PostgreSQL数据库视图及子查询使用操作
目录
- 视图
- 创建视图
- 使用视图
- 视图更新:
- 删除视图:
- 子查询
- 关联子查询
视图
表里面保存的是实际数据,视图里面保存的是SELECT语句(视图本身不存储数据)。
从视图中读取数据,此时视图在内部执行SELECT语句,创建一张临时表。
使用视图的好处:其一,视图不保存数据,节省存储设备容量。其二,将频繁使用的SELECT语句保存成视图,每次使用这些语句时候,不用重复书写,只需调用视图。其三,数据保存到表中,要显式的执行SQL更新语句才能更新数据,而视图中的数据会随着原表的变化自动更新。
创建视图
格式:
CREATE VIEW 视图名称(<视图列名1>,<视图列名2>,...) AS <SELECT语句>
例子:
CREATE VIEW ProductSum (product_type, cnt_product) AS SELECT product_type, COUNT(*) FROM Product GROUP BY product_type;
使用视图
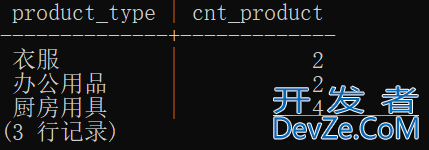
可见,如果使用视图,不用每次都写GROUP BY等一些语句从Product表中取数据。
并且,如果Product表中数据更新,视图也自动更新。
这是因为,视图就是保存好的SELECT语句。
SELECT product_type, cnt_product FROM ProductSum;
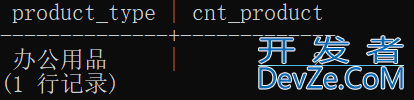
多重视图:以视图为基础创建视图。但是这样会降低SQL性能。
CREATE VIEW ProductSumA (product_type, cnt_product) AS SELECT product_type, cnt_product FROM ProductSum WHERE product_type = '办公用品';
定义视图时,不能用ORDER BY子句。因为视图和表,数据行都没有顺序。
(PostgreSQL里面,定义视图时候可以用ORDER BY子句,有些DBMS不行)
视图更新:
如果定义视图的SELECT语句满足一些条件,视图可以被更新。
SELECT子句没用DISTINCT、FROM子句只有一张表、没用GROUP BY、没用HAVING。
通过汇总得到的数据无法更新,这是因为视图和表要同时更新。
如果给上面的ProductSum中添加(‘食物’,3)的数据,原表就需要增加三行种类为食物的数据,但是这些数据我们都不知道,因此没法更新表中的数据。
可以更新下面这样,不通过汇总得到的视图。
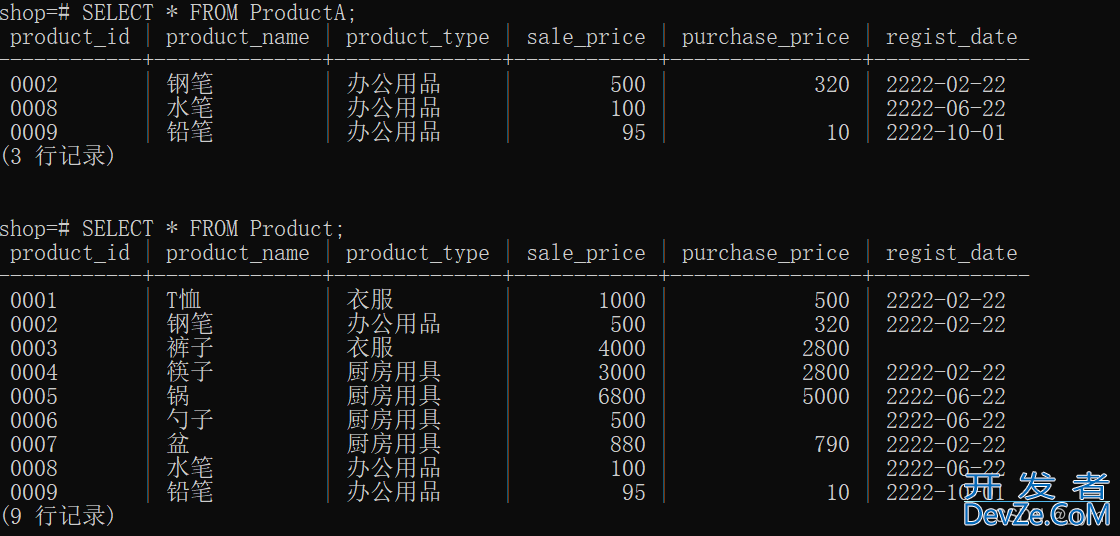
CREATE VIEW ProductA (product_id, product_name, product_type, sale_price, purchase_price, regist_date) AS SELECT * FROM Product WHERE product_type = '办公用品';
向视图插入数据。
INSERT INTO ProductA VALUES ('0009', '铅笔', '办公用品', 95, 10, '2222-10-1');
此时可看到,视图和表都更新了。
删除视图:
格式
DROP VIEW 视图名称(<视图列名1>,<视图列名2>,...)
例子
DROP VIEW ProductSum;
然后报错
ERROR: cannot drop view productsum because other objects depend on it 描述: view productsuma depends on view productsum 提示: Use DROP ... CASCADE to drop the dependent objects too.
这是因为前面以ProductSum为基础,创建了一个ProductSumA视图。
可以像下面这样删除ProductSum和与之关联的视图。
DROP VIEW ProductSum CASCADE;
子查询
子查询,相当于一次性视图。
定编程客栈义视图ProductSum
CREATE VIEW ProductSum (product_type, cnt_product) AS SELECT product_type, COUNT(*) FROM Product GROUP BY product_type;
子查询:将定义视图的SELECT语句直接用到FROM子句里面。
AS ProductSum,ProductSum是子查询的名称。执行完外边的SELECT语句,子查询就消失了。
下面代码,执行顺序,先是FROM子句里面的SELECT语句,然后是外边的SELECT语句。
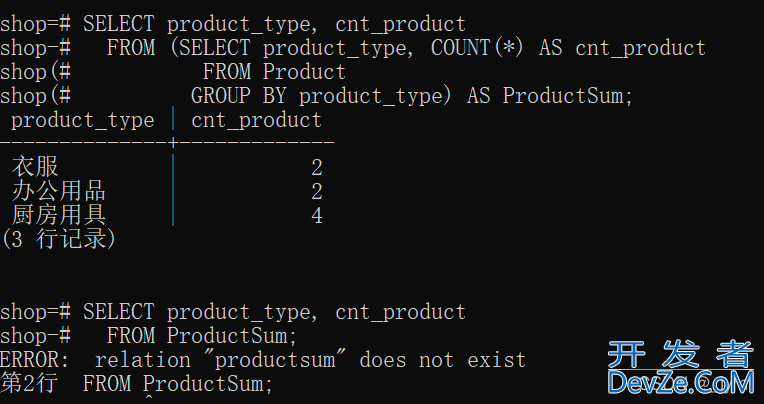
SELECT product_type, cnt_product
FROM (SELECT product_type, COUNT(*) AS cnt_product
FROM Product
GROUP BY product_type) AS ProductSum;
下面再次查看ProductSum发现,ProductSum已经不存在了。由此看出,子查询是一次性的,并不像视图一样保存到硬盘里面。
在子查询的FROM子句里面,可以继续使用子查询。
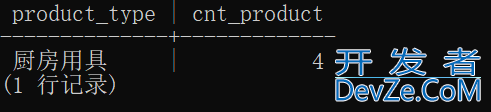
下面就是把ProductSum里面cnt_product = 4的数据选出来了。
SELECT product_type, cnt_product
FROM (SELECT *
FROM (SELECT product_type, COUNT(*) AS cnt_produ编程客栈ct
FROM Product
GROUP BY product_type) AS ProductSum
WHERE cnt_product = 4) AS ProductSum2;
标量子查询scalar subquery,返回表中某一行某一列的值(单一值)的子查询。
可以在WHERE子句中使用标量子查询。
由于WHERE子句中无法使用聚合函数,像下面的语句就是错误的。
SELECT product_id, product_name, sale_price FROM Product WHERE sale_price > AVG(sale_price);
可以通过下面这样去实现。
SELECT product_id, product_name, sale_price FROM Product WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price) FROM Product);SELECT product_id, product_name, sale_price
FROM Product
WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM Product);
在任何使用单一值的地方,都可以使用标量子查询。
在SELECT子句中使用标量子查询:
SELECT product_id, product_name, sale_price, (SELECT AVG(sale_price) FROM Product) AS avg_price FROM Product;SELECT product_id,
product_name,
sale_price,
(SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM Product) AS avg_price
FROM Product;
在HAVING子句中使用标量子查询:
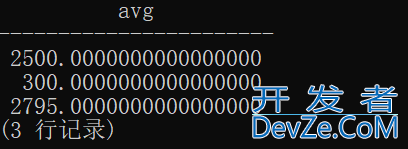
不同商品种类的平均销售单价与全部商品的销售单价相比。
SELECT product_type, AVG(sale_price)
FROM Product
GROUP BY product_type
HAVING AVG(sale_price) > (SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM Product);
标量子查询不能返回多行结果,如果返回多行结果,那就是一个普通的子查询,不能用到需要单一输入值的地方了。
关联子查询
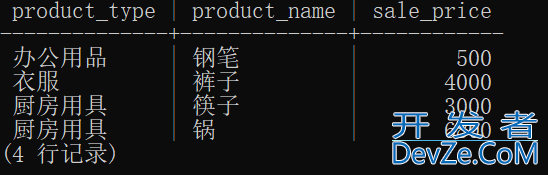
现在要选取各个商品种类里面,高于该商品种类平均销售价的商品。
按照商品种类计算llmoXY平均价格:
SELECT AVG(sale_price) FROM Product GROUP BY produc开发者_Kafkat_type;
因为有三种商品,上面这个查询返回三个结果。
那么就不能用下面这种方法了。因为子查询不是标量子查询,不能在WHERE子句里面用。
SELECT product_id, product_name, sale_price
FROM Product
WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price)
llmoXY FROM Product
GROUP BY product_type);
在细分的组内进行比较的时候,用到关联子查询。
在子查询里面添加了一个WHERE子句。目的是在同一商品种类中对各商品销售单价和平均单价比较。
由于比较对象是同一个Product表,所以用了P1、P2两个别名。
使用关联子查询,用<表名>.<列名>形式,限定product_type,对平均单价比较。
SELECT product_type, product_name, sale_price
FROM Product AS P1
WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM Product AS P2
WHERE P1.product_type = P2.product_type
GROUP BY product_type);
而且,不加GROUP BY,也能得到相同结果:
SELECT product_type, product_name, s编程客栈ale_price
FROM Product AS P1
WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM Product AS P2
WHERE P1.product_type = P2.product_type);
以上就是PostgreSQL数据库视图及子查询使用操作的详细内容,更多关于PostgreSQL数据库的视图子查询的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!




 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论