pandas中的DataFrame数据遍历解读
目录
- pandas DataFrame数据遍历
- 读取csv内容,格式与数据类型如下
- 按行遍历数据:iterrows
- 按行遍历数据:itertuples
- 按列遍历数据:iteritems
- 读取和修改某一个数据
- 遍历dataframe中每一个数据
- dataframe遍历效率对比
- 构建数据
- 9种遍历方法
- 效率对比
- 说下结论
- 总结
pandas DataFrame数据遍历
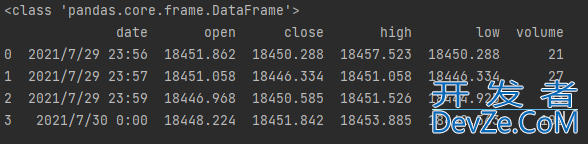
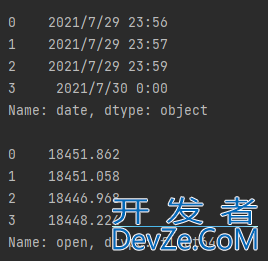
读取csv内容,格式与数据类型如下
data = pd.read_csv('save\LH8888.csv')
print(type(data))
print(data)
输出结果如下:
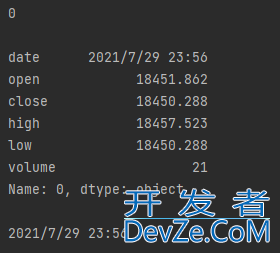
按行遍历数据:iterrows
获取行名:名字、年龄、身高、体重
for i, line in data.iterrows():
print(i)
print(line)
print(line['date'])
输出结果如下:
i:是数据的索引,表示第几行数据line:是每一行的具体数据line[‘date’]:通过字典的方式,能够读取数据
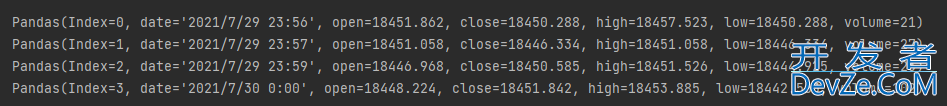
按行遍历数据:itertuples
for line in data.itertuples():
print(line)
输出结果如下:
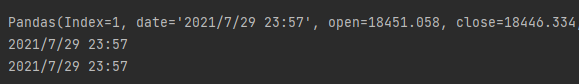
访问date方式如下:
for line in data.itertuples():
print(line)
print(getattr(line, 'date'))
print(line[1])
输出结果如下:
按列遍历数据:iteritems
for i, index in data.iteritems():
print(index)
输出结果如下,使用方式同iterrows。
读取和修改某一个数据
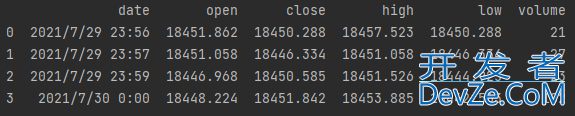
例如:我们想要读取 行索引为:1,列索引为:volume的值 27,代码如下:
iloc:需要输入索引值,索引从0开始loc:需要输入对应的行名和列名
print(data.iloc[1, 5]) print(data.loc[1, 'volume'])
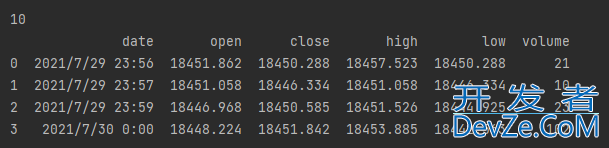
例如:我们想要将 行索引为:1,列索引为:volume的值 27 修改为10,代码如下:
data.iloc[1, 5] = 10 print(data.loc[1, 'volume']) print(data)
输出结果如下:
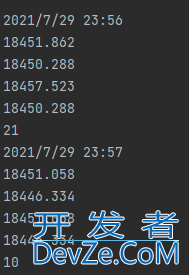
遍历dataframe中每一个数据
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
for j in range(data.shape[1]):
print(data.iloc[i, j])
输出结果如下,按行依次打印:
dataframe遍历效率对比
构建数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 生成樣例數據
def gen_sample():
aaa = np.random.uniform(1,1000,3000)
bbb = np.random.uniform(1,1000,3000)
ccc = np.random.uniform(1,1000,3000)
ddd = np.random.uniform(1,1000,3000)
return pd.DataFrame({'aaa':aaa,'bbb':bbb, 'ccc': ccc, 'ddd': ddd})
9种遍历方法
# for + iloc 定位
def method0_sum(DF):
for i in range(len(DF)):
a = DF.iloc[i,0] + DF.iloc[i,1]
# for + iat 定位
def method1_sum(DF):
for i in rang开发者_JS教程e(len(DF)):
a = DF.iat[i,0] + DF.iat[i,1]
# pandaswww.devze.com.DataFrame.iterrows() 迭代器
def method2_sum(DF):
for index, rows in http://www.devze.comDF.iterrows():
a = rows['aaa'] + rows['bbb']
# pandas.DataFrame.apply 迭代
def method3_sum(DF):
a = DF.apply(lambda x: x.aaa + x.bbb, axis=1)
# pandas.DataFrame.apply 迭代
def method4_sum(DF):
a = DF[['aaa','bbb']].apply(lambda x: x.aaa + x.bbb, axis=1)
# 列表
def method5_sum(DF):
a = [ a+b for a,b in zip(DF['aaa'],DF['bbb']) ]
# pandas
def method6_sum(DF):
a = DF['aaa'] + DF['bbb']
# numpy
def method7_sum(DF):
a = DF['aaa'].values + DF['bbb'].values
# for + itertuples
def method8_sum(DF):
for row in DF.itertuples():
a = getattr(row, 'aaa') + getattr(row, 'bbb')
效率对比
df = gen_sample()
print('for + iloc 定位:')
%timeit method0_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('for + iat 定位:')
%timeit method1_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('apply 迭代:')
%timeit method3_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('apply 迭代 + 兩列:')
%timeit method4_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('列表:')
%timeit method5_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('pandas 数组操作:')
%timeit method6_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('numpy 数组操作:')
%timeit method7_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('for itertuples')
%timeit method8_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('for iteritems')
%timeit method9_sum(df)
df = gen_sample()
print('for iterrows:')
%timeit method2_sum(df)
结果:
for + iloc 定位:
225 ms ± 9.14 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)for + iat 定位:201 ms ± 6.37 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)apply 迭代:88.3 ms ± 2.3 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)apply 迭代 + 兩列:91.2 ms ± 5.29 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)列表:1.12 ms ± 54.7 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)pandas 数组操作:262 µs ± 9.21 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)numpy 数组操作:14.4 µs ± 383 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)for itertuples6.4 ms &plusm编程客栈n; 265 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)for iterrows:330 ms ± 22.3 ms jsper loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
说下结论
numpy数组 > iteritems > pandas数组 > 列表 > itertuples > apply > iat javascript> iloc > iterrows
itertuples > iterrows ;快50倍
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论