如何使用Java爬虫批量爬取图片
目录
- Java爬取图片
- 爬取思路
- 具体步骤
- 具体代码
- 实体类 Picture 和 工具类 HeaderUtil
- 下载类
- 最重要的类:解析页面类 PictureSpider
- 启动类 BootStrap
- 爬取结果
- 注意事项
- 总结
Java爬取图片
现在开始学习爬虫,对于爬虫的入门来说,图片相对来说是比较容易获取的,因为大部分图片都不是敏感数据,所以不会遇到什么反爬措施,对于入门爬虫来说是比较合适的。
使用技术:Java基础知识、HttpClient 4.x 、jsoup
学习目标:下载静态资源图片。
爬取思路
对于这种图片的获取,其实本质上就是就是文件的下载(HttpClient)。但是因为不只是获取一张图片,所以还会有一个页面解析的处理过程(Jsoup)。
Jsoup:解析html页面,获取图片的链接。
HttpClient:请求图片的链接,保存图片到本地。
具体步骤
首先进入首页分析,主要有以下几个分类(这里不是全部分类,但是这几个也足够了,这只是学习技术而已。),我们的目标就是获取每个分类下的图片。
这里来分析一下网站的结构,我这里就简单一点吧。 下面这张图片是大致的结构,这里选取一个分类标签进行说明。 一个分类标签页含有多个标题页,然后每个标题页含有多个图片页。(对应标题页的几十张图片)
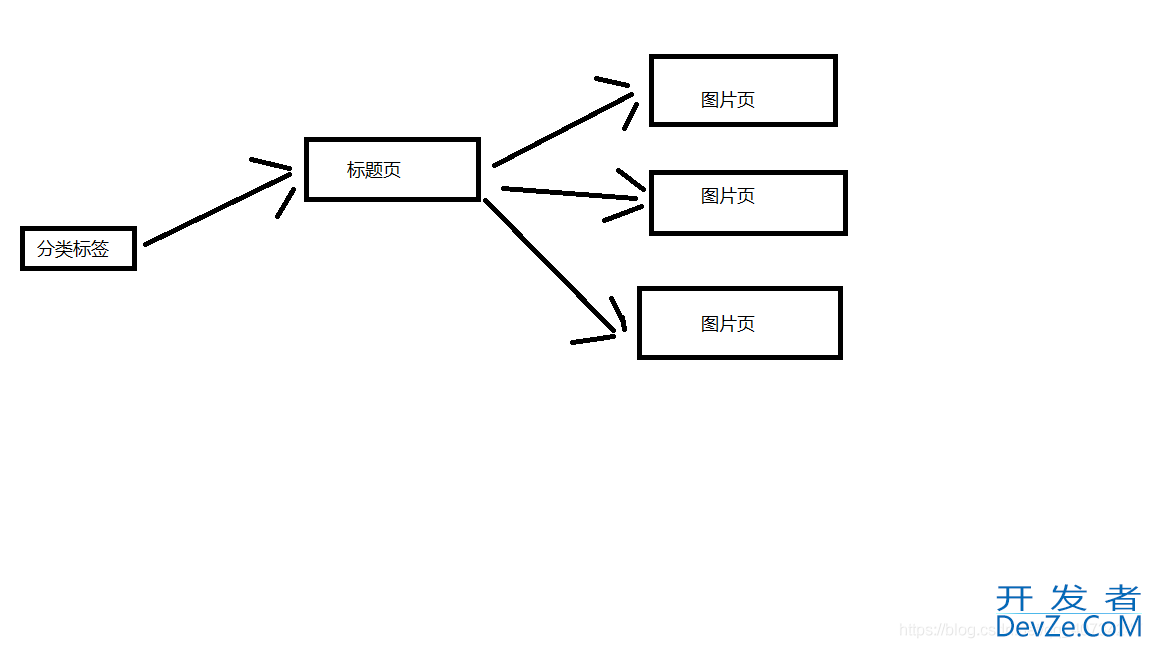
对网站的结构有了大致了解之后,就可以着 手开始爬取图片了。 这里还有一个需要注意,大概是前辈们做得太过了,导致这个网站已经开始有反爬虫机制了。不过,幸好它还不是很强大,我们还是可以绕过去的。这个网站的反爬虫机制主要就是:UA、Referer。
这是从知乎上面学习到的经验。
具体代码
导入项目依赖jar包坐标或者直接下载对应的jar包,导入项目也可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.11.3</version>
</dependency>
实体类 Picture 和 工具类 HeaderUtil
实体类:把属性封装成一个对象,这样调用方便一点。
package com.picture;
public class Picture {
private String title;
private String url;
public Picture(String title, String url) {
this.title = title;
this.url = url;
}
public String getTitle() {
return this.title;
}
public String getUrl() {
return this.url;
}
}
工具类:不断变换 UA(我也不知道有没有用,不过我是使用自己的ip,估计用处不大了)
package com.picture;
public class HeaderUtil {
public static String[] headers = {
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/39.0.2171.95 Safari/537.36",
"Mozilla/5.0 (MACintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/35.0.1916.153 Safari/537.36",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:30.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/30.0",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.75.14 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/7.0.3 Safari/537.75.14",
"Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 10.0; Windows NT 6.2; Win64; x64; Trident/6.0)",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; it; rv:1.8.1.11) Gecko/20071127 Firefox/2.0.0.11",
"Opera/9.25 (Windows NT 5.1; U; en)",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; .NET CLR 2.0.50727)",
"Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Konqueror/3.5; linux) KHTML/3.5.5 (like Gecko) (KUbuntu)",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux i686; en-US; rv:1.8.0.12) Gecko/20070731 Ubuntu/dapper-security Firefox/1.5.0.12",
"Lynx/2.8.5rel.1 libwww-FM/2.14 SSL-MM/1.4.1 GNUTLS/1.2.9",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux i686) AppleWebKit/535.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Ubuntu/11.04 Chromium/16.0.912.77 Chrome/16.0.912.77 Safari/535.7",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux i686; rv:10.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/10.0 "
};
}
下载类
多线程实在是太快了,再加上我只有一个ip,没有代理ip可以用(我也不太了解),使用多android线程被封ip是很快的。
package com.picture;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Random;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import com.m3u8.HttpClientUtil;
public class SinglePictureDownloader {
private String referer;
private CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
private Picturpythone picture;
private String filePath;
public SinglePictureDownloader(Picture picture, String referer, String filePath) {
this.httpClient = HttpClientUtil.getHttpClient();
this.picture = picture;
this.referer = referer;
this.filePath = filePath;
}
public void download() {
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(picture.getUrl());
Random rand = new Random();
//设置请求头
get.setHeader("User-Agent", HeaderUtil.headers[rand.nextInt(HeaderUtil.headers.length)]);
get.setHeader("referer", referer);
System.out.println(referer);
HttpEntity entity = null;
try (CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(get)) {
www.devze.com int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (statusCode == 200) {
entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
File picFile = new File(filePath, picture.getTitle());
try (OutputStream out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(picFile))) {
entity.writeTo(out);
System.out.println("下载完毕:" + picFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//关闭实体,关于 httpClient 的关闭资源,有点不太了解。
EntityUtils.consume(entity);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
这是获取 HttpClient 连接的工具类,避免频繁创建连接的性能消耗。(但是因为我这里是使用单线程来爬取,所以用处就不大了。我就是可以只使用一个HttpClient连接来爬取,这是因为我刚开始是使用多线程来爬取的,但是基本获取几张图片就被禁掉了,所以改成单线程爬虫。所以这个连接池也就留下来了。)
package com.m3u8;
import org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager;
public class HttpClientUtil {
private static final int TIME_OUT = 10 * 1000;
private static PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager pcm; //HttpClient 连接池管理类
private static RequestConfig requestConfig;
static {
requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(TIME_OUT)
.setConnectTimeout(TIME_OUT)
.setSocketTimeout(TIME_OUT).build();
pcm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
pcm.setMaxTotal(50);
pcm.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(10); //这里可能用不到这个东西。
}
public static CloseableHttpClient getHttpClient() {
return HttpClients.custom()
.setConnectionManager(pcm)
.setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig)
.build();
}
}
最重要的类:解析页面类 PictureSpider
package com.picture;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.jsoup.Jsoup;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Document;
import org.jsoup.select.Elements;
import com.m3u8.HttpClientUtil;
/**
* 首先从顶部分类标题开始,依次爬取每一个标题(小分页),每一个标题(大分页。)
* */
public class PictureSpider {
private CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
private String referer;
private String rootPath;
private String filePath;
public PictureSpider() {
httpClienthttp://www.devze.com = HttpClientUtil.getHttpClient();
}
/**
* 开始爬虫爬取!
*
* 从爬虫队列的第一条开始,依次爬取每一条url。
*
* 分页爬取:爬10页
* 每个url属于一个分类,每个分类一个文件夹
* */
public void start(List<String> urlList) {
urlList.stream().forEach(url->{
this.referer = url;
String dirName = url.substring(22, url.length()-1); //根据标题名字去创建目录
//创建分类目录
File path = new File("D:/DragonFile/DBC/mzt/", dirName); //硬编码路径,需要用户自己指定一个
if (!path.exists()) {
path.mkdir();
rootPath = path.toString();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { //分页获取图片数据,简单获取几页就行了
this.page(url + "page/"+ 1);
}
});
}
/**
* 标题分页获取链接
* */
public void page(String url) {
System.out.println("url:" + url);
String html = this.getHtml(url); //获取页面数据
Map<String, String> picMap = this.extractTitleUrl(html); //抽取图片的url
if (picMap == null) {
return ;
}
//获取标题对应的图片页面数据
this.getPictureHtml(picMap);
}
private String getHtml(String url) {
String html = null;
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(url);
get.setHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3100.0 Safari/537.36");
get.setHeader("referer", url);
try (CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(get)) {
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (statusCode == 200) {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
html = EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTf-8"); //关闭实体?
}
}
else {
System.out.println(statusCode);
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return html;
}
private Map<String, String> extractTitleUrl(String html) {
if (html == null) {
return null;
}
Document doc = Jsoup.parse(html, "UTF-8");
Elements pictures = doc.select("ul#pins > li");
//不知为何,无法直接获取 a[0],我不太懂这方面的知识。
//那我就多处理一步,这里先放下。
Elements pictureA = pictures.stream()
.map(pic->pic.getElementsByTag("a").first())
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(Elements::new));
return pictureA.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(
pic->pic.getElementsByTag("img").first().attr("alt"),
pic->pic.attr("href")));
}
/**
* 进入每一个标题的链接,再次分页获取图片的链接
* */
private void getPictureHtml(Map<String, String> picMap) {
//进入标题页,在标题页中再次分页下载。
picMap.forEach((title, url)->{
//分页下载一个系列的图片,每个系列一个文件夹。
File dir = new File(rootPath, title.trim());
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdir();
filePath = dir.toString(); //这个 filePath 是每一个系列图python片的文件夹
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 60; i++) {
String html = this.getHtml(url + "/" + i);
if (html == null) {
//每个系列的图片一般没有那么多,
//如果返回的页面数据为 null,那就退出这个系列的下载。
return ;
}
Picture picture = this.extractPictureUrl(html);
System.out.println("开始下载");
//多线程实在是太快了(快并不是好事,我改成单线程爬取吧)
SinglePictureDownloader downloader = new SinglePictureDownloader(picture, referer, filePath);
downloader.download();
try {
Thread.sleep(1500); //不要爬的太快了,这里只是学习爬虫的知识。不要扰乱别人的正常服务。
System.out.println("爬取完一张图片,休息1.5秒。");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* 获取每一页图片的标题和链接
* */
private Picture extractPictureUrl(String html) {
Document doc = Jsoup.parse(html, "UTF-8");
//获取标题作为文件名
String title = doc.getElementsByTag("h2")
.first()
.text();
//获取图片的链接(img 标签的 src 属性)
String url = doc.getElementsByAttributeValue("class", "main-image")
.first()
.getElementsByTag("img")
.attr("src");
//获取图片的文件扩展名
title = title + url.substring(url.lastIndexOf("."));
return new Picture(title, url);
}
}
启动类 BootStrap
这里有一个爬虫队列,但是我最终连第一个都没有爬取完,这是因为我计算失误了,少算了两个数量级。但是,程序的功能是正确的。
package com.picture; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * 爬虫启动类 * 开发者_C入门*/ public class BootStrap { public static void main(String[] args) { //反爬措施:UA、refer 简单绕过就行了。 //refer https://www.mzitu.com //使用数组做一个爬虫队列 String[] urls = new String[] { "https://www.mzitu.com/xinggan/", "https://www.mzitu.com/zipai/" }; // 添加初始队列,启动爬虫 List<String> urlList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(urls)); PictureSpider spider = new PictureSpider(); spider.start(urlList); } }
爬取结果
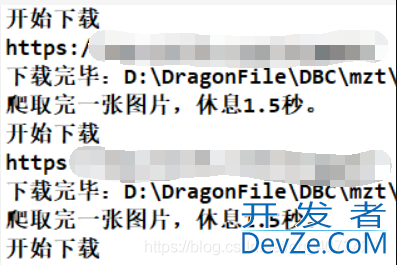

注意事项
这里有一个计算失误,代码如下:
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { //分页获取图片数据,简单获取几页就行了
this.page(url + "page/"+ 1);
}
这个 i 的取值过大了,因为我计算的时候失误了。如果按照这个情况下载的话,总共会下载:4 * 10 * (30-5) * 60 = 64800 张。(每一页是含有30个标题页,大概5个是广告。) 我一开始以为只有几百张图片! 这是一个估计值,但是真实的下载量和这个不会差太多的(没有数量级的差距)。所以我下载了一会发现只下载了第一个队列里面的图片。当然了,作为一个爬虫学习的程序,它还是很合格的。
这个程序只是用来学习的,我设置每张图片的下载间隔时间是1.5秒,而且是单线程的程序,所以速度上会显得很慢。但是那样也没有关系,只要程序的功能正确就行了,应该没有人会真的等到图片下载完吧。
那估计要好久了:64800*1.5s = 97200s = 27h,这也只是一个粗略的估计值,没有考虑程序的其他运行时间,不过其他时间可以基本忽略了。
总结
虽然说Java比较麻烦(相对于python,确实是不够简洁了)。但是我们学习的是技术呀,这点小困难还是能克服的,如果你只是想要下载图片,那还是去看python的爬虫吧。Java的HttpClient也就够学一段时间了,发现这个东西真的是挺好用的,但是我也只是学习了一点点。这个类库,不仅可以用来写爬虫(做爬虫只是它功能比较强大而已),而且还能做很多有趣的事情。爬虫,还是很有意思的,有很多有趣的地方,可以让我们探索。但是,也要注意,本意是学习技术,不能搞破坏。
到此这篇关于如何使用Java爬虫批量爬取图片的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java爬虫批量爬取图片内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!







 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论