pytorch使用-tensor的基本操作解读
目录
- 一、tejsnsor加减乘除
- 二、tensor矩阵运算
- 四、tensor切片操作
- 五、tensor改变形状
- 六、tensor 和 numpy.array相互转换
- 七、tensor 转到GPU上
- 总结
一、tensor加减乘除
加法操作
import torch x = torch.randnwww.devze.com(2, 3) y = torch.randn(2, 3) z = x + y print(z) z = torch.add(x, y) print(z) y.add_(x) print(y)
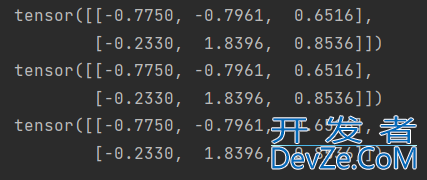
其他操作类似:减法:sub(-), 乘法:mul(*), 除法:div(/)
二、tensor矩阵运算
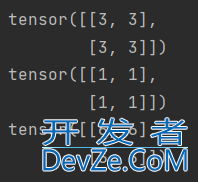
# 二维矩阵相乘 a = torch.full([2, 2], 3, dtype=torch.long) b = torch.ones(2, 2, dtype=torch.long) print(a) print(b) print(torch.mm(a, b))
# matmul 和 @ 可以用于二维矩阵计算,也可以是多维 # 四维,计算的时候就是前两维不变,后两维进行计算。 a = torch.rand(1, 1, 3, 2) b = torch.rand(1, 1, 2, 4) c = torch.matmul(a, b) print(a) print(b) print(c)

pow
a = torch.full([2, 2], 6) print(a.pow(3)) a = torch.full([2, 2], 6) print(a**2)
sqrt: 平方根rsqrt: 平方根倒数
a = torch.full([2, 2], 1024) print(a.sqrt()) print(a.rsqrt()) print(a**0.5)
exp log
a = torch.ones(2, 2) print(torch.exp(a)) print(torch.log(a)) print(torch.log2(a))
.flphpoor()——往下近似.ceil(php)——往上近似.trunc()——裁剪为整数部分.frac()——裁剪成小数部分
a = torch.tensor(3.1415926) print(a.floor()) print(a.ceil()) print(a.trunc()) print(a.frac())
torch.round()——四舍五入
a = torch.tensor(3.1415926) print(a.round())
.item() 转化为python number
x = torch.randn(1) print(x) print(x.item())

四、tensor切片操作
a = torch.randn(4, 3) print(a) # 取第二列 print(a[:, 1]) # 取前两列 print(a[:, :2])

五、tensor改变形状
x = torch.randn(4, 4) y = x.view(16) # -1, 自动匹配个数 z = x.view(-1, 8) print(x) print(y) print(z)

六、tensor 和 numpy.array相互转换
# 底层内存共享 x = torch.ones(5) print(x) y = x.numpy() print(y) x.add_(1) print(y)
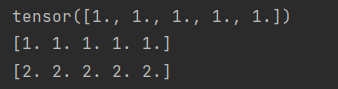
import numpy as np x = np.ones(5) y = torch.from_numpy(x) print(y)

七、tensor 转到GPU上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
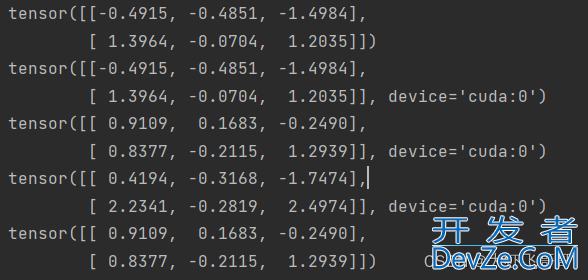
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(androidx)
y = x.to(device)
print(y)
z = torch.randn(2, 3, device="cuda")
print(z)
# 同时在GPU上才能相加
print(y + z)
# 转换会cpu
print(z.to("cpu"))
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。






 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论