pytorch建立mobilenetV3-ssd网络并进行训练与预测方式
目录
- Step1:搭建mobilenetV3-ssd网络框架
- 需要提前准备的函数和类
- mobilenetV3_large
- 调用mobilenetV3的ssd网络
- Step2:训练
- 训练数据预处理(VOC形式的dbb数据)
- 数据检测
- 编写训练程序
- step3:预测
- 总结
这篇文章记录的是我在公司实习用深度学习做车辆信息识别项目时,用来做车辆检测的算法。
因为我们公司面向的边缘端计算,边缘盒子的计算能力有限,所以我们在做算法研究时,就尽量选用轻量级算法,所以目标检测算法用mobilenetV3-ssd,这是一个精度能达到很高,权值很小的算法,我比较喜欢。
Step1:搭建mobilenetV3-ssd网络框架
它的网络原理很简单,就是把传统的ssd算法里面的VGG网络换成了mobilenetV3,其他的都一样。
需要提前准备的函数和类
在真的写网络框架之前,我们需要把网络中需要调用的一些激活函数和卷积块先写好。
先是mobilenetV3需要调用的两个激活函数,一个注意力模型SeModule,和卷积块block。
class hswish(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
out = x * F.relu6(x + float(3.0), inplace=True) / float(6.0)
return out
class hsigmoid(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
out = F.relu6(x + float(3.0), inplace=True) / float(6.0)
return out
class SeModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_size, reduction=4):
super(SeModule, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.se = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_size, in_size // reduction, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BATchNorm2d(in_size // reduction),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_size // reduction, in_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_size),
hsigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.se(x)
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size, in_size, expand_size, out_size, nolinear, semodule, stride):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.se = semodule
self.output_status = False
if kernel_size == 5 and in_size == 160 and expand_size == 672:
self.output_status = True
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_size, expand_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_size)
self.nolinear1 = nolinear
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(expand_size, expand_size, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=kernel_size//2, groups=expand_size, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_size)
self.nolinear2 = nolinear
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(expand_size, out_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_size)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
if stride == 1 and in_size != out_size:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_size, out_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_size),
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.nolinear1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
if self.output_status:
expand = out
out = self.nolinear2(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
out = self.bn3(self.conv3(out))
if self.se != None:
out = self.se(out)
out = out + self.shortcut(x) if self.stride==1 else out
if self.output_status:
return (expand, out)
return out
然后是ssd网络需要调用的卷积块。
def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride, groups=1, activation=nn.ReLU6):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False, groups=groups),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
activation(inplace=True)
)
def conv_1x1_bn(inp, oup, groups=1, activation=nn.ReLU6):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False, groups=groups),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
activation(inplace=True)
)
class AuxiliaryConvolutions(nn.Module):
"""
辅助卷积层
"""
def __init__(self):
super(AuxiliaryConvolutions, self).__init__()
self.extra_convs = []
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(960, 256))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_bn(256, 256, 2, groups=256))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(256, 512, groups=1))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(512, 128))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_bn(128, 128, 2, groups=128))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(128, 256))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(256, 128))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_bn(128, 128, 2, groups=128))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(128, 256))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(256, 64))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_bn(64, 64, 2, groups=64))
self.extra_convs.append(conv_1x1_bn(64, 128))
self.extra_convs = nn.Sequential(*self.extra_convs)
self.init_conv2d()
def init_conv2d(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, conv7_feats):
"""
Forward propagation.
:param conv7_feats: lower-level conv7 feature map
:return: higher-level feature maps conv8_2, conv9_2, conv10_2, and conv11_2
"""
outs = []
out=conv7_feats
for i, conv in enumerate(self.extra_convs):
out = conv(out)
if i % 3 == 2:
outs.append(out)
conv8_2_feats=outs[0]
conv9_2_feats=outs[1]
conv10_2_feats=outs[2]
conv11_2_feats=outs[3]
return conv8_2_feats, conv9_2_feats, conv10_2_feats, conv11_2_feats
class PredictionConvolutions(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_classes):
"""
预测卷积层
"""
super(PredictionConvolutions, self).__init__()
self.n_classes = n_classes
n_boxes = {'conv4_3': 4,
'conv7': 6,
'conv8_2': 6,
'conv9_2': 6,
'conv10_2': 6,
'conv11_2': 6}
input_channels=[672, 960, 512, 256, 256, 128]
self.loc_conv4_3 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[0], n_boxes['conv4_3'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.loc_conv7 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[1], n_boxes['conv7'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.loc_conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[2], n_boxes['conv8_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.loc_conv9_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[3], n_boxes['conv9_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.loc_conv10_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[4], n_boxes['conv10_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.loc_conv11_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[5], n_boxes['conv11_2'] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.cl_conv4_3 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[0], n_boxes['conv4_3'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.cl_conv7 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[1], n_boxes['conv7'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.cl_conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[2], n_boxes['conv8_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.cl_conv9_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[3], n_boxes['conv9_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.cl_conv10_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[4], n_boxes['conv10_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.cl_conv11_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels[5], n_boxes['conv11_2'] * n_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.init_conv2d()
def init_conv2d(self):
"""
Initialize convolution parameters.
"""
for c in self.children():
if isinstance(c, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(c.weight)
nn.init.constant_(c.bias, 0.)
def forward(self, conv4_3_feats, conv7_feats, conv8_2_feats, conv9_2_feats, conv10_2_feats, conv11_2_feats):
batch_size = conv4_3_feats.size(0)
l_conv4_3 = self.loc_conv4_3(conv4_3_feats)
l_conv4_3 = l_conv4_3.permute(0, 2, 3,
1).contiguous()
l_conv4_3 = l_conv4_3.view(batch_size, -1, 4)
l_conv7 = self.loc_conv7(conv7_feats)
l_conv7 = l_conv7.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
l_conv7 = l_conv7.view(batch_size, -1, 4)
l_conv8_2 = self.loc_conv8_2(conv8_2_feats)
l_conv8_2 = l_conv8_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
l_conv8_2 = l_conv8_2.view(batch_size, -1, 4)
l_conv9_2 = self.loc_conv9_2(conv9_2_feats)
l_conv9_2 = l_conv9_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
l_conv9_2 = l_conv9_2.view(batch_size, -1, 4)
l_conv10_2 = self.loc_conv10_2(conv10_2_feats)
l_conv10_2 = l_conv10_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
l_conv10_2 = l_conv10_2.view(batch_size, -1, 4)
l_conv11_2 = self.loc_conv11_2(conv11_2_feats)
l_conv11_2 = l_conv11_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
l_conv11_2 = l_conv11_2.view(batch_size, -1, 4)
c_conv4_3 = self.cl_conv4_3(conv4_3_feats)
c_conv4_3 = c_conv4_3.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
c_conv4_3 = c_conv4_3.view(batch_size, -1,self.n_classes)
c_conv7 = self.cl_conv7(conv7_feats)
c_conv7 = c_conv7.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
c_conv7 = c_conv7.view(batch_size, -1,self.n_classes)
c_conv8_2 = self.cl_conv8_2(conv8_2_feats)
c_conv8_2 = c_conv8_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
c_conv8_2 = c_conv8_2.view(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
c_conv9_2 = self.cl_conv9_2(conv9_2_feats)
c_conv9_2 = c_conv9_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
c_conv9_2 = c_conv9_2.view(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
c_conv10_2 = self.cl_conv10_2(conv10_2_feats)
c_conv10_2 = c_conv10_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
c_conv10_2 = c_conv10_2.view(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
c_conv11_2 = self.cl_conv11_2(conv11_2_feats)
c_conv11_2 = c_conv11_2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
c_conv11_2 = c_conv11_2.view(batch_size, -1, self.n_classes)
locs = torch.cat([l_conv4_3, l_conv7, l_conv8_2, l_conv9_2, l_conv10_2, l_conv11_2], dim=1)
classes_scores = torch.cat([c_conv4_3, c_conv7, c_conv8_2, c_conv9_2, c_conv10_2, c_conv11_2],dim=1)
return locs, classes_scores
mobilenetV3_large
class MobileNetV3_Large(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(MobileNetV3_Large, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm编程客栈2d(16)
self.hs1 = hswish()
self.bneck = nn.Sequential(
Block(3, 16, 16, 16, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 1),
Block(3, 16, 64, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 2),
Block(3, 24, 72, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 1),
Block(5, 24, 72, 40, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(40), 2),
Block(5, 40, 120, 40, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(5, 40, 120, 40, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(3, 40, 240, 80, hswish(), None, 2),
Block(3, 80, 200, 80, hswish(), None, 1),
Block(3, 80, 184, 80, hswish(), None, 1),
Block(3, 80, 184, 80, hswish(), None, 1),
Block(3, 80, 480, 112, hswish(), SeModule(112), 1),
Block(3, 112, 672, 112, hswish(), SeModule(112), 1),
Block(5, 112, 672, 160, hswish(), SeModule(160), 1),
Block(5, 160, 672, 160, hswish(), SeModule(160), 2),
Block(5, 160, 960, 160, hswish(), SeModule(160), 1),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(160, 960, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(960)
self.hs2 = hswish()
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(960, 1280)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1280)
self.hs3 = hswish()
self.linear4 = nn.Linear(1280, 1000)
self.init_weights() #这个是加载预训练权值或初始化权值
# def load_pretrained_layers(self,pretrained):
# pretrained_state_dict = torch.load(pretrained)
# self.load_state_dict(pretrained_state_dict)
# for param in self.parameters():
# param.requires_grad = False
# print("\nLoaded base model.\n")
def init_weights(self, pretrained=None):#如果不用预训练权值,把pretrained设为None就行
if isinstance(pretrained, str): #判断一个对象是否是一个已知类型
checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained,map_location='cpu') ["state_dict"]
self.load_state_dict(checkpoint,strict=False)
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True # to be or not to be
# also load module
# if isinstance(checkpoint, OrderedDict):
# state_dict = checkpoint
# elif isinstance(checkpoint, dict) and 'state_dict' in checkpoint:
# state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
# else:
# print("No state_dict found in checkpoint file")
# if list(state_dict.keys())[0].startswith('module.'):
# state_dict = {k[7:]: v for k, v in checkpoint['state_dict'].items()}
# # load state_dict
# if hasattr(self, 'module'):
# self.module.load_state_dict( state_dict,strict=False)
# else:
# self.load_state_dict(state_dict,strict=False)
print("\nLoaded base model.\n")
elif pretrained is None:
print("\nNo loaded base model.\n")
for m in self.modules(): #self.modules()里面存储了net的所有模块。
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out') #用kaiming正态分布进行初始化。
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.hs1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
for i, block in enumerate(self.bneck):
out = block(out)
if isinstance(out, tuple):
conv4_3_feats =out[0]
out = out[1]
out = self.hs2(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
conv7_feats=out
return conv4_3_feats,conv7_feats
调用mobilenetV3的ssd网络
class SSD300(nn.Module):
"""
The SSD300 network - encapsulates the base MobileNet network, auxiliary, and prediction convolutions.
"""
def __init__(self, n_classes):
super(SSD300, self).__init__()
self.n_classes = n_classes
self.base = MobileNetV3_Large(num_classes=self.n_classes)
self.aux_convs = AuxiliaryConvolutions()
self.pred_convs = PredictionConvolutions(n_classes)
self.rescale_factors = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, 672, 1, 1))
nn.init.constant_(self.rescale_factors, 20)
self.priors_cxcy = self.create_prior_boxes() #这是在初始化先验框?
def forward(self, image):
conv4_3_feats, conv7_feats = self.base(image)
norm = conv4_3_feats.pow(2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).sqrt()+1e-10
conv4_3_feats = conv4_3_feats / norm
conv4_3_feats = conv4_3_feats * self.rescale_factors
conv8_2_feats, conv9_2_feats, conv10_2_feats, conv11_2_feats = self.aux_convs(conv7_feats)
locs, classes_scores = self.pred_convs(conv4_3_feats, conv7_feats, conv8_2_feats, conv9_2_feats, conv10_2_feats,conv11_2_feats)
return locs, classes_scores
def create_prior_boxes(self):
fmap_dims = {'conv4_3': 19,
'conv7': 10,
'conv8_2': 5,
'conv9_2': 3,
'conv10_2': 2,
'conv11_2': 1}
obj_scales = {'conv4_3': 0.1,
'conv7': 0.2,
'conv8_2': 0.375,
'conv9_2': 0.55,
'conv10_2': 0.725,
'conv11_2': 0.9}
ASPect_ratIOS = {'conv4_3': [1., 2., 0.5],
'conv7': [1., 2., 3., 0.5, .333],
'conv8_2': [1., 2., 3., 0.5, .333],
'conv9_2': [1., 2., 3., 0.5, .333],
'conv10_2': [1., 2., 3., 0.5, .333],
'conv11_2': [1., 2., 3., 0.5, .333]}
fmaps = list(fmap_dims.keys())
prior_boxes = []
for k, fmap in enumerate(fmaps):
for i in range(fmap_dims[fmap]):
for j in range(fmap_dims[fmap]):
cx = (j + 0.5) / fmap_dims[fmap]
cy = (i + 0.5) / fmap_dims[fmap]
for ratio in aspect_ratios[fmap]:
prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, obj_scales[fmap] * sqrt(ratio), obj_scales[fmap] / sqrt(ratio)])
if ratio == 1.:
try:
additional_scale = sqrt(obj_scales[fmap] * obj_scales[fmaps[k + 1]])
except开发者_JAVA开发 IndexError:
additional_scale = 1.
prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, additional_scale, additional_scale])
prior_boxes = torch.FloatTensor(prior_boxes).to(device)
prior_boxes.clamp_(0, 1)
return prior_boxes
def detect_objects(self, predicted_locs, predicted_scores, min_score, max_overlap编程客栈, top_k):
"""
For each class, perform Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on boxes that are above a minimum threshold.
:param min_score: minimum threshold for a box to be considered a match for a certain class
:param max_overlap: maximum overlap two boxes can have so that the one with the lower score is not suppressed via NMS
:param top_k: if there are a lot of resulting detection across all classes, keep only the top 'k'
:return: detections (boxes, labels, and scores), lists of length batch_size
"""
batch_size = predicted_locs.size(0)
n_priors = self.priors_cxcy.size(0)
predicted_scores = F.softmax(predicted_scores, dim=2)
all_images_boxes = list()
all_images_labels = list()
all_images_scores = list()
assert n_priors == predicted_locs.size(1) == predicted_scores.size(1)
for i in range(batch_size):
decoded_locs = cxcy_to_xy(
gcxgcy_to_cxcy(predicted_locs[i], self.priors_cxcy))
image_boxes = list()
image_labels = list()
image_scores = list()
max_scores, best_label = predicted_scores[i].max(dim=1)
for c in range(1, self.n_classes):
class_scores = predicted_scores[i][:, c]
score_above_min_score = class_scores > min_score
n_above_min_score = score_above_min_score.sum().item()
if n_above_min_score == 0:
continue
class_scores = class_scores[score_above_min_score]
class_decoded_locs = decoded_locs[score_above_min_score]
class_scores, sort_ind = class_scores.sort(dim=0, descending=True)
class_decoded_locs = class_decoded_locs[sort_ind]
overlap = find_jaccard_overlap(class_decoded_locs, class_decoded_locs)
suppress = torch.zeros((n_above_min_score), dtype=torch.bool).to(device)
for box in range(class_decoded_locs.size(0)):
if suppress[box] == 1:
continue
suppress = torch.max(suppress, overlap[box] > max_overlap)
suppress[box] = 0
image_boxes.append(class_decoded_locs[~suppress])
image_labels.append(torch.LongTensor((~ suppress).sum().item() * [c]).to(device))
image_scores.append(class_scores[~suppress])
if len(image_boxes) == 0:
image_boxes.append(torch.FloatTensor([[0., 0., 1., 1.]]).to(device))
image_labels.append(torch.LongTensor([0]).to(device))
image_scores.append(torch.FloatTensor([0.]).to(device))
image_boxes = torch.cat(image_boxes, dim=0)
image_labels = torch.cat(image_labels, dim=0)
image_scores = torch.cat(image_scores, dim=0)
n_objects = image_scores.size(0)
if n_objects > top_k:
image_scores, sort_ind = image_scores.sort(dim=0, descending=True)
image_scores = image_scores[:top_k]
image_boxes = image_boxes[sort_ind][:top_k]
image_labels = image_labels[sort_ind][:top_k]
all_images_boxes.append(image_boxes)
all_images_labels.append(image_labels)
all_images_scores.append(image_scores)
return all_images_boxes, all_images_labels, all_images_scores
Step2:训练
关键在于训练,这里会利用pytorch的语法规则进行训练。
训练数据预处理(VOC形式的dbb数据)
本来是想在这写用VOC2007进行训练,但是后来想想,人总是要进步嘛,不能总是利用VOC官方给的数据训练吧,所以这里还是清楚的讲一下怎么将dbb数据转换成VOC格式,并且进行训练。
首先,去官网下载dbb数据。
然后,利用下面这个程序,将json格式的标注文件装换成XML格式的标注文件。
import os
from json import loads
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
def jsonToXml(json_path, xml_path):
#@abstract: transfer json file to xml file
#json_path: complete path of the json file
#xml_path: complete path of the xml file
with open(json_path,'r',encoding='UTF-8')as json_file:
load_dict=loads(json_file.read())
#print(load_dict)
my_item_func = lambda x: 'Annotation'
xml = dicttoxml(load_dict,custom_root='Annotations',item_func=my_item_func,attr_type=False)
dom = parseString(xml)
#print(dom.toprettyxml())
#print(type(dom.toprettyxml()))
with open(xml_path,'w',encoding='UTF-8')as xml_file:
xml_file.write(dom.toprettyxml())
def json_to_xml(json_dir, xml_dir):
#transfer all json file which in the json_dir to xml_dir
if(os.path.exists(xml_dir)==False): #如果没有这个文件夹,就生成这个文件夹
os.makedirs(xml_dir)
dir = os.listdir(json_dir)
i=0
for file in dir:
file_list=file.split(".")
if(file_list[-1] == 'json'):
jsonToXml(os.path.join(json_dir,file),os.path.join(xml_dir,file_list[0]+'.xml'))
i=i+1
print('处理了第:',i,'个')
if __name__ == '__main__':
#transfer multi files
j_dir = "train" #存放json文件的文件夹路径
x_dir = "train_xml" #存放xml文件的文件夹路径,里面不需要有文件
json_to_xml(j_dir, x_dir)
然后,利用下面这个程序,生成ImageSets/main里面的train.txt文件。
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.7 # 可以自己设置
train_percent = 0.8 # 可以自己设置
xmlfilepath = f"Annotations" # 地址填自己的
txtsavepath = f"ImageSets/Main"
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
print('Well finshed')
然后,就是一个标准的VOC格式的dbb训练数据啦,简单不简单牙。
数据检测
注意,这里一定不要省,不然你训练的时候很容易出问题。比如dbb数据里面有些特征框没标注好,标注成了一条直线,导致训练的loss值会变成inf,你需要找出那些没标注好的图片然后把它删了。
我写的检查程序如下。注意,检查出来,删掉之后,要重新生成ImageSet/Main下的train.txt文件。
import json
with open('processed_data\TRAIN_objects.json','r') as obj:
a=json.load(obj)
with open('processed_data\TRAIN_images.json','r') as obj:
b=json.load(obj)
for i in range(0,len(a),1):
boxes=a[i]['boxes']
for boxe in boxes:
if boxe[0]==boxe[2]:
print(b[i])
if boxe[1]==boxe[3]:
print(b[i])
编写训练程序
import time
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.optim
import torch.utils.data
from model import SSD300, MultiBoxLoss
from datasets import PascalVOCDataset
from utils import *
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import ReduceLROnPlateau
# Data parameters
data_folder = 'processed_data' #训练数据路径文件所在的文件夹
keep_difficult = True #在voc数据标注里面,有difficult这一项,这里就是决定要不要用这个。
# Model parameters
# Not too many here since the SSD300 has a very specific structure
n_classes = len(label_map) # 分类的类别数,这个label_map是从utils里面导入进来的。
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Learning parameters
#checkpoint=None
checkpoint = 'weights/MobilenetV3_Large-ssd300.pth.tar' #这个是导入预训练权值。
batch_size = 16 # batch size
# iterations = 120000 # number of iterations to train 120000
workers = 8 #导入数据的进程数。进程数越多,导入得更快。
print_freq = 10 #决定每过多少个batchsize输出一次训练信息。
lr =1e-3 # learning rate
#decay_lr_to = 0.1 # decay learning rate to this fraction of the existing learning rate
momentum = 0.9 # momentum
weight_decay = 5e-4 # weight decay:加入权重衰减,收敛得会更快。
grad_clip = None #这是决定是否采用clip gradients方法,clip gradients方法是一种解决梯度爆炸的方法。
cudnn.benchmark = True #这是一种提高训练效率的方法,一般都会加
def main():
"""
Training.
"""
global start_epoch, label_map, epoch, checkpoint, decay_lr_at
#初始化模型,或者加载预训练权重
if checkpoint is None:
#如果没有预训练权重,则初始化模型
print("checkpoint none")
start_epoch = 0
model = SSD300(n_classes=n_classes) #在这个地方导入模型
# Initialize the optimizer, with twice the default learning rate for biases, as in the original Caffe repo
biases = list()
not_biases = list()
for param_name, param in model.named_parameters(): #model.named_parameters()给出网络的名字和参数迭代器
if param.requires_grad: #判断是否是需要求导的参数
if param_name.endswith('.bias'): #如果是以bias结尾的参数名,则需要加偏置。
biases.append(param)
else: #否则不需要加偏置。
not_biases.append(param)
# differnet optimizer
# optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=[{'params': biases, 'lr': 2 * lr}, {'params': not_biases}],
# lr=lr, momentum=momentum, weight_decay=weight_decay)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=[{'params': biases, 'lr': lr}, {'params': not_biases}],
lr=lr, momentum=momentum, weight_decay=weight_decay)
#optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=[{'params':model.parameters(), 'lr': 2 * lr}, {'params': model.parameters}], lr=lr, momentum=momentum, weight_decay=weight_decay)
else:
print("checkpoint load")
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint,map_location='cuda:0')
start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1 #这个是告诉你,这个预训练权值之前已经训练了多少次迭代
print('\nLoaded checkpoint from epoch %d.\n' % start_epoch)
model = checkpoint['model']
optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
# Move to default device
model = model.to(device)
criterion = MultiBoxLoss(priors_cxcy=model.priors_cxcy).to(device) #初始化损失函与先验框,这个model.priors_cxcy返回的是一组初始化产生的先验框
# Custom dataloaders
train_dataset = PascalVOCDataset(data_folder,split='train',keep_difficult=keep_difficult) #返回image, boxes, labels, difficulties
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn, num_workers=workers,
pin_memory=True) #将数据按照batchsize封装成tensor。
# Calculate total number of epochs to train and the epochs to decay learning rate at (i.e. convert iterations to epochs)
# To convert iterations to epochs, divide iterations by the number of iterations per epoch
# now it is mobilenet v3,VGG paper trains for 120,000 iterations with a batch size of 32, decays after 80,000 and 100,000 iterations,
epochs = 800
# decay_lr_at =[154, 193]
# print("decay_lr_at:",decay_lr_at)
print("epochs:",epochs)
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups: #动态调节优化器学习率
optimizer.param_groups[1]['lr']=lr
print("learning rate. The new LR is %f\n" % (optimizer.param_groups[1]['lr'],))
# Epochs,I try to use different learning rate shcheduler
#different scheduler six way you could try
#scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer,T_max = (epochs // 7) + 1)
# 下面这句话是根据epoch动态调整学习率的方法
scheduler = ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer,mode="min",factor=0.1,patience=15,verbose=True, threshold=0.00001, threshold_mode='rel', cooldown=0, min_lr=0, eps=1e-08)
for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs): #在这里面训练
# Decay learning rate at particular epochs
# if epoch in decay_lr_at:
# adjust_learning_rate_epoch(optimizer,epoch)
# One epoch's training
train(train_loader=train_loader,
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
epoch=epoch)
print("epoch loss:",train_loss)
scheduler.step(train_loss) #这一步是对学习率进行调整
# Save checkpoint
save_checkpoint(epoch, model, optimizer)
def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
model.train() #启用BatchNormalization与Dropout
batch_time = AverageMeter() #AverageMeter()这个类是用来记录数据的最新,平均,总和,计数的值的,里面就两个函数(reset和update)看源码就懂了
data_time = AverageMeter()
losses = AverageMeter()
start = time.time()
global train_loss
# Batches
for i, (images, boxes, labels, _) in enumerate(train_loader):
data_time.update(time.time() - start)
# if(i%200==0):
# adjust_learning_rate_iter(optimizer,epoch)
# print("batch id:",i)#([8, 3, 300, 300])
#N=8
# Move to default device
images = images.to(device) # (batch_size (N), 3, 300, 300)
boxes = [b.to(device) for b in boxes]
labels = [l.to(device) for l in labels]
# Forward prop.
predicted_locs, predicted_scores = model(images) # (N, anchor_boxes_size, 4), (N, anchor_boxes_size, n_classes)
# Loss
loss = criterion(predicted_locs, predicted_scores, boxes, labels) # Scalar
train_loss=loss
#print("training",train_loss)
# Backward prop.
optimizer.zero_grad()#初始化梯度
loss.backward()# 根据loss的值求相应weight的梯度
# Clip gradients, if necessary
if grad_clip is not None: #防止梯度爆炸用的
clip_gradient(optimizer, grad_clip)
# Update model
optimizer.step() #这一步是更新权值
losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
batch_time.update(time.time() - 编程客栈start)
start = time.time()
# Print status
if i % print_freq == 0:
print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}][{3}]\t'
'Batch Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
'Data Time {data_time.val:.3f} ({data_time.avg:.3f})\t'
'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'.format(epoch, i, len(train_loader),optimizer.param_groups[1]['lr'],
batch_time=batch_time,
data_time=data_time, loss=losses))
#break #test
del predicted_locs, predicted_scores, images, boxes, labels # free some memory since their histories may be stored
def adjust_learning_rate_epoch(optimizer,cur_epoch):
"""
Scale learning rate by a specified factor.
:param optimizer: optimizer whose learning rate must be shrunk.
:param scale: factor to multiply learning rate with.
"""
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = param_group['lr'] * 0.1
print("DECAYING learning rate. The new LR is %f\n" % (optimizer.param_groups[1]['lr'],))
#warmup ,how much learning rate.
def adjust_learning_rate_iter(optimizer,cur_epoch):
if(cur_epoch==0 or cur_epoch==1 ):
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] =param_group['lr'] + 0.0001
print("DECAYING learning rate iter. The new LR is %f\n" % (optimizer.param_groups[1]['lr'],))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
这个程序是以调用json格式的数据进行读取训练数据和训练标签的,所以,训练之前还需要转一下数据格式,代码如下。
#使用注意事项,使用试记得修改voc_labels为你自己训练数据的标签
#from utils import create_data_lists
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import json
# Label map
#voc_labels = ('aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow', 'diningtable',
#'dog', 'horse', 'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tvmonitor')
#voc_labels=('bus','car')
voc_labels=('bus', 'traffic light', 'traffic sign', 'person', 'bike', 'truck', 'motor编程客栈', 'car', 'train','rider')
label_map = {k: v + 1 for v, k in enumerate(voc_labels)}
label_map['background'] = 0
rev_label_map = {v: k for k, v in label_map.items()} # Inverse mapping
def parse_annotation(annotation_path):
tree = ET.parse(annotation_path)
root = tree.getroot()
boxes = list()
labels = list()
difficulties = list()
for category in root.iter('category'):
difficult=int(0.)
label=category.text.lower().strip()
if label not in label_map:
continue
labels.append(label_map[label])
difficulties.append(difficult)
for box2d in root.iter('box2d'):
x1=int(float(box2d.find('x1').text))
y1=int(float(box2d.find('y1').text))
x2=int(float(box2d.find('x2').text))
y2=int(float(box2d.find('y2').text))
boxes.append([x1,y1,x2,y2])
return {'boxes': boxes, 'labels': labels,'difficulties':difficulties}
def create_data_lists(voc07_path,output_folder):
"""
Create lists of images, the bounding boxes and labels of the objects in these images, and save these to file.
:param voc07_path: path to the 'VOC2007' folder
:param voc12_path: path to the 'VOC2012' folder
:param output_folder: folder where the JSONs must be saved
"""
voc07_path = os.path.abspath(voc07_path)
train_images = list()
train_objects = list()
n_objects = 0
# Training data
path=voc07_path
# Find IDs of images in training data
print(path)
with open(os.path.join(path, 'ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt')) as f:
ids = f.read().splitlines()
for id in ids:
# Parse annotation's XML file
objects = parse_annotation(os.path.join(path, 'Annotations', id + '.xml'))
if len(objects) == 0:
continue
n_objects += len(objects)
train_objects.append(objects)
train_images.append(os.path.join(path, 'JPEGImages', id + '.jpg'))
assert len(train_objects) == len(train_images)
# Save to file
with open(os.path.join(output_folder, 'TRAIN_images.json'), 'w') as j: #写入训练图片路径
json.dump(train_images, j)
with open(os.path.join(output_folder, 'TRAIN_objects.json'), 'w') as j: #写入训练标签信息
json.dump(train_objects, j)
with open(os.path.join(output_folder, 'label_map.json'), 'w') as j: #写入训练标签类别
json.dump(label_map, j) # save label map too
print('\nThere are %d training images containing a total of %d objects. Files have been saved to %s.' % (
len(train_images), n_objects, os.path.abspath(output_folder)))
# Test data
test_images = list()
test_objects = list()
n_objects = 0
# Find IDs of images in the test data
with open(os.path.join(voc07_path, 'ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt')) as f:
ids = f.read().splitlines()
for id in ids:
# Parse annotation's XML file
objects = parse_annotation(os.path.join(voc07_path, 'Annotations', id + '.xml'))
if len(objects) == 0:
continue
test_objects.append(objects)
n_objects += len(objects)
test_images.append(os.path.join(voc07_path, 'JPEGImages', id + '.jpg'))
assert len(test_objects) == len(test_images)
# Save to file
with open(os.path.join(output_folder, 'TEST_images.json'), 'w') as j:
json.dump(test_images, j)
with open(os.path.join(output_folder, 'TEST_objects.json'), 'w') as j:
json.dump(test_objects, j)
print('\nThere are %d test images containing a total of %d objects. Files have been saved to %s.' % (
len(test_images), n_objects, os.path.abspath(output_folder)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
create_data_lists(voc07_path='D:/study/internship/work_file/Dataset/bdd100k/bdd1k',output_folder='processed_data')
训练过程如下图所示。
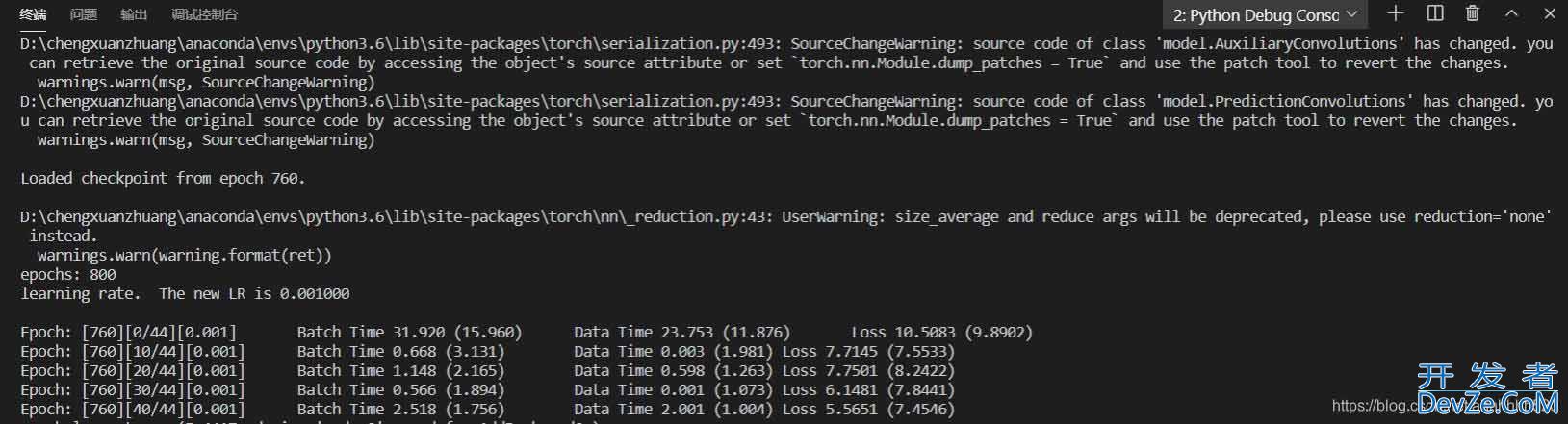
step3:预测
终于到预测啦,享受革命成果的时候到了。
代码如下。注意,虽然在程序中没有引入神经网络模型文件,但是这个模型文件是必须在相对路径下才能运行的,因为这个模型文件的名字保存在权重文件里面,会要调用的。
from torchvision import transforms
from utils import *
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import time
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Load model checkpoint
checkpoint = 'checkpoint_ssd300.pth.tar'
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint,map_location='cuda:0')
print(checkpoint)
start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
print('\nLoaded checkpoint from epoch %d.\n' % start_epoch)
model = checkpoint['model']
model = model.to(device)
model.eval() #如果是预测,使用这个;如果是训练,使用model.train()
def detect(original_image, min_score, max_overlap, top_k, suppress=None):
"""
Detect objects in an image with a trained SSD300, and visualize the results.
:param original_image: image, a PIL Image
:param min_score: minimum threshold for a detected box to be considered a match for a certain class
:param max_overlap: maximum overlap two boxes can have so that the one with the lower score is not suppressed via Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)
:param top_k: if there are a lot of resulting detection across all classes, keep only the top 'k'
:param suppress: classes that you know for sure cannot be in the image or you do not want in the image, a list
:return: annotated image, a PIL Image
"""
# Transform
resize = transforms.Resize((300, 300))
to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor() #这句话
normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
image = normalize(to_tensor(resize(original_image)))
# Move to default device
image = image.to(device) #这句话是将图片的张量读取到GPU上。
# Forward prop.
predicted_locs, predicted_scores = model(image.unsqueeze(0)) #unsqueeze用于添加维度。
###############################################后面都是解码与画图了
# Detect objects in SSD output
det_boxes, det_labels, det_scores = model.detect_objects(predicted_locs, predicted_scores, min_score=min_score,
max_overlap=max_overlap, top_k=top_k) #将预测结果进行解码
# Move detections to the CPU
det_boxes = det_boxes[0].to('cpu')
# Transform to original image dimensions
original_dims = torch.FloatTensor(
[original_image.width, original_image.height, original_image.width, original_image.height]).unsqueeze(0)
det_boxes = det_boxes * original_dims
# Decode class integer labels
det_labels = [rev_label_map[l] for l in det_labels[0].to('cpu').tolist()]
print(det_labels)
# If no objects found, the detected labels will be set to ['0.'], i.e. ['background'] in SSD300.detect_objects() in model.py
if det_labels == ['background']:
# Just return original image
return original_image
# Annotate
annotated_image = original_image
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(annotated_image)
font = ImageFont.truetype("simhei.ttf", 15)
# Suppress specific classes, if needed
for i in range(det_boxes.size(0)):
if suppress is not None:
if det_labels[i] in suppress:
continue
# Boxes
box_location = det_boxes[i].tolist()
draw.rectangle(xy=box_location, outline=label_color_map[det_labels[i]])
draw.rectangle(xy=[l + 1. for l in box_location], outline=label_color_map[
det_labels[i]]) # a second rectangle at an offset of 1 pixel to increase line thickness
# draw.rectangle(xy=[l + 2. for l in box_location], outline=label_color_map[
# det_labels[i]]) # a third rectangle at an offset of 1 pixel to increase line thickness
# draw.rectangle(xy=[l + 3. for l in box_location], outline=label_color_map[
# det_labels[i]]) # a fourth rectangle at an offset of 1 pixel to increase line thickness
# Text
text_size = font.getsize(det_labels[i].u编程客栈pper())
text_location = [box_location[0] + 2., box_location[1] - text_size[1]]
textbox_location = [box_location[0], box_location[1] - text_size[1], box_location[0] + text_size[0] + 4.,
box_location[1]]
draw.rectangle(xy=textbox_location, fill=label_color_map[det_labels[i]])
draw.text(xy=text_location, text=det_labels[i].upper(), fill='white',
font=font)
del draw
return annotated_image
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = 'feiji1.jpg'
original_image = Image.open(img_path, mode='r')
original_image = original_image.convert('RGB')
detect(original_image, min_score=0.2, max_overlap=0.5, top_k=200).show()
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论