C++ IO设备读写功能实现详解
目录
- 1 输入输出IO流
- 1.1 图解输入输出流
- 1.2 输入输出流类库
- 2 文件读写操作
- 2.1 文件的打开方式
- 2.2 文件读写类库的头文件
- 2.3 文本文件读写
- 使用ofstream来写文本
- 使用ifstream读取文件
- 使用fstream来读写文件
- 2.4 二进制的读写
- 2.4.1 二进制写
- 2.4.2 二进制读
- 2.5 按照特殊格式读写
- 2.5.1 特殊格式写入
- 2.5.2 特殊格式读取
- 2.6 文件流标志
- 2.7 文件指针
- 输入流指针seekg
- 输入流指针tellg
- 输出流指针seekp
1 输入输出IO流
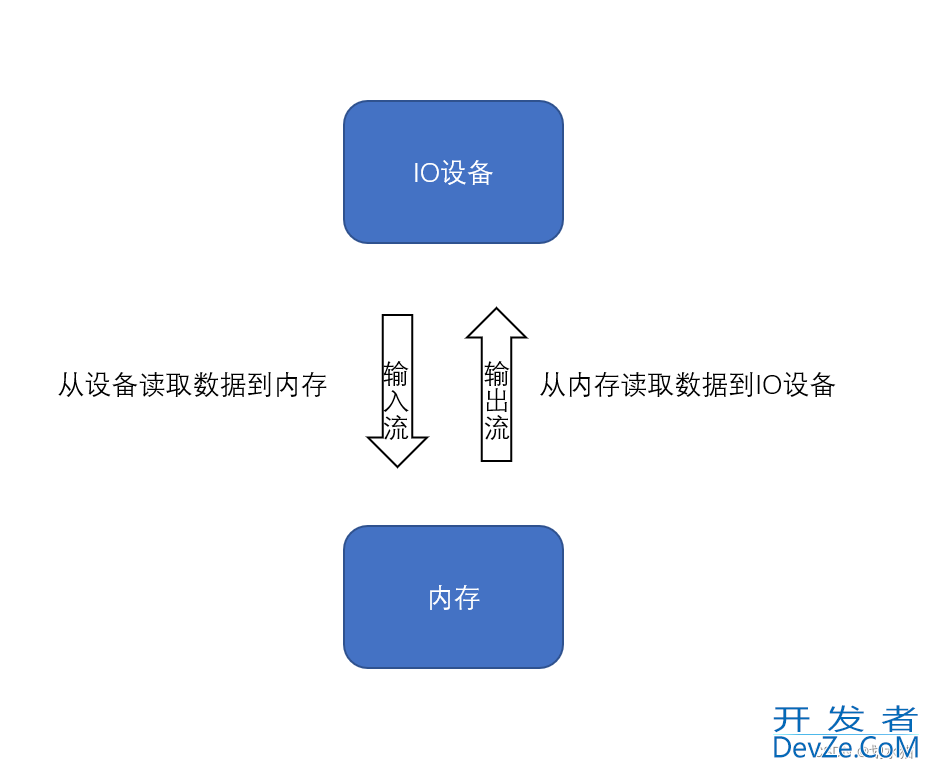
1.1 图解输入输出流
IO设备:文件、终端(DOS黑框框)、特殊的数据类型(streamstring)
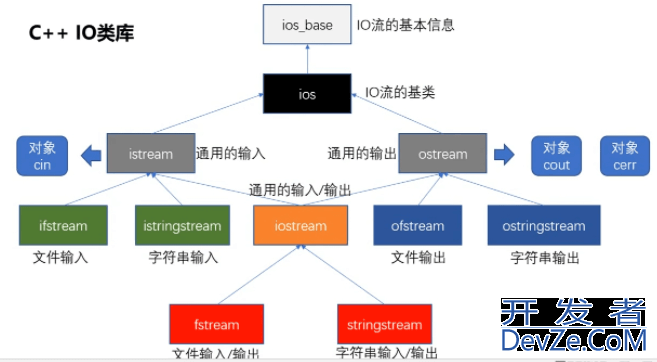
1.2 输入输出流类库
C++中的输入输出流是靠定义好的类库来操作的
2 文件读写操作
2.1 文件的打开方式
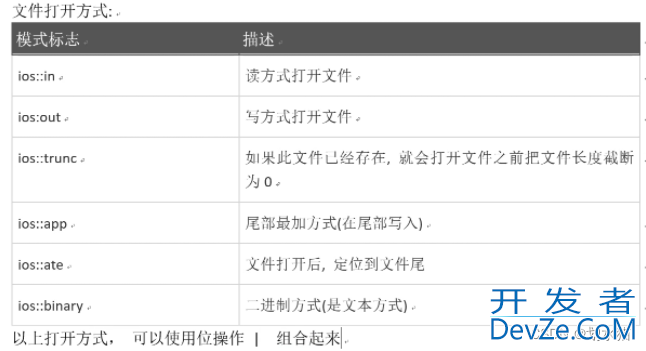
2.2 文件读写类库的头文件
头文件:fstream
ofstream:读写
istream:读操作
ofstream:写操作
2.3 文本文件读写
使用ofstream来写文本
ofstream写入文件默认打开方式是IOS::trunc,即没有文件那么创建,该文件存在并且有内容会直接清空内容
#include<iostream>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ofstream outfile;
string name;
int age;
cin >> name >> age;
outfile.open("C:/Users/98207/desktop/test.txt", ios::out); // 写入文件,没有文件会新建
outfile << name << endl;
outfile << age;
outfile.close(); // 文件结束需要关闭
return 0;
}
使用ifstream读取文件
程序:
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ifstream infile;
string str;
int age;
infile.open("C:/Users/98207/desktop/test.txt", ios::in); // 读取文件
while (1) {
if (infile.eof()) {
break;
}
infile >> str;
cout << str << endl;;
// getline(infile, str);
// cout << str << endl;
}编程客栈
infile .close();
return 0;
}
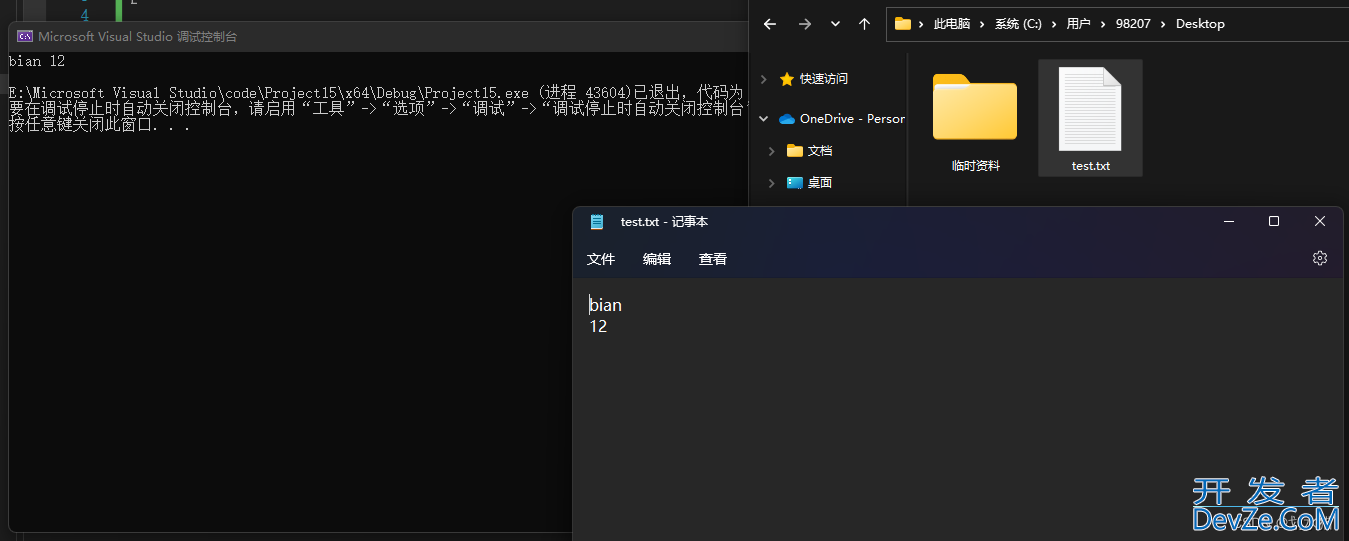
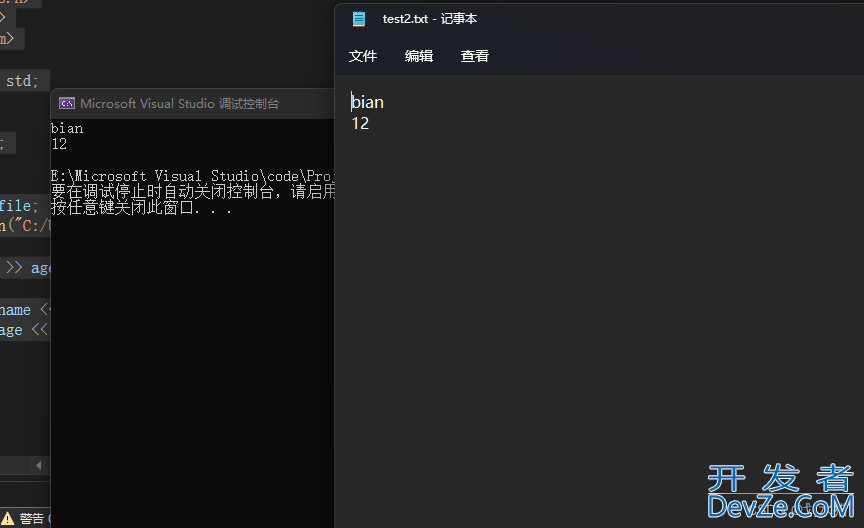
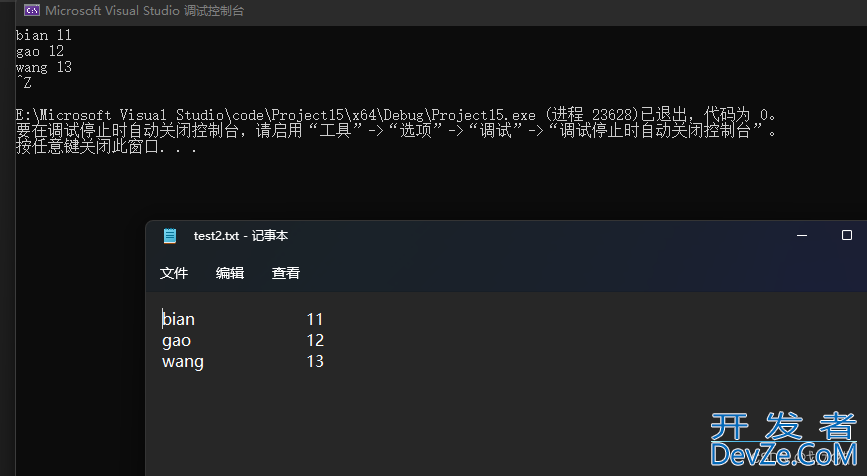
结果:
bian
12
使用fstream来读写文件
写入文件fstream默认不会截断文件
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string name;
int age;
fstream outfile;
outfile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/test2.txt", ios::out);
cin >> name >> age;
outfile << name << endl;
outfile << age;
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
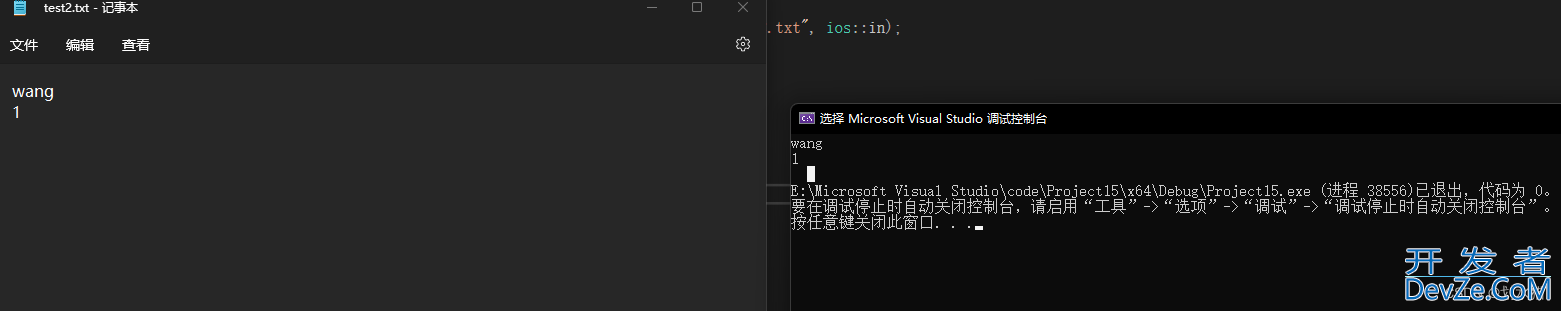
读取文件
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string>
编程#inchttp://www.devze.comlude<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
fstream infile;
infile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/test2.txt", ios::in开发者_Go开发);
while (1) {
if (infile.eof()) {
break;
}
infile >> str;
cout << str << endl;
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}
2.4 二进制的读写
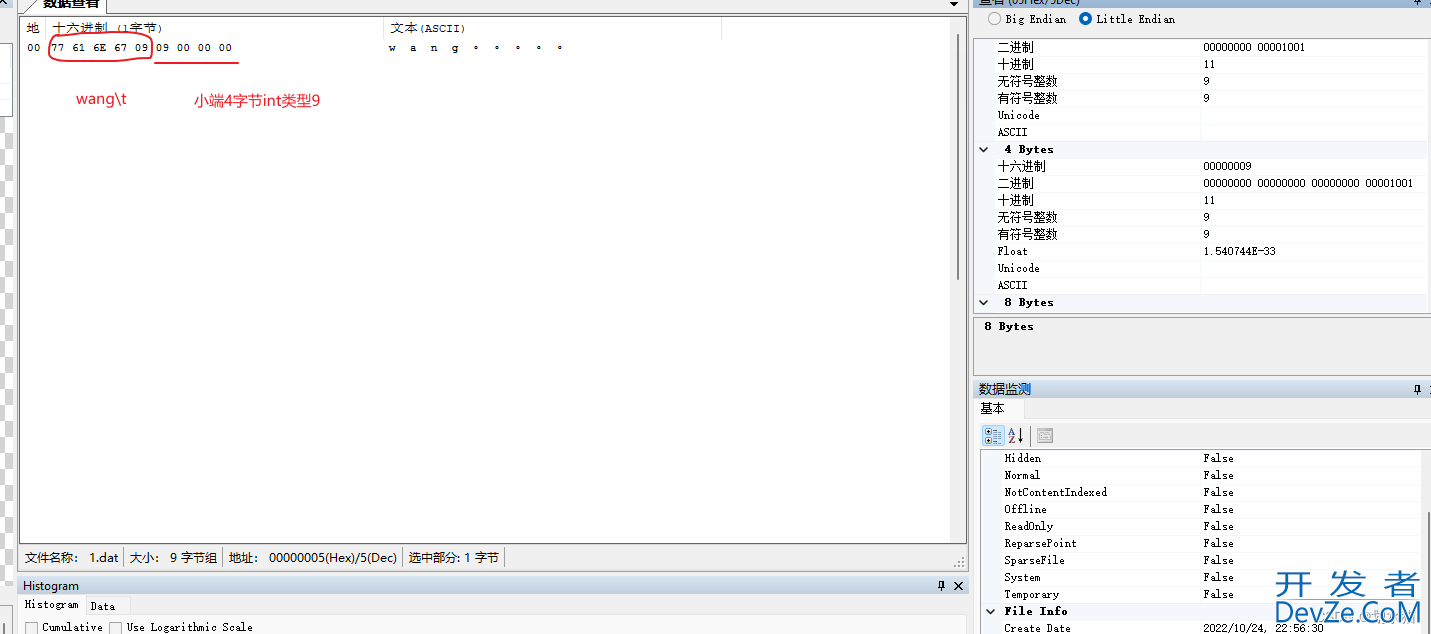
二进制和文本写区别在于数字,二进制数字是把实际字节数写入进去。
比如整数9,那么写入的是4个char字符0009,至于存储的大小端方式要看cpu。
2.4.1 二进制写
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
fstream outfile;
char name[20];
int age;
// 为什么保存格式是dat,因为使用文本格式会按照文本格式解析,最后出来的是乱码
outfile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/1.dat", ios::trunc | ios::out | ios::binary);
cin >> name >> age;
outfile << name << '\t';
outfile.write((char*)&age, sizeof(age)); // 二进制写
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
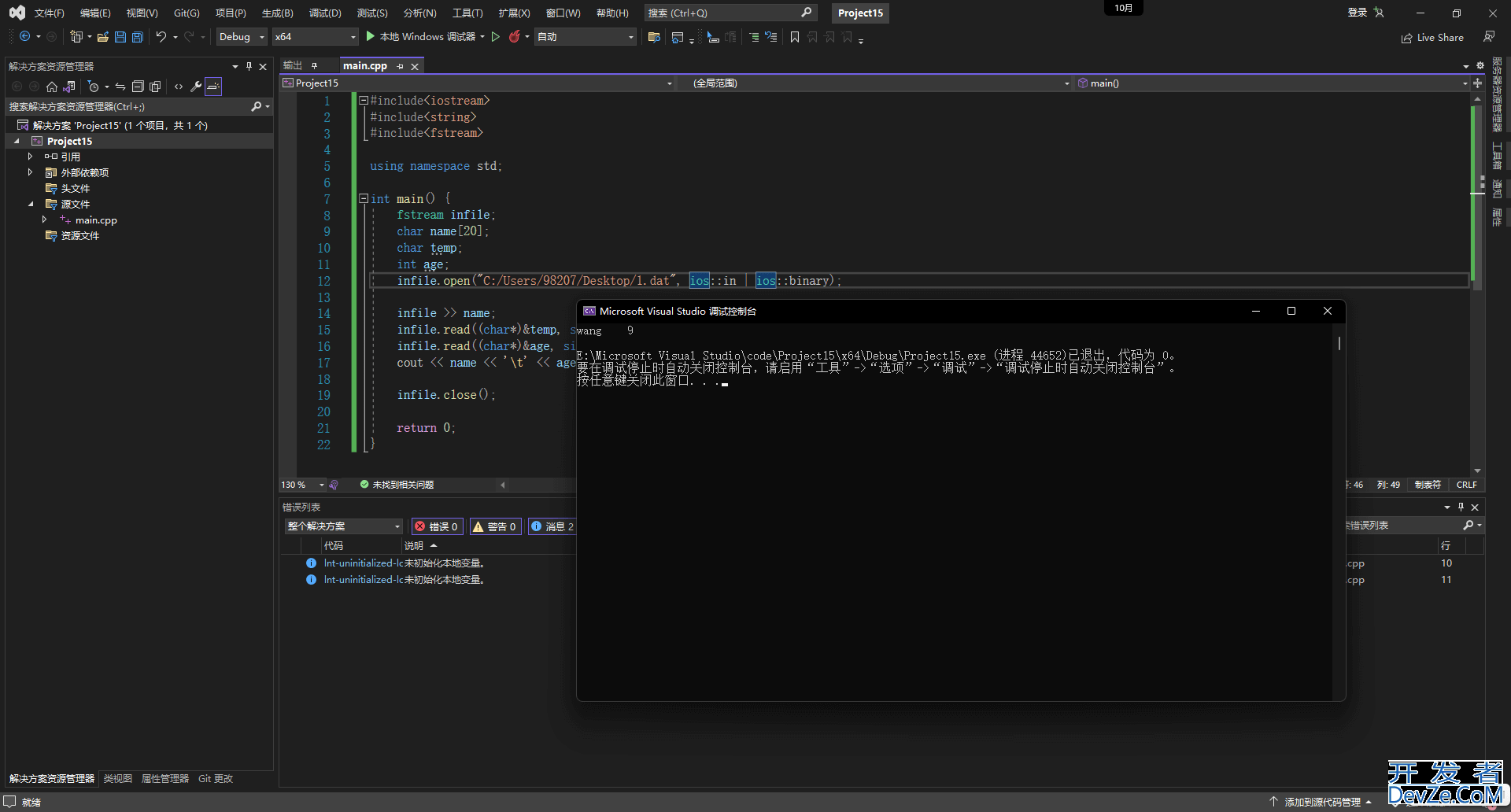
2.4.2 二进制读
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
fstream infile;
char name[20];
char temp;
int age;
infile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/1.dat", ios::in | ios::binary);
infile >> 编程客栈name;
infile.read((char*)&temp, sizeof(temp)); // 丢弃制表符
infile.read((char*)&age, sizeof(age));
cout << name << '\t' << age << endl;
infile.close();
return 0;
}
2.5 按照特殊格式读写
2.5.1 特殊格式写入
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream> //ofstream
#include<sstream> // stringstream
using namespace std;
int main() {
stringstream ret;
ofstream outfile;
string name;
int age;
outfile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/test2.txt"javascript, ios::out | ios::trunc);
while (1) {
cin >> name >> age;
if (cin.eof()) {
break;
}
ret << name << "\t\t\t" << age << endl; // ret会累积
// outfile << ret.str();
// ret.clear();
}
outfile << ret.str();
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
2.5.2 特殊格式读取
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string> // getline, string
using namespace std;
int main() {
fstream infile;
string str;
char name[20];
int age;
infile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/test2.txt", ios::in);
while (1) {
getline(infile, str);
if (infile.eof()) {
break;
}
sscanf_s(str.c_str(), "%s %d", name, sizeof(name), & age); // 这里的参数只能是char类型,这里的空格会替换文件的制表符或者空格
cout << name << "\t\t\t" << age << endl;
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}

2.6 文件流标志
这里常用的就是is_open()和eof()

2.7 文件指针
输入流指针seekg
原形:basic_istream& seekg( off_type off, // 偏移量
std::ios_base::seekdir dir); // 起始位置
作用:设置输入流位置
参数1:偏移量
参数2:相对位置
- beg 相对于开始位置
- cur 相对于当前位置
- end 相对于结束位置
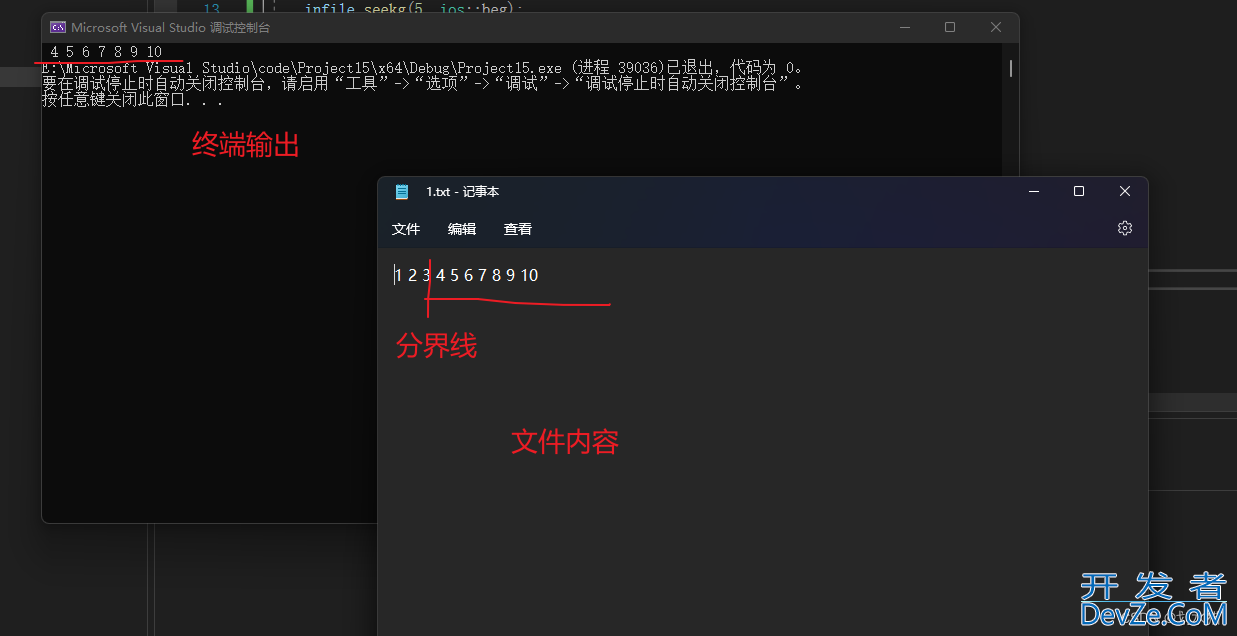
从开始位置文件指针偏移5个字节,然后读取内容
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// ofstream infile;
ifstream infile;
string str;
infile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/1.txt", ios::in);
infile.seekg(5, ios::beg); // 从开始位置偏移5个字节
while (1) {
getline(infile, str);
cout << str;
if (infile.eof()) {
break;
}
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}
输入流指针tellg
作用:返回输入流的当前位置(距离文件的起始位置的偏移量)
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ifstream infile;
string str;
infile.open("C:/Users/98207/Desktop/1.txt", ios::in);
infile.seekg(5, ios::beg); // 设置偏移量位5个字节
cout << "文件指针偏移量:" << infile.tellg() << endl; // 相对于文件起始位置
infile.close();
return 0;
}
结果:
文件指针偏移量:5
E:\Microsoft Visual Studio\code\Project15\x64\Debug\Project15.exe (进程 68440)已退出,代码为 0。
要在调试停止时自动关闭控制台,请启用“工具”->“选项”->“调试”->“调试停止时自动关闭控制台”。按任意键关闭此窗口. . .
输出流指针seekp
作用:设置输出流位置
函数原形:basic_ostream& seekp( off_type off, // 偏移量
std::ios_base::seekdir dir ); // 起始位置
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ofstream outfile;
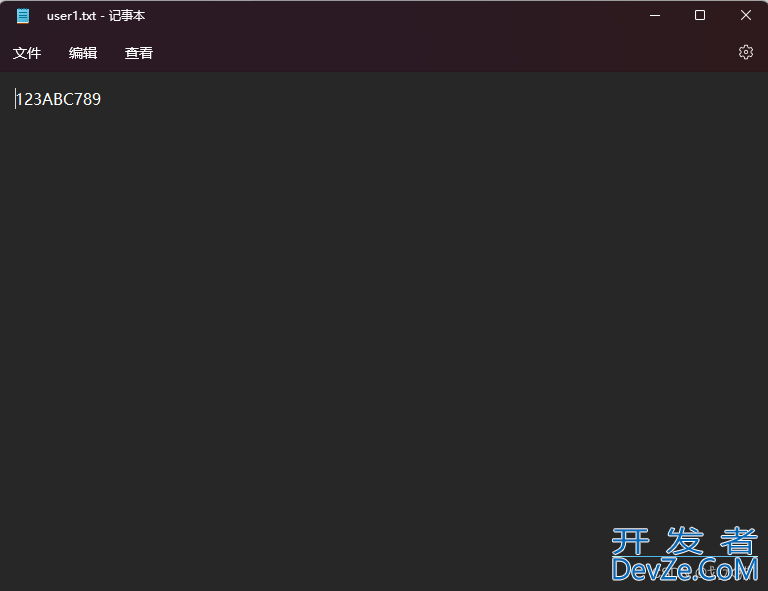
outfile.open("user1.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
outfile << "123456789";
outfile.seekp(3, ios::beg); // 指针先指向开头,然后向后偏移三个字节
outfile << "ABC";
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
到此这篇关于C++ IO设备读写功能实现详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ IO设备读写内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论