天数 Date& operator+=(int day); //其结果为日期 // 日期+天数 Date operator+(int day); // 日期-天数 Date operator-(int day); // 日期-=天数 Date& operator-=(int day); // 前置++ Date& operator++(); //天数加1 // 后置++ Date operator++(int); // 后置-- Date operator--(int); //天数减1 // 前置-- Date& operator--(); // >运算符重载 bool operator>(const Date& d); //比较日期大小 // ==运算符重载 bool operator==(const Date& d); // >=运算符重载 bool operator >= (const Date& d); // <运算符重载 bool operator < (const Date& d); // <=运算符重载 bool operator <= (const Date& d); // !=运算符重载 bool operator != (const Date& d); // 日期-日期 返回天数 int operator-(const Date& d);
声明的方法要有其意义,比如日期和天数相乘就没有意义,也没必要声明。
方法的实现
获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);
闰年
一年有365天,但地球公转的周期比一年多了大约5.82个小时。所以每过4年,二月的28天就要变成29天,即4年一润。但每四年都要润一次的话,每过100年,我们计算的天数要比地球公转的天数多了大概0.75天,所以二月的28天保持不变,即百年不润。100年不润是为了补足4年一润的精度,而400一润是为了补足100年不润的精度。只有这样,日期才不会与四季脱离。
总结就是:四年一润,百年不润,四百年又一润。
翻译成计算机语言就是
year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0
有了闰年的概念,那么获取某年某月的天数的代码就可以实现了
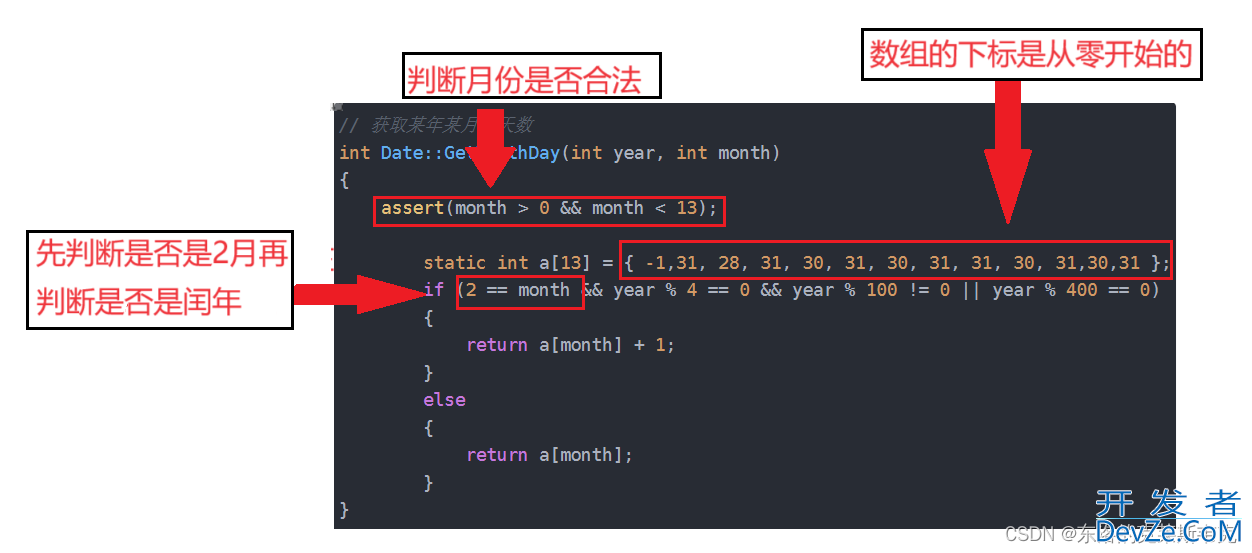
// 获取某年某月的天数
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
assert(month > 0 && month < 13);
static int a[13] = { -1,31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31,30,31 };
if (2 == month && year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0)
{
return a[month] + 1;
}
else
{
return a[month];
}
}
下图是代码控制的细节
下面加*的函数不做重点
*全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 2024, int month = 4, int day = 18);
Date::Date(int year, int month, pythonint day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
注意:全缺省构造函数在定义的时候不需要给缺省值。
拷贝构造函数
Date(const Date& d);
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
赋值运算符重载
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
return *this;
}
析构函数
因为没有涉及到资源管理可以不写,编译器会自动生成默认的析构函数。
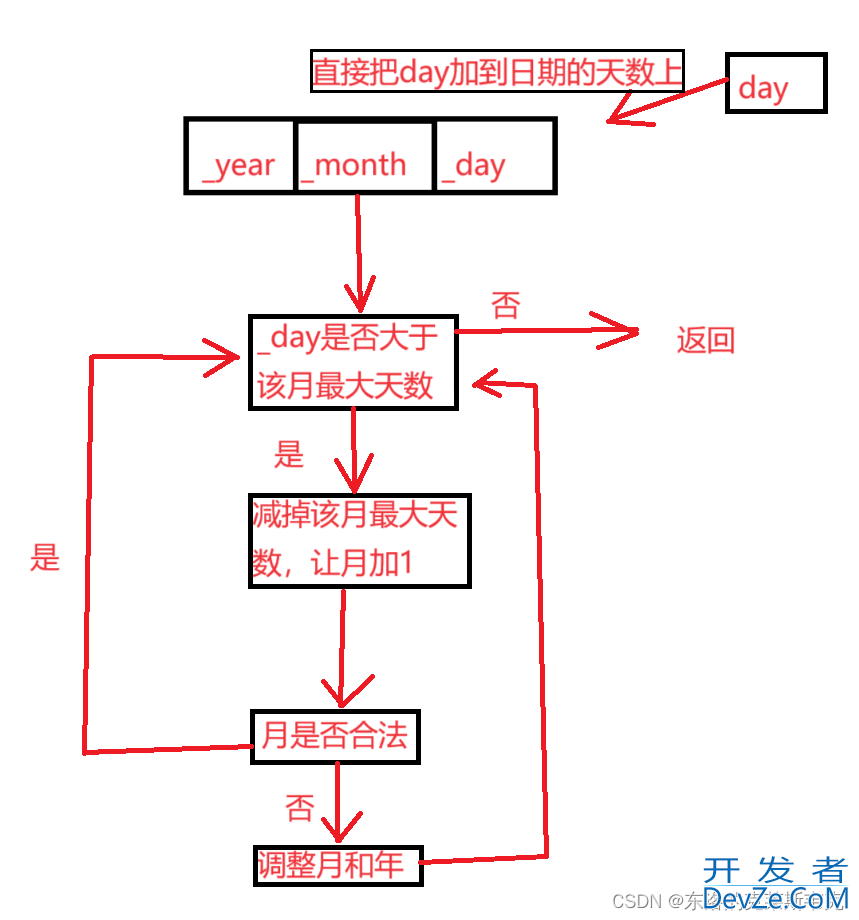
日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);思路:可以把要加的天数直接加到日期的天数上,如果日期的天数没有超过该月的最大天数,直接返回日期。如果超过了,就写个循环往前进位,直到日期的天数小于该月的最大天数,然后再返回日期。
逻辑示意图
代码
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day; //把天数加到日期的天数上
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) //如果日期的天数大于该月最大天数就进位
{
_day -MsngEM= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); //要想进位,得把该月的最大天数减掉
++_month; //进位
if (_month > 12) //如果月不合法就调整月
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this; //返回日期,因为出了作用域不会销毁,可以引用返回
}
*this是返回声明在头文件中的日期类,该类出了该函数的作用域不会销毁,所以传引用返回,提高效率。
日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
实现日期+天数的时候不用把类似于日期+=天数的逻辑再写一遍,可以直接复用。
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this; //在实例化对象的时候,调用拷贝构造函数,将日期类的数据拷贝给临时对象
tmp += day; //直接复用+=的逻辑
return tmp;
}
日期加天数不能改变日期的值,所以要创建临时对象。临时对象出了作用域就销毁了,所以不能传引用返回。
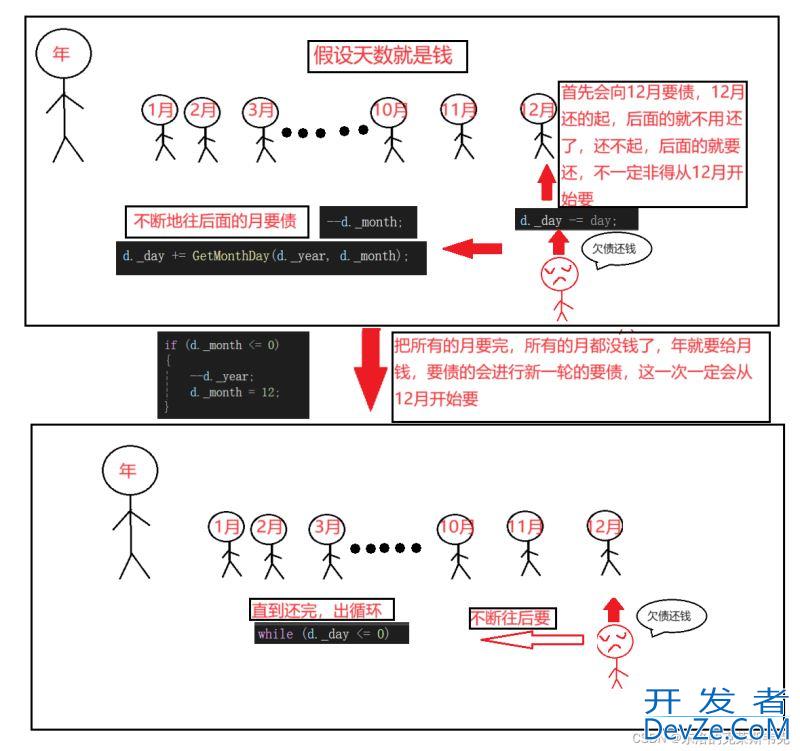
日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
在实现日期+=天数和日http://www.devze.com期+天数的时候,先实现了+=的逻辑,在实现+的逻辑的时候复用+=的逻辑。现在反过来,先实现-的逻辑,在实现-=的逻辑的时候复用-的逻辑。
思路:把天数直接和日期中的天数相减。若不为负数,直接返回。若为负数,则需要写个循环不断向前借位,如果把月借成负数就向年借,然后调整月,再调整日,直到日大于零为止。因为日期-天数不改变日期,所以要创建临时的对象。
代码
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date d = (*this); //创建临时对象,把日期类的数据拷贝给临时对象
d._day -= day; //让日期的天数直接和天数相减
while (d._day <= 0) //日期的天数小于零就调整
{
--d._month; //该月已经是负的,应该往下个月借天数
if (d._month <= 0) //月不合法就调整月
{http://www.devze.com
--d._year;
d._month = 12;
}
d._day += GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month); //把该月的所有天数都借给日期的天数
}
return d;
}
逻辑示意图
因为临时对象出了作用域要销毁,所以不能传引用返回。
日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
直接复用-的逻辑,代码如下
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
return *this = *this - day;
}
前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
实现前置++就不需要复杂的逻辑了,只需要控制年月日的进位即可。代码如下
Date& Date::operator++() //前置++需要先++在使用,所以不需要创建临时对象,返回值可以是引用
{
++_day; //天数加一
if (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) //如果天数不符合该月最大天数,则需要调整
{
++_month; //让月加一
if (_month > 12) //月不合法就调整月
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
_day = 1; 让天数置一
}
return *this; //返回该类
}
后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
可直接复用前置++,后置++需要先使用再++,所以需要创建临时对象,代码如下
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date d = *this;
++(*this);
return d;
}
后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
与++的实现不同,--的话先实现后置再实现前置。代码如下
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date d = *this; // 创建临时对象,保存日期类中的值
--_day; //日期类中的天数减一
if (_day <= 0) //这里可以不用写小于,因为一天一天的减是不可能跨过零来到负数的
{
--_month; //如果天数等于零了,就需要借上个月的天数,月要减一
if (_month <= 0) //月不合法就调整月
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day = GetMonthDay(_year, _month); //把天数置成该月最大天数
}
return d; //返回保存好的数据,这样就实现了后置--的效果
}
前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
直接复用后置--,代码如下
Date& Date::operator--()
{
(*this)--;
return *this;
}
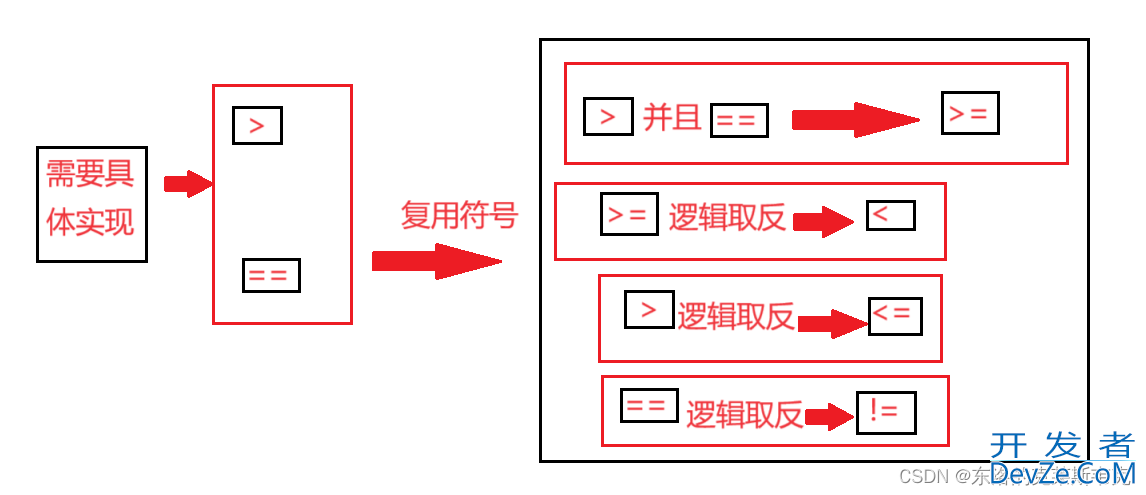
实现比较大小运算符重载思路
小编先理一下思路,方便大家理解。
要实现比较大小的运算符有 >, ==, >=, < , <= , !=。只需要实现> 和 ==就可以复用并实现后四个运算符。如下图
>运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(co编程nst Date& d)
代码如下
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year) //年大就大
{
return true;
}
if (_year == d._year)//年相等比月
{
if (_month > d._month) //月大就大
{
return true;
}
if (_month == d._month) //月相等比天
{
if (_day > d._day) //天大就大
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false; //不然就是小的
}
==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
年月日都相等才相等,代码如下
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
*> = 运算符复用实现其他比较运算符重载
这里不做重点,大家可以点击“目录”,再点击”日期-日期“即可跳过
>=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return (*this) > d || (*this) == d;
}
<运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date & d)
{
return !((*this) >= d);
}
<=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !((*this) > d);
}
!=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !((*this) == d);
}
日期-日期
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
参数:第一个参数为隐含的this指针,第二个参数为 const Date&,传引用是为了提高传值效率。
返回值:日期-日期代表的是两个日期之间相差的天数,返回值类型为 int。
思路1:可以先算出两个日期相差多少年,把每一年的总天数加在一起,但要判断该年是否为闰年。
思路2:直接复用++运算符,在设一个变量,每加一天,变量就加一。
下面用思路2实现,代码如下
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
int counst = 0; //定义一个变量,保存天数
if ((*this) == d) //如果两个日期相等,直接返回零
{
return 0;
}
else if ((*this) > d)
{
Date tmp = d; //如果this的的日期大,就给d创建临时变量tmp,然tmp小日期去追this大日期
while ((*this) != tmp)
{
++tmp;
counst++;
}
return counst;
}
else
{
Date tmp = (*this); //同上
while (tmp != d)
{
++tmp;
counst++;
}
return counst;
}
}
代码错误和bug分享
小编在实现方法的时候把域作用限定符写在了返回值的前面,如下
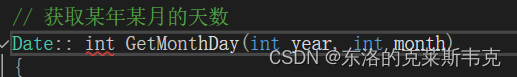
大家不要这样写呀。
在写前置++的时候写了一个不易察觉的bug,写完测了几组数据没问题,但其他方法调用的时候却出问题了,调了好久才发现,如下代码,大家能看出来哪里出错了吗
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++() // bug分享
{
++_day;
if (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
++_month;
if (_month > 12)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
_day = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
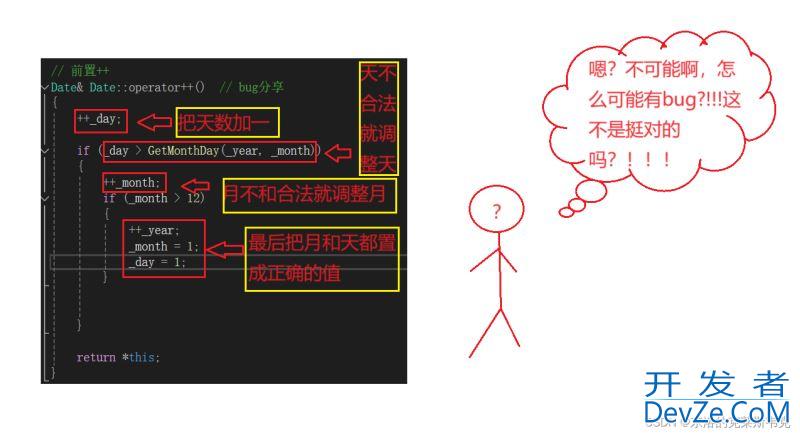
哈哈,其实正是因为逻辑太顺了,忽略了一些情况如下图
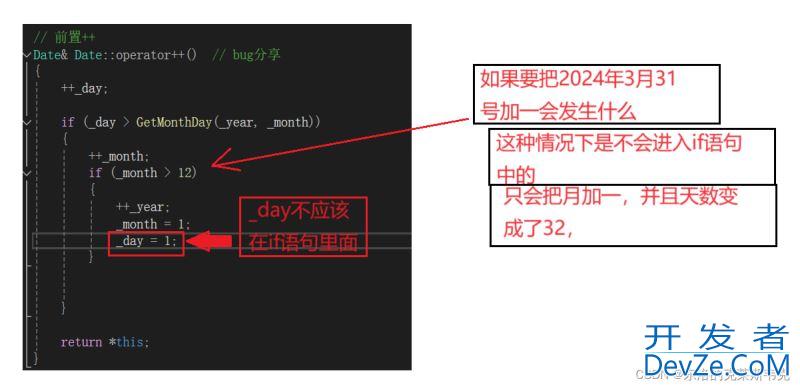
大家在测方法的时候尽量要跨过几个平年和闰年,这样方法才有可信度。
以上就是详解如何用C++写一个日期计算器的详细内容,更多关于C++日期计算器的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论