MySQL约束和表的复杂查询操作大全
目录
- 一. 数据库约束
- 1. 数据库常用约束
- 2. not null 约束
- 3. unique约束
- 4. default设置默认值
- 5. primary key约束
- 6. 分库分表下的自增主键
- 7. foreign key约束
- 8. 主键,外键,uniqe运用原理
- 二. 表的设计
- 1. 一对一关系
- 2. 一对多关系
- 三. 表的复杂查询操作
- 1. 将一个表中的数据插入到另一个表中
- 2. 聚合查询
- 2.1 聚合函数
- 2.2 分组查询
- 2.3 having
- 3. 多表查询(联合查询)
- 3.1 笛卡尔积
- 3.2 内连接
- 3.3 外连接
- 3.4 自连接
- 3.5 子查询
- 3.6 合并查询
SQL查询中各个关键字的执行先后顺序:
from > on> join > where > group by > with > having > select > distinct > order by > limit
一. 数据库约束
约束是关系型数据库的一个重要功能, 添加到库中的数据需要保证其的正确性; 约束, 就是让数据库帮助程序员更好的检查数据是否正确.
1. 数据库常用约束
- not null - 指示某列不能存储 NULL 值.
- unique - 保证某列的每行必须有唯一的值.
- default - 规定没有给列赋值时的默认值.
- primary key - not null 和 unique 的结合。确保某列(或两个列多个列的结合)有唯一标识,有助于更容易更快速地找到表中的一个特定的记录.
- foreign key - 保证一个表中的数据匹配另一个表中的值的参照完整性.
- check - 保证列中的值符合指定的条件; 对于mysql数据库,对check子句进行分析,但是忽略check子句(MySQL5中不支持check).
2. not null 约束
在创建表的时候使用, 对某一列使用该约束, 则该列的值不能为null.
语法:
create table 表名 (变量 类型 not null, ...);
示例:
-- 创建student表并对id字段使用not null约束
mysql> create table student (id int not null, name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
-- id默认值为null,但此时id不允许为null,所以插入数据时id要有具体的值
mysql> desc student;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- id值为null,插入失败
mysql> insert into student values (null, '张三');
ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'id' cannot be null
-- 不指定id列,其默认值为null,插入失败
mysql> insert into student (name) values ('张三');
ERROR 1364 (HY000): Field 'id' doesn't have a default value
-- id不为null, 插入成功
mysql> insert into student values (1, '张三');
Query OK, 1 编程row affected (0.00 sec)
注意:
not null 约束可以同时对多个列使用.
-- 如果存在student表则删除 mysql> drop table if exists student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) -- id和name字段都使用not null约束 mysql> create table student (id int not null, name varchar(20) not null); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) -- 查看表结构 mysql> desc student; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3. unique约束
在创建表的时候使用, 对某一列使用该约束, 则该列的值不能重复.
语法:
create table 表名 (变量 类型 unique, ...);
示例:
mysql> drop table if exists student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) -- 创建student表,字段id和name都使用约束unique mysql> create table student (id int unique, name varchar(20) unique); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) -- 查看表结构 mysql> desc student; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | UNI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | UNI | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) -- 第一次插入数据,无重复数据,成功插入 mysql> insert into student values (1, '张三'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -- 只要id/name字段中有重复的数据,插入失败 mysql> insert into student values (1, '李四'); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'id' mysql> insert into student values (2, '张三'); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '张三' for key 'name'
4. default设置默认值
在创建表的时候使用, 可以设置列的默认值.
语法:
create table 表名 (变量 类型 default 默认值, ...);
示例:
mysql> drop table if exists student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) -- 设置字段name的默认值为'匿名' mysql> create table student (id int, name varchar(20) default '匿名'); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) -- 查看表结构 mysql> desc student; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | 匿名 | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) -- 只指定id列插入 mysql> insert into student (id) values (1); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -- name用默认值填充 mysql> select * from student; +------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | 匿名 | +------+--------+ 1 row in set编程 (0.00 sec)
5. primary key约束
primary key是主键约束, 是一条记录的身份标识, 相当于not null和 unique结合的效果, 在创建表时使用, 对`某一列使用该约束, 则该列的值必须是唯一的且不能是null.
实际开发中, 大部分的表, 一般都会带有一个主键, 主键往往是一个整数表示的id.
语法:
create table 表名 (变量 类型 primary key, ...);
示例:
mysql> drop table if exists student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) -- 设置id字段为主建 mysql> create table student (id int primary key, name varchar(20)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) -- 查看表结构 mysql> desc student; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec) -- id不重复,插入成功 mysql> insert into student values (1, '张三'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -- id不重复,插入成功 mysql> insert into student values (2, '李四'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -- id重复,插入失败 mysql> insert into student values (1, '王五'); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY' -- id为null,插入失败 mysql> insert into student values (null, '赵六'); ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'id' cannot be null -- 查看插入结果 mysql> select * from student; +----+--------+ | id | name | +----+--------+ | 1 | 张三 | | 2 | 李四 | +----+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
上面主键描述的列的值是我们自己手动去添加, mysql中还支持自增主键, 使用自增主键描述列可以不去手动设置值, 在插入记录时, 它会自动从1开始自增(未设置初始值的情况下).
当然, 使用了自增主键我们也可以去手动添加值, 但当我们手动设置一个之后, 后面插入记录再让它自增, 此时的值会基于我们设置的那个值开始自增.
语法:
create table (变量 类型 primary key auto_increment, ...);
示例:
要注意的是下面插入记录时id列的null并不是将id设置为null, 而是将id的赋值交给数据库来使用自增主键
mysql> drop table if exists student;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table student (
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into student values
-> (null, '张三'), (null, '李四'), (null, '王五'),
-> (100, '赵六'), (null, '赵钱'), (null, '孙李');
Query OK, 6 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 6 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from student;
+-----+--------+
| id | name |
+-----+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
| 100 | 赵六 |
| 101 | 赵钱 |
| 102 | 孙李 |
+-----+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
在mysql中,一个表中只能有一个主键, 虽然主键不能有多个, 但mysql允许把多个列放到一起共同作为一个主键(联合主键).
语法:
primary key (列名, 列名, ...);
示例:
mysql> drop table if exists student;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> create table student (
-> id int,
-> name varchar(20),
-> primary key (id, name)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> desc student;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6. 分库分表下的自增主键
学习阶段的mysql的数据量较小, 所有的数据都在一个mysql服务器上, 此时每个表中的自增主键都可以很到的工作, 考虑下面的场景:
如果mysql的数据量很大,一台主机放不下, 就需要进行分库分表, 使用多个主机来进行存储, 本质上就是,把一张大表分成两个/多个小的表, 每个数据库服务器, 分别只存一部分数据; 此时的增主键如何保证在多个主机上不重复呢?

在这个场景下, 如果再新插入一个数据, 这个数据就会落在三个服务器之一, 新的这个数据的主键id,如何分配才能保证不重复呢?
这里涉及到一个"分布式系统中唯一id生成算法", 实现公式如下:
实现公式=时间戳+主机编号+随机因子
时间戳保证在不同时间下的id不同, 再和主机编号组合保证如果再同一时间有不同的数据分散到不同主机上的id不同, 最后再和一个随机因子组合保证多个数据到同一个主机时id不同, 结合这三个部分,就可以得到一个全局唯一的id.
7. foreign key约束
foreign key是外键约束, 用来约束两张表之间的关系(相互约束), 在创建表时使用, 使用该约束要求表中某个记录必须在另外一个表里存在.
例如一张学生表的字段有学号, 姓名, 班级号, 还有一张表是班级表, 字段有班级号和班级名, 该学生表中的学生所在班级都能在班级表里面找到, 此时就可以对学生表的班级号使用外键约束, 让学生表与班级表联系起来; 我们发现学生表中的数据要依赖于班级表的数据, 班级表的数据对学生表产生约束力(父亲对孩子有约束力), 此处起到约束作用的班级表就叫做"父表" (parent),被约束的这个表就叫做“子表" (child).
语法:
-- 父表已经创建的前提下 create table 表名 ( 变量 类型,... foreign key (子表中的一个变量) references 父表名 (父表中的一个变量) );
示例:
-- class为父表
mysql> create table class(
-> class_id int primary key auto_increment,
-> class_name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 查看class表结构
mysql> desc class;
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| class_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| class_name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 给class表插入数据
mysql> insert into class values (null, '1班'), (null, '2班'), (null, '三班');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看插入结果
mysql> select * from class;
+----------+------------+
| class_id | class_name |
+----------+------------+
| 1 | 1班 |
| 2 | 2班 |
| 3 | 三班 |
+----------+------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop table if exists student;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
-- student为子表, 字段class_id添加外键约束
mysql> create table student (
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20),
-> class_id int,
-> foreign key (class_id) references class(class_id)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 查看student表结构
mysql> desc student;
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| class_id | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 给student表插入数据
mysql> insert into student (name, class_id) values
-> ('张三', 3), ('李四', 1), ('王五', 2), ('赵六', 1);
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看插入结果
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------+----------+
| id | name | class_id |
+----+--------+----------+
| 1 | 张三 | 3 |
| 2 | 李四 | 1 |
| 编程客栈 3 | 王五 | 2 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 1 |
+----+--------+----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 插入班级表中不存在的班级,插入失败
mysql> insert into student (name, 2) values ('孙李', 4);
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '2) values ('孙李', 4)' at line 1
使用外键约束的数据表, 依赖于另一个表, 这个被依赖的表称为父表, 被约束的表被称为子表, 当在子表插入记录时,必须在父表中存在某一对应关系才能插入.
外键约束不仅约束着子表,同时也约束着父表, 我们尝试修改或者删除班级表中class_id的值, 且学生表中存在班级为此id的学生, 此时是不能成功修改或删除的.
mysql> update class set class_id = 5 where class_id = 1; ERROR 1451 (23000): Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`Java_rong`.`student`, CONSTRAINT `student_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`class_id`)) mysql> delete from class where class_id = 2; ERROR 1451 (23000): Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`java_rong`.`student`, CONSTRAINT `student_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`class_i编程客栈d`)) mysql>
要删除/修改的父表中的记录, 前提是子表中没有记录与父表中的记录相关联.
mysql> insert into class values(4, '四班'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> delete from class where class_id = 4; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
当子表中插入的记录和父表建立联系后, 此时就不能直接删除父表了, 要删除父表要先删除子表.
-- 直接删除class表,删除失败 mysql> drop table class; ERROR 1217 (23000): Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails -- 先删除子表student,删除成功 mysql> drop table student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) -- 删除子表student后再删除父表class,删除成功 mysql> drop table class; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
实际开发中, 很多时候删除表并不会真的将数据都清除, 而是采用逻辑删除, 也就是再表中来设置一个属性开关, 通过这个属性来看是否可以使用表中的数据, 这样做就可以避免触发外键约束的限制了.
8. 主键,外键,uniqe运用原理
当字段被主键/unique约束时, 是如何保证记录不重复的?
当字段被外键约束时, 如何知道子表中待插入的数据在父表中是否存在?
其实不难想到, 不管是使用上面的哪个约束, 先要有查询过程, 查询满足条件后才会完成插入操作.但要注意这里的查询不会是遍历查询, 那样的话时间开销就太大了, mysql中通过索引来完成查询, 索引能加快查询效率(mysql专栏中写有介绍索引的博客可以参考).
对于外键约束, 子表插入数据前在父表会有查询操作, 被依赖的这一列必须要要有索, 如果使用primary key或者unique约束该列, 则该列会自动创建索引.
所以上面的学生表与班级表的示例, 虽然我们没有主动对父表中的class_id列创建索引, 但是该列使用了主键约束, 就会自动创建索引.
二. 表的设计
1. 一对一关系
以学校中的教务系统为例, 学生这个实体有学号,姓名等属性, 登录教务系统的账号也是一个实体, 有用户名,密码等属性; 显而易见的, 一个学生只能有一个账号, 像这样就是一对一的关系.
那么最重要的就是要在数据库中表示这种关系.
方案一
可以将这两个实体信息在一个表中描述, 那么一条记录就对应一个关系.
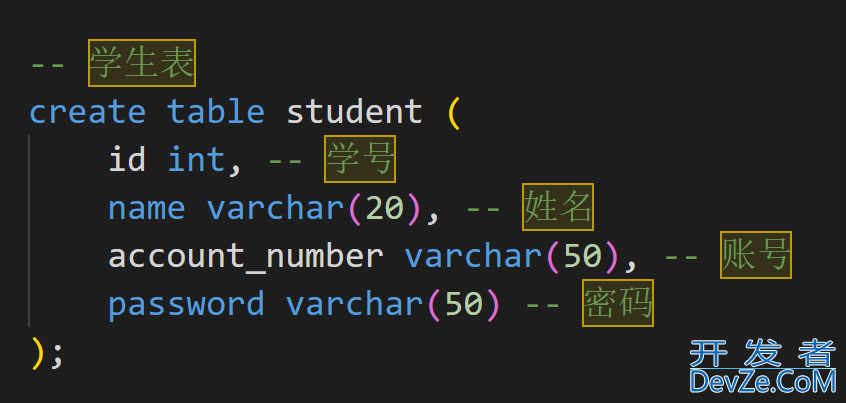
方案二
分别有学生表和用户表两张表相互关联, 学生表中添加一列来与用户表关联或者用户表中添加一列来与学生表关联
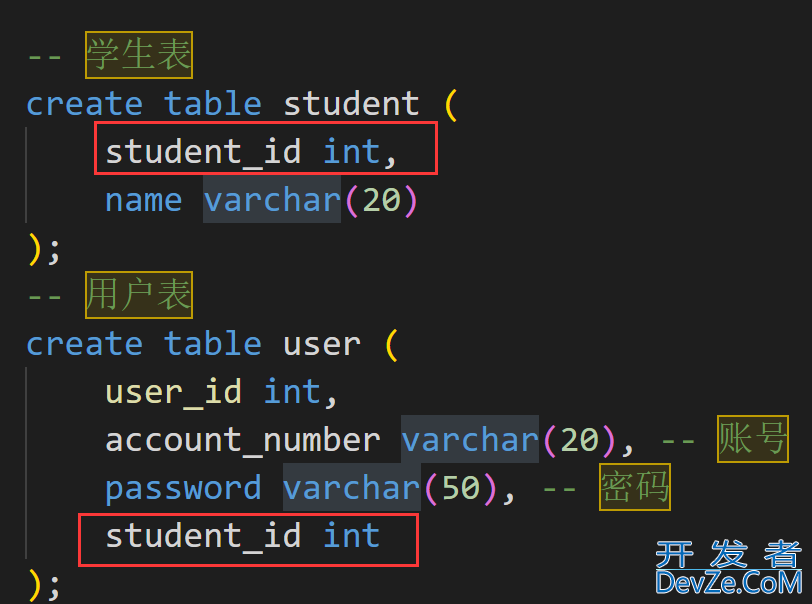
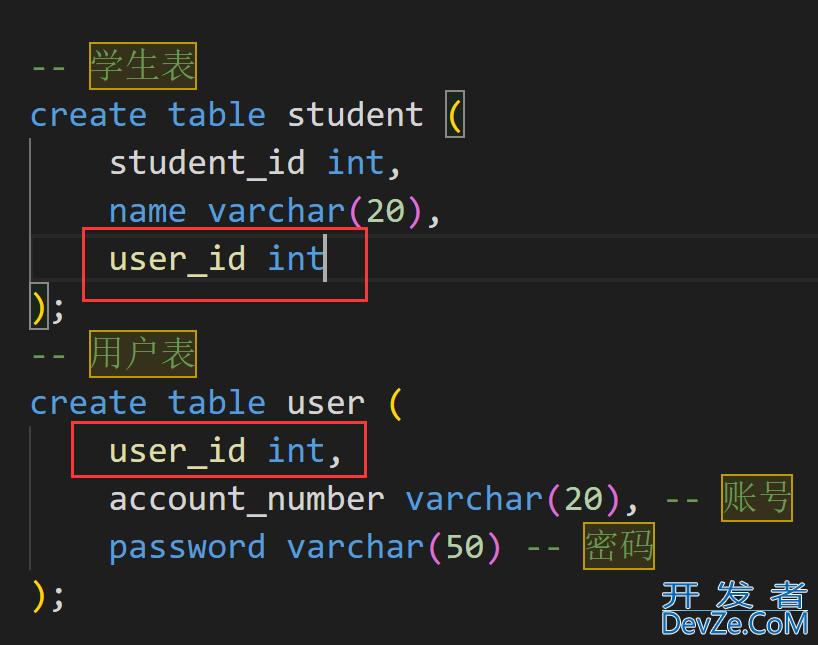
2. 一对多关系
例如学生与班级之间的关系就是一对多的关系, 一个学生只能在一个班级中, 而一个班级可以有多名学生.
用如下方式在数据库中表示一对多的关系.
方案一
在班级表中添加一列, 用来存放一个班里面所有学生的记录, 但这种想法在mysql中是实现不了的, 因为mysql中没有类似于数组的类型.
方案二
在学生表中添加一列, 存放学生所在的班级.
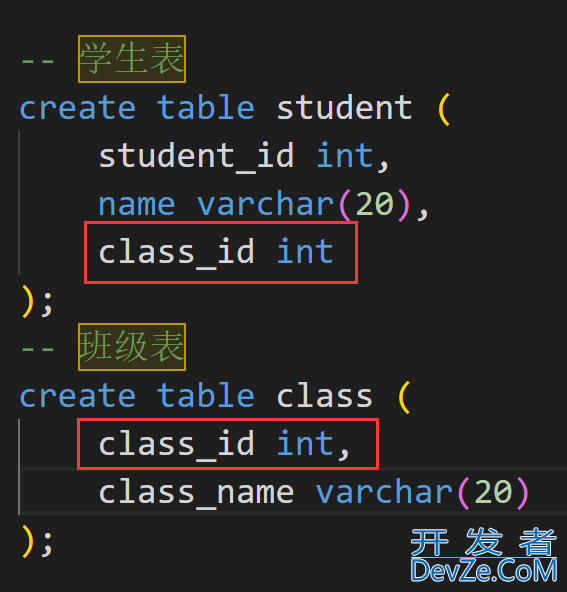
3. 多对多关系
学生与课程之间多对多的关系, 一个学生可以学习多门课程, 一门课程中有多名学生学习.
只有一种方案来表示这种关系, 如下:
建立一个关联表, 来关联学生表和课程表, 这个关联表中至少有两列, 一列用来存放学生学号与学生表关联, 另一列存放课程号与课程表关联, 这样两表就可以通过这个关联表来实现多对多的关系.
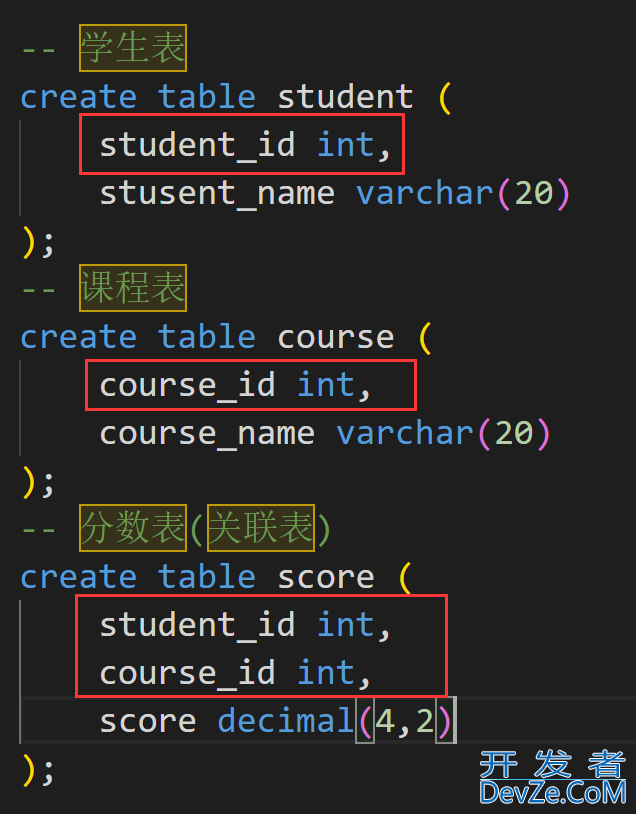
补充: 建表时可以使用合适的约束使得数据间关系的描述更准确.
三. 表的复杂查询操作
1. 将一个表中的数据插入到另一个表中
将表a中的数据插入到表b, 实质上是先查询a表中的数据生成临时表, 再将临时表中的数据插入表中, 要注意的是查询出来的记录(临时表)的列需要和表b相对应才能插入成功.
语法:
insert into b select select 与表b列相对应的列 from a;
示例:
下面有a,b,c三个表, 其中a,b两表的列是对应的, c和a的不对应, 将a表中的数据插入到b表和c表中.
mysql> create table a (id int, name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> insert into a values
-> (1,'喜羊羊'), (2, '美羊羊'), (3, '懒洋洋');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from a;
+------+-----------+
| id | name |
+------+-----------+
| 1 | 喜羊羊 |
| 2 | 美羊羊 |
| 3 | 懒洋洋 |
+------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table b (id int, name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
-- a表和b表的列相对应,不需要调整
mysql> insert into b select * from a;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from b;
+------+-----------+
| id | name |
+------+-----------+
| 1 | 喜羊羊 |
| 2 | 美羊羊 |
| 3 | 懒洋洋 |
+------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table c (name varchar(20), id int);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
-- a和c的列不对应,需要调整
mysql> insert into c select name, id from a;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from c;
+-----------+------+
| name | id |
+-----------+------+
| 喜羊羊 | 1 |
| 美羊羊 | 2 |
| 懒洋洋 | 3 |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2. 聚合查询
2.1 聚合函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| count(列名或表达式) | 返回查询到的数据的个数 |
| sum(列名或表达式) | 返回查询到的数据的和 |
| avg(列名或表达式) | 返回查询到的数据的平均值 |
| max(列名或表达式) | 返回查询到的数据的最大值 |
| min(列名或表达式) | 返回查询到的数据的最小值 |
注意: 代码中的函数名和( )之间不能有空格.
上面的聚合函数在使用时可以在列名或表达式前加上关键字distinct先让查询到的数据去重, 然后再进行计算.
这些聚合函数是针对一个或多个列的行来进行运算的, 其中sum,avg,max,min这几个聚合函数只能针对数值类型进行计算, 不能是字符串和日期类型.
下面给出这些聚合函数的一些使用示例, 首先创建表并插入数据, 如下:
-- 创建考试成绩表
mysql> create table exam_result (
-> id int,
-> name varchar(20), -- 姓名
-> chinese decimal(4, 1), -- 语文成绩
-> math decimal(4, 1), -- 数学成绩
-> english decimal(4, 1) -- 英语成绩
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 插入数据
mysql> insert into exam_result values
-> (1, '喜羊羊', 67, 98, 56),
-> (2, '懒羊羊', 87.5, 78, 77),
-> (3, '美羊羊', 88, 98.5, 90),
-> (4, '沸羊羊', 82, 84, 67),
-> (5, '暖羊羊', 55.5, 85, 45),
-> (6, '黑大帅', 70, 73, 78.5),
-> (7, '潇洒哥', null, 75, 65),
-> (8, null, null, 75, 65);
Query OK, 8 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 8 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 插入结果
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+------+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+------+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 喜羊羊 | 67.0 | 98.0 | 56.0 |
| 2 | 懒羊羊 | 87.5 | 78.0 | 77.0 |
| 3 | 美羊羊 | 88.0 | 98.5 | 90.0 |
| 4 | 沸羊羊 | 82.0 | 84.0 | 67.0 |
| 5 | 暖羊羊 | 55.5 | 85.0 | 45.0 |
| 6 | 黑大帅 | 70.0 | 73.0 | 78.5 |
| 7 | 潇洒哥 | NULL | 75.0 | 65.0 |
| 8 | NULL | NULL | 75.0 | 65.0 |
+------+-----------+---------+------+---------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
count函数
使用count函数可以计算数据表中有多少行, 统计全表行数可以直接使用*来匹配所有的行或者使用一个常量表达式.
-- 表中有8行数据 mysql> select count(*) from exam_result; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 8 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -- 函数参数给一个常量表达式也行 mysql> select count(1) from exam_result; +----------+ | count(1) | +----------+ | 8 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -- 也可以起一个别名 mysql> select count(*) as 全表行数 from exam_result; +--------------+ | 全表行数 | +--------------+ | 8 | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
还有一个需要注意的点, 聚合函数在计算时不会将null计入在内, 比如统计班级中的有多个有效的语文成绩.
-- chinese 为 NULL 的数据不会计入结果 mysql> select count(chinese) from exam_result; +----------------+ | count(chinese) | +----------------+ | 6 | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
sum函数
-- 统计所有同学语文成绩的总和 mysql> select sum(chinese) from exam_result; +--------------+ | sum(chinese) | +--------------+ | 450.0 | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -- 统计英语成绩不及格同学(<60)成绩的总和 mysql> select sum(english) from exam_result where english < 60; +--------------+ | sum(english) | +--------------+ | 101.0 | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -- 如果没有匹配的记录, 返回null mysql> select sum(english) from exam_result where english < 10; +--------------+ | sum(english) | +--------------+ | NULL | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
avg函数
-- 统计所有同学总分的平均分 mysql> select avg(chinese + math + english) as 平均总分 from exam_result; +--------------+ | 平均总分 | +--------------+ | 230.00000 | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
max函数
-- 统计英语最高分 mysql> select max(english) from exam_result; +--------------+ | max(english) | +--------------+ | 90.0 | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
min函数
-- 统计 > 70 分以上的数学最低分 mysql> select min(math) from exam_result where math > 70; +-----------+ | min(math) | +-----------+ | 73.0 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
最后要注意聚合函数是不能嵌套使用的.
mysql> select count(count(math)) from exam_result; ERROR 1111 (HY000): Invalid use of group function
2.2 分组查询
sql中分组操作通过group by关键字实现, 一般AEKBO和聚合函数结合使用, 通过指定分组条件实现分组查询.
语法:
select 列, ... from 表名 (条件筛选) group by 分组条件,即列名;
其中, 上面的条件筛选可以使用where, order by, limit等来实现, 条件筛选不是必写项.
示例:
创建一个不同职位的薪水表
-- 创建员工表
mysql> create table emp (
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> role varchar(20) not null,
-> salary decimal(20, 2)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
-- 添加记录
mysql> insert into emp values
-> (null, "马云", "老板", 100000000),
-> (null, "马化腾", "老板", 120000000),
-> (null, "张三", "开发", 10000),
-> (null, "李四", "开发", 11000),
-> (null, "王五", "开发", 11000),
-> (null, "赵六", "测试", 8000),
-> (null, "孙李", "测试", 9000);
Query OK, 7 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 7 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看表中数据
mysql> select * from emp;
+----+-----------+--------+--------------+
| id | name | role | salary |
+----+-----------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | 马云 | 老板 | 100000000.00 |
| 2 | 马化腾 | 老板 | 120000000.00 |
| 3 | 张三 | 开发 | 10000.00 |
| 4 | 李四 | 开发 | 11000.00 |
| 5 | 王五 | 开发 | 11000.00 |
| 6 | 赵六 | 测试 | 8000.00 |
| 7 | 孙李 | 测试 | 9000.00 |
+----+-----------+--------+--------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询每种岗位员工薪水的平均值, 最高值, 最低值.
mysql> select role, avg(salary), max(salary), min(salary) from emp group by role;
+--------+------------------+--------------+--------------+
| role | avg(salary) | max(salary) | min(salary) |
+--------+------------------+--------------+--------------+
| 开发 | 10666.666667 | 11000.00 | 10000.00 |
| 测试 | 8500.000000 | 9000.00 | 8000.00 |
| 老板 | 110000000.000000 | 120000000.00 | 100000000.00 |
+--------+------------------+--------------+--------------+
3 rows in set (0.03 sec)
-- 也可以起一个别名~~
mysql> select role, avg(salary) as 平均薪水,
-> max(salary) as 最高薪水, min(salary) as 最低薪水 from emp group by role;
+--------+------------------+--------------+--------------+
| role | 平均薪水 | 最高薪水 | 最低薪水 |
+--------+------------------+--------------+--------------+
| 开发 | 10666.666667 | 11000.00 | 10000.00 |
| 测试 | 8500.000000 | 9000.00 | 8000.00 |
| 老板 | 110000000.000000 | 120000000.00 | 100000000.00 |
+--------+------------------+--------------+--------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.3 having
在上面分组查询的基础上, 分组查询也可以添加指定条件, 这里的条件分有下面两种情况:
- 分组之前指定条件, 也就是先筛选再分组, 使用
where关键字. - 分组之后指定条件, 也就是先分组再筛选, 使用
group by关键字.
上面的两种指定条件的查询方式可以同时都使用, 也可以只使用其中一种.
语法:
关于where和group by语法上有一点要注意区分, where语句紧跟在表名后, 而having跟在group by后.
-- having语法 select 聚合函数(或者列), ... from 表名 group by 列 having 条件; -- where语法 select 聚合函数(或者列), ... from 表名 where 条件 group by 列;
示例:
老板的共资太高, 不能代表大众的平均薪资, 查询结果不显示老板的平均薪资.
-- 使用where示例 mysql> select role, avg(salary) as 平均薪水 from emp where role != '老板' group by role; +--------+--------------+ | role | 平均薪水 | +--------+--------------+ | 开发 | 10666.666667 | | 测试 | 8500.000000 | +--------+--------------+ 2 rows in set (0.02 sec) -- 使用having示例 mysql> select role, avg(salary) as 平均薪水 from emp group by role having role != '老板'; +--------+--------------+ | role | 平均薪水 | +--------+--------------+ | 开发 | 10666.666667 | | 测试 | 8500.000000 | +--------+--------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3. 多表查询(联合查询)
3.1 笛卡尔积
笛卡尔乘积是指在数学中, 两个集合X和Y的笛卡尓积(Cartesian product), 又称直积, 表示为X×Y, 第一个对象是X的成员而第二个对象是Y的所有可能有序对的其中一个成员.
假设集合A={a, b}, 集合B={0, 1, 2}, 则两个集合的笛卡尔积为
{(a, 0), (a, 1), (a, 2), (b, 0), (b, 1), (b, 2)}.
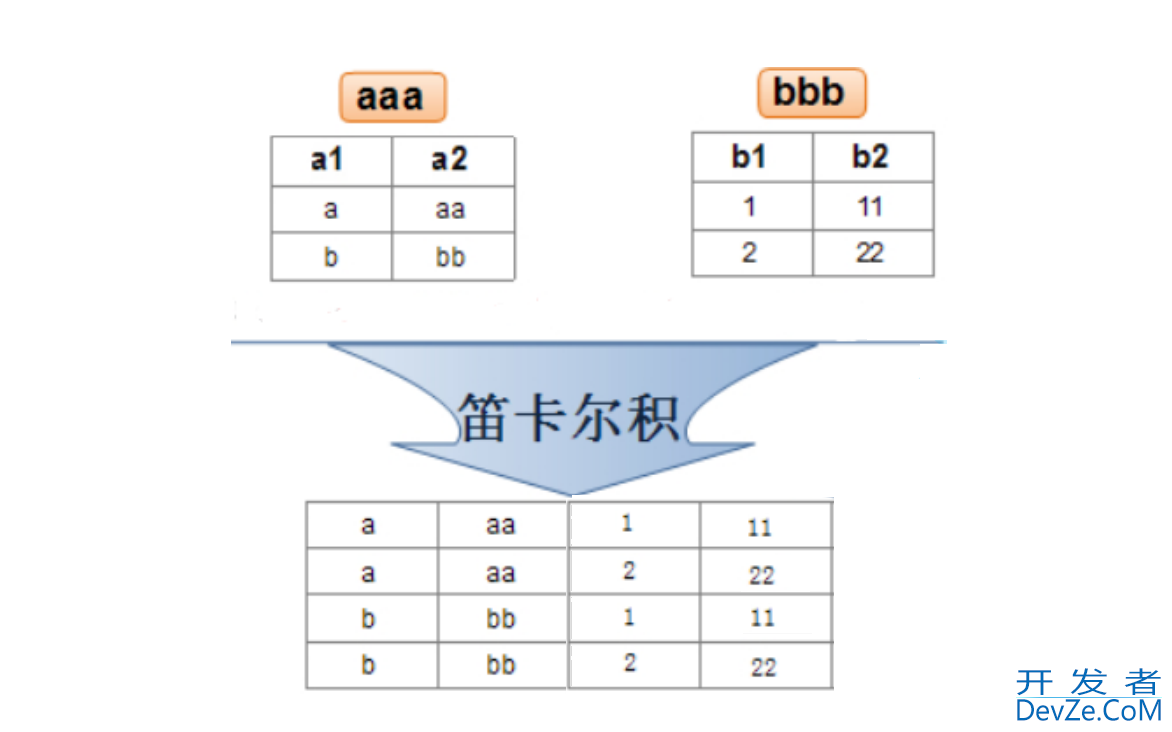
联合查询也叫多表查询, 是基于笛卡尔积来实现的, 多表查询先基于笛卡尔积将多个表合并, 然后对合并后的表去筛选有效的记录.
将多个表进行笛卡尔积的语法:
select 列, ... from 表名1, 表名2, ...;
示例:
将下面的student和class两个表进行笛卡尔积.
-- class表,有两条记录代表2个班级
mysql> create table class (class_id int, name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into class values (1, '软件1班'), (2, '软件2班');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from class;
+----------+------------+
| class_id | name |
+----------+------------+
| 1 | 软件1班 |
| 2 | 软件2班 |
+----------+------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- student表,有四条记录代表4个班级
mysql> create table student(id int, name varchar(20), class_id int);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into student values
-> (1, '张三', 1), (2, '李四', 1), (3, '王五', 2), (4, '赵六', 2);
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from student;
+------+--------+----------+
| id | name | class_id |
+------+--------+----------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 |
| 2 | 李四 | 1 |
| 3 | 王五 | 2 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 2 |
+------+--------+----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 两个表进行笛卡尔积,得到 4*2=8 条记录
mysql> select * from student, class;
+------+--------+----------+----------+------------+
| id | name | class_id | class_id | name |
+------+--------+----------+----------+------------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 软件1班 |
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 2 | 软件2班 |
| 2 | 李四 | 1 | 1 | 软件1班 |
| 2 | 李四 | 1 | 2 | 软件2班 |
| 3 | 王五 | 2 | 1 | 软件1班 |
| 3 | 王五 | 2 | 2 | 软件2班 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 2 | 1 | 软件1班 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 2 | 2 | 软件2班 |
+------+--------+----------+----------+------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
对n条记录的表A和m条记录的表B进行笛卡尔积,一共会产生n*m条记录, 当两张表的数据量很大的时候, 这个操作就非常危险了, 所以多表查询在实际工作中要慎重使用.
上面得到两表的笛卡尔积的结果后, 观察表中数据, 只有两表的class_id相等的记录才是有效数据, 所以我们还需要再通过一些限制条件来筛选出有效的数据.
上面这两张表中存在同名情况, 可以使用表名.列名的形式来访问区分对应表中的列.
-- 筛选出有效数据
mysql> select id, student.name,student.class_id, class.name
-> from student, class where student.class_id = class.class_id;
+------+--------+----------+------------+
| id | name | class_id | name |
+------+--------+----------+------------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 软件1班 |
| 2 | 李四 | 1 | 软件1班 |
| 3 | 王五 | 2 | 软件2班 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 2 | 软件2班 |
+------+--------+----------+------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
下面再创建几个表来演示之后的内容
drop table if exists classes;
drop table if exists student;
drop table if exists course;
drop table if exists score;
create table classes (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), `desc` varchar(100));
create table student (id int primary key auto_increment, sn varchar(20), name varchar(20), qq_mail varchar(20) ,
classes_id int);
create table course(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
create table score(score decimal(3, 1), student_id int, course_id int);
insert into classes(name, `desc`) values
('计算机系2019级1班', '学习了计算机原理、C和Java语言、数据结构和算法'),
('中文系2019级3班','学习了中国传统文学'),
('自动化2019级5班','学习了机械自动化');
insert into student(sn, name, qq_mail, classes_id) values
('09982','黑旋风李逵','xuanfeng@qq.com',1),
('00835','菩提老祖',null,1),
('00391','白素贞',null,1),
('00031','许仙','xuxian@qq.com',1),
('00054','不想毕业',null,1),
('51234','好好说话','say@qq.com',2),
('83223','tellme',null,2),
('09527','老外学中文','foreigner@qq.com',2);
insert into course(name) values
('Java'),('中国传统文化'),('计算机原理'),('语文'),('高阶数学'),('英文');
insert into score(score, student_id, course_id) values
-- 黑旋风李逵
(70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(33, 1, 5),(98, 1, 6),
-- 菩提老祖
(60, 2, 1),(59.5, 2, 5),
-- 白素贞
(33, 3, 1),(68, 3, 3),(99, 3, 5),
-- 许仙
(67, 4, 1),(23, 4, 3),(56, 4, 5),(72, 4, 6),
-- 不想毕业
(81, 5, 1),(37, 5, 5),
-- 好好说话
(56, 6, 2),(43, 6, 4),(79, 6, 6),
-- tellme
(80, 7, 2),(92, 7, 6),
一共有四张表, classes为班级表, student为学生表, course表为课程表, score为成绩表, 其中学生与班级的关系是一对多,学生与课程之间的关系是多对多.
drop table if exists classes;
drop table if exists student;
drop table if exists course;
drop table if exists score;
create table classes (
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
`desc` varchar(100)
);
create table student (
id int primary key auto_increment,
sn varchar(20), name varchar(20),
qq_mail varchar(20),
classes_id int
);
create table course (
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
create table score (
score decimal(3, 1),
student_id int,
course_id int
);
insert into classes(name, `desc`) values
('计算机系2019级1班', '学习了计算机原理、C和Java语言、数据结构和算法'),
('中文系2019级3班','学习了中国传统文学'),
('自动化2019级5班','学习了机械自动化');
insert into student(sn, name, qq_mail, classes_id) values
('09982','黑旋风李逵','xuanfeng@qq.com',1),
('00835','菩提老祖',null,1),
('00391','白素贞',null,1),
('00031','许仙','xuxian@qq.com',1),
('00054','不想毕业',null,1),
('51234','好好说话','say@qq.com',2),
('83223','tellme',null,2),
('09527','老外学中文','foreigner@qq.com',2);
insert into course(name) values
('Java'),('中国传统文化'),('计算机原理'),
('语文'),('高阶数学'),('英文');
insert into score(score, student_id, course_id) values
-- 黑旋风李逵
(70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(33, 1, 5),(98, 1, 6),
-- 菩提老祖
(60, 2, 1),(59.5, 2, 5),
-- 白素贞
(33, 3, 1),(68, 3, 3),(99, 3, 5),
-- 许仙
(67, 4, 1),(23, 4, 3),(56, 4, 5),(72, 4, 6),
-- 不想毕业
(81, 5, 1),(37, 5, 5),
-- 好好说话
(56, 6, 2),(43, 6, 4),(79, 6, 6),
-- tellme
(80, 7, 2),(92, 7, 6);
mysql> select * from classes;
+----+-------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | name | desc |
+----+-------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 计算机系2019级1班 | 学习了计算机原理、C和Java语言、数据结构和算法 |
| 2 | 中文系2019级3班 | 学习了中国传统文学 |
| 3 | 自动化2019级5班 | 学习了机械自动化 |
+----+-------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-------+-----------------+------------------+------------+
| id | sn | name | qq_mail | classes_id |
+----+-------+-----------------+------------------+------------+
| 1 | 09982 | 黑旋风李逵 | xuanfeng@qq.com | 1 |
| 2 | 00835 | 菩提老祖 | NULL | 1 |
| 3 | 00391 | 白素贞 | NULL | 1 |
| 4 | 00031 | 许仙 | xuxian@qq.com | 1 |
| 5 | 00054 | 不想毕业 | NULL | 1 |
| 6 | 51234 | 好好说话 | say@qq.com | 2 |
| 7 | 83223 | tellme | NULL | 2 |
| 8 | 09527 | 老外学中文 | foreigner@qq.com | 2 |
+----+-------+-----------------+------------------+------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from course;
+----+--------------------+
| id | name |
+----+--------------------+
| 1 | Java |
| 2 | 中国传统文化 |
| 3 | 计算机原理 |
| 4 | 语文 |
| 5 | 高阶数学 |
| 6 | 英文 |
+----+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from score;
+-------+------------+-----------+
| score | student_id | course_id |
+-------+------------+-----------+
| 70.5 | 1 | 1 |
| 98.5 | 1 | 3 |
| 33.0 | 1 | 5 |
| 98.0 | 1 | 6 |
| 60.0 | 2 | 1 |
| 59.5 | 2 | 5 |
| 33.0 | 3 | 1 |
| 68.0 | 3 | 3 |
| 99.0 | 3 | 5 |
| 67.0 | 4 | 1 |
| 23.0 | 4 | 3 |
| 56.0 | 4 | 5 |
| 72.0 | 4 | 6 |
| 81.0 | 5 | 1 |
| 37.0 | 5 | 5 |
| 56.0 | 6 | 2 |
| 43.0 | 6 | 4 |
| 79.0 | 6 | 6 |
| 80.0 | 7 | 2 |
| 92.0 | 7 | 6 |
+-------+------------+-----------+
20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
下面的内容就是根据这几张表来示范多表查询的, 多表查询进行笛卡尔积再筛选出有效数据其实是在将多个表进行连接的的过程.
常用的连接方式有: 内连接和外连接(外连接分为左外连接和右外连接), 如果多表之间的记录数据均有对应, 内外连接的查询结果是没有区别的; 而如果多表之间的记录数据有存在不对应的情况, 那么内外连接就有一定的区别了, 内链接只会查询显示多表对应的记录, 左外连接会把左表的记录都显示出来, 右表中不对应的地方用null填充, 而右外连接就会把右表的记录都显示出来, 左表中不对应的地方用null填充.
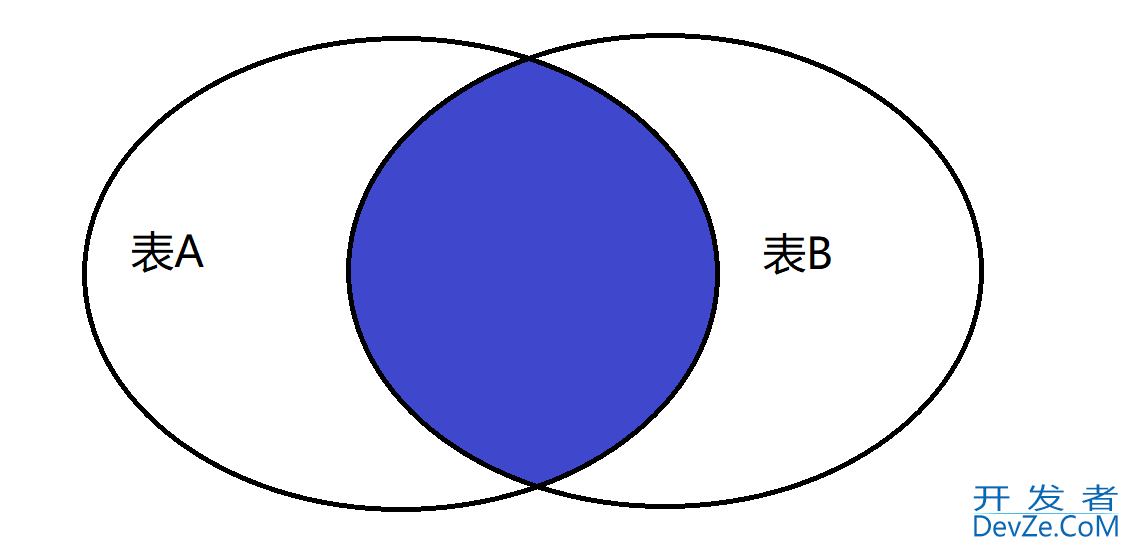
3.2 内连接
语法:
其中inner可以省略
select 字段 from 表1, 表2, ... where 条件; select 字段 from 表1 inner join 表2 on 条件 join 表3 on 条件...;
类连接查询类似于交集, 如下图:
示例:
查询许仙同学的成绩.
这里来逐步分析出正确的sql语句.
1.首先成绩的获取是从分数表中获取, 还需要获取许仙的个人信息, 所以需要对学生表和分数表进行笛卡尔积.
select * from student, score;
2.然后加入连接条件筛选出有效的数据;.
select * from student, score where student.id = score.student_id; select * from student, score where student.id = score.student_id;
3.再根据需求加入必要的限制条件.
select * from student, score where student.id = score.student_id;
4.最后再把不必要的列去掉, 对查询的列进行精简, 只保留要输出的列得到最终结果.
mysql> select student.name, score.score from student, score
-> where student.id = score.student_id and student.name = '许仙';
+--------+-------+
| name | score |
+--------+-------+
| 许仙 | 67.0 |
| 许仙 | 23.0 |
| 许仙 | 56.0 |
| 许仙 | 72.0 |
+--------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
也可以使用join on关键字实现.
select student.name, score,score from student join score on student.id = score.student_id and name = '许仙';
查询所有同学的总成绩及个人信息.
1.需要先将学生表和分数表进行笛卡尔积
select * from student, score;
2.加上连接条件,筛选出有效数据
select * from student, score where student.id = score.student_id;
3.将所有记录以姓名分组, 再使用sum()函数计算总分完成聚合查询.
mysql> select name, sum(score.score) as 总分 from student, score
-> where student.id = score.student_id group by student.name;
+-----------------+--------+
| name | 总分 |
+-----------------+--------+
| tellme | 172.0 |
| 不想毕业 | 118.0 |
| 好好说话 | 178.0 |
| 白素贞 | 200.0 |
| 菩提老祖 | 119.5 |
| 许仙 | 218.0 |
| 黑旋风李逵 | 300.0 |
+-----------------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)
也可以使用join on实现
select name, sum(score.score) as 总分 from student join score on student.id = score.student_id group by student.name;
查看所有同学的各科成绩及个人信息.
1.先对学生表, 课程表, 成绩表进行笛卡尔积.
select * from student, course, score;
2。加入连接条件, 三张表需要两个连接条件.
select * from student, course, score where student.id = score.student_id and course.id = score.course_id;
3.最后根据精简要显示的列完成查询.
mysql> select student.name as 学生姓名, course.name as 课程名称, score.score from student, course, score
-> where student.id = score.student_id and course.id = score.course_id;
+-----------------+--------------------+-------+
| 学生姓名 | 课程名称 | score |
+-----------------+--------------------+-------+
| 黑旋风李逵 | Java | 70.5 |
| 黑旋风李逵 | 计算机原理 | 98.5 |
| 黑旋风李逵 | 高阶数学 | 33.0 |
| 黑旋风李逵 | 英文 | 98.0 |
| 菩提老祖 | Java | 60.0 |
| 菩提老祖 | 高阶数学 | 59.5 |
| 白素贞 | Java | 33.0 |
| 白素贞 | 计算机原理 | 68.0 |
| 白素贞 | 高阶数学 | 99.0 |
| 许仙 | Java | 67.0 |
| 许仙 | 计算机原理 | 23.0 |
| 许仙 | 高阶数学 | 56.0 |
| 许仙 | 英文 | 72.0 |
| 不想毕业 | Java | 81.0 |
| 不想毕业 | 高阶数学 | 37.0 |
| 好好说话 | 中国传统文化 | 56.0 |
| 好好说话 | 语文 | 43.0 |
| 好好说话 | 英文 | 79.0 |
| tellme | 中国传统文化 | 80.0 |
| tellme | 英文 | 92.0 |
+-----------------+--------------------+-------+
20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
也可以使用join on实现
select student.name as 学生姓名, course.name as 课程名称, score.score from student join score on student.id = score.student_id join course on course.id = score.course_id;
3.3 外连接
外连接分为左外连接,右外连接, 左外连接是以左表为主, 右外连接以右表为主.
外连接是通过join on关键字来实现.
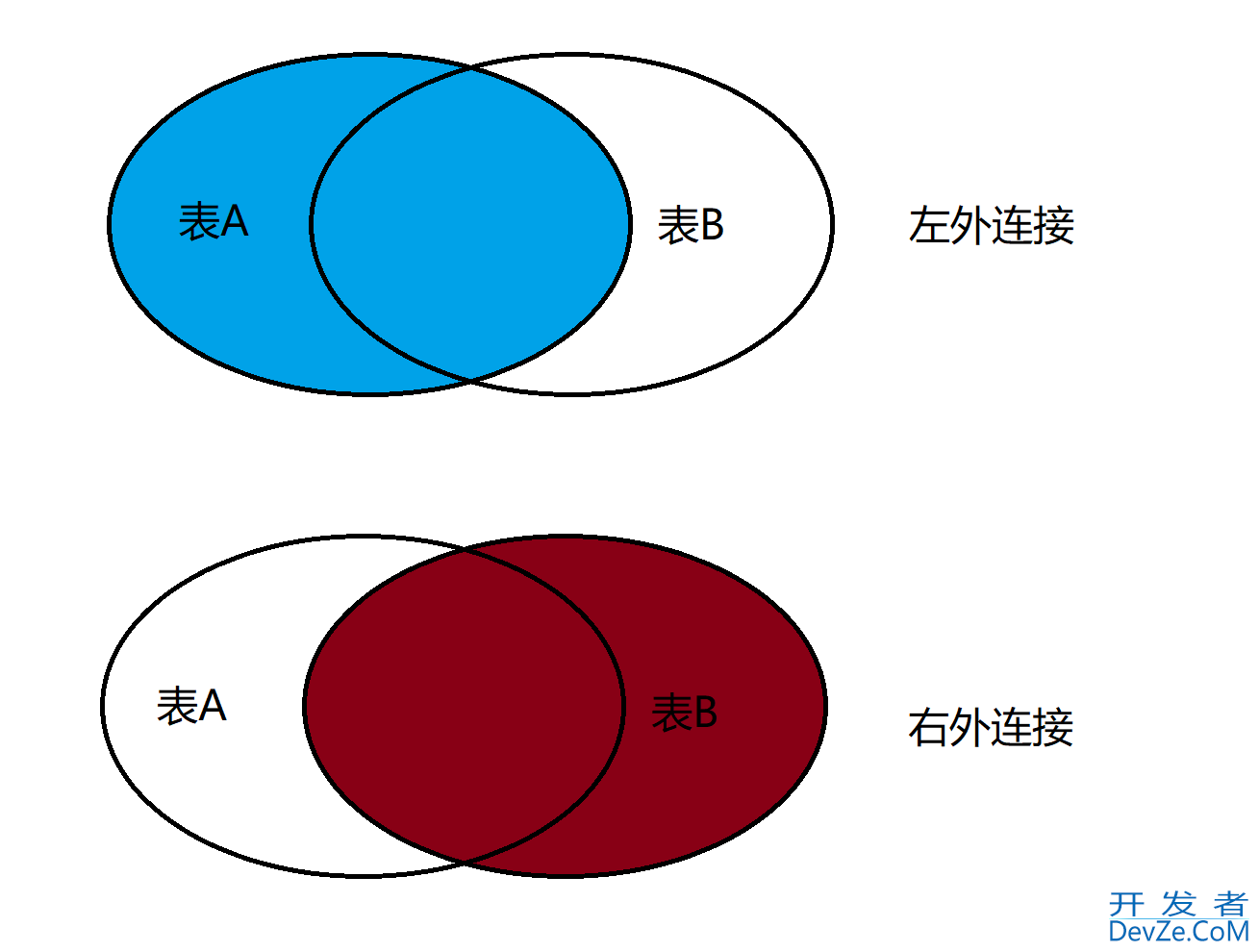
语法:
-- 左外连接 select 字段 from 表A left join 表B on 条件 ...; -- 右外连接 select 字段 from 表A right join 表B on 条件 ...;
示例:
-- 建表A和B mysql> create table A(id int, name varchar(20)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> insert into A values (1, "张三"), (2, "李四"), (4, "王五"); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> create table B(A_id int, score decimal(4,1)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> insert into B values (1, 66.6), (2, 88.8), (3, 99.9); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from A; +------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | 张三 | | 2 | 李四 | | 4 | 王五 | +------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from B; +------+-------+ | A_id | score | +------+-------+ | 1 | 66.6 | | 2 | 88.8 | | 3 | 99.9 | +------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用左外连接多表查询:
mysql> select * from A left join B on A.id=B.A_id; +------+--------+------+-------+ | id | name | A_id | score | +------+--------+------+-------+ | 1 | 张三 | 1 | 66.6 | | 2 | 李四 | 2 | 88.8 | | 4 | 王五 | NULL | NULL | +------+--------+------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用右外连接多表查询:
mysql> select * from A right join B on A.id=B.A_id; +------+--------+------+-------+ | id | name | A_id | score | +------+--------+------+-------+ | 1 | 张三 | 1 | 66.6 | | 2 | 李四 | 2 | 88.8 | | NULL | NULL | 3 | 99.9 | +------+--------+------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用内连接多表查询:
mysql> select * from A join B on A.id=B.A_id; +------+--------+------+-------+ | id | name | A_id | score | +------+--------+------+-------+ | 1 | 张三 | 1 | 66.6 | | 2 | 李四 | 2 | 88.8 | +------+--------+------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.4 自连接
自连接也是多表查询的一种, 上面介绍的是多张不同的表连接在一起的查询, 而自连接是 是指在同一张表连接自身进行查询, 也就是说自连接是多张相同的表进行笛卡尔积, 自连接的主要使用场景是记录分布在不同的行上不方便进行比较查询, 自连接就可以将不同行的数据转化在同一行的不同列上以方便数据的比较查询.
语法:
select 字段 from 表A, 表A,... where 条件;
示例:
还是使用上面3.1中的表数据, 查询 所有“计算机原理”成绩比“Java”成绩高的成绩信息.
首先查询 询“计算机原理”和“Java”课程的id.
mysql> select id, name from course where name = 'Java' or name = '计算机原理'; +----+-----------------+ | id | name | +----+-----------------+ 开发者_Mysql| 1 | Java | | 3 | 计算机原理 | +----+-----------------+ 2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
将两个相同成绩表进行笛卡尔积, 两张相同的表存在列同名情况, 使用表名.列名来指定是哪一个表的列, 表中有效的记录要满足下面的条件:
- 两表学生id相同.
- 使左边的表保留课程
id为3的数据, 右边的表保留课程id为1的数据, 左边的成绩是计算机原理, 右边的成绩是Java. - 左边的分数要大于右边的分数.
加上这些限制条件就可以完成要求的查询.
mysql> select * from score as s1, score as s2 where
-> s1.student_id=s2.student_id and s1.course_id=3
-> and s2.course_id=1 and s1.score>s2.score;
+-------+------------+-----------+-------+------------+-----------+
| score | student_id | course_id | score | student_id | course_id |
+-------+------------+-----------+-------+------------+-----------+
| 98.5 | 1 | 3 | 70.5 | 1 | 1 |
| 68.0 | 3 | 3 | 33.0 | 3 | 1 |
+-------+------------+-----------+-------+------------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
指定列显示, 只保留满足条件的学生id.
mysql> select s1.student_id from score as s1, score as s2 where
-> s1.student_id=s2.student_id and s1.course_id=3
-> and s2.course_id=1 and s1.score>s2.score;
+------------+
| student_id |
+------------+
| 1 |
| 3 |
+------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.5 子查询
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询, 将多步查询转化为一步查询, 但实际上并不建议使用子查询, 因为不管写什么代码代码, 要么追求的是可读性,可维护性来提高开发效率, 要么是追求程序跑的快来提升运行效率; 而子查询哪个都实现不了, 当嵌套了很多层查询, 这sql代码可能就看不懂了, 容易出错, 而且维护困难.
单行子查询 : 返回一行记录的子查询
查询与“不想毕业” 同学的同班同学
先演示逐步查询的过程.
-- 先查询不想毕业同学的班级id mysql> select classes_id, name from student where name = '不想毕业'; +------------+--------------+ | classes_id | name | +------------+--------------+ | 1 | 不想毕业 | +------------+--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -- 然后查询和不想毕业班级id相同的同学 mysql> select name from student where classes_id = 1 and name != '不想毕业'; +-----------------+ | name | +-----------------+ | 黑旋风李逵 | | 菩提老祖 | | 白素贞 | | 许仙 | +-----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
子查询就是相当于把上面两个过程合并了.
mysql> select name from student where classes_id =
-> (select classes_id from student where name='不想毕业') and name != '不想毕业';
+-----------------+
| name |
+-----------------+
| 黑旋风李逵 |
| 菩提老祖 |
| 白素贞 |
| 许仙 |
+-----------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
多行子查询 : 返回多行记录的子查询.
查询“语文”或“英文”课程的成绩信息
逐步查询过程.
-- 先根据课程名查询出课程id mysql> select id, name from course where name = '语文' or name = '英文'; +----+--------+ | id | name | +----+--------+ | 4 | 语文 | | 6 | 英文 | +----+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) -- 然后根据课程id查询课程成绩 mysql> select * from score where course_id = 4 or course_id = 6; +-------+------------+-----------+ | score | student_id | course_id | +-------+------------+-----------+ | 98.0 | 1 | 6 | | 72.0 | 4 | 6 | | 43.0 | 6 | 4 | | 79.0 | 6 | 6 | | 92.0 | 7 | 6 | +-------+------------+-----------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用子查询, 由于返回的是多条记录, 所以不能再使用等号, 这里使用in操作符.
mysql> select * from score where course_id in
-> (select id from course where name='语文' or name='英文');
+-------+------------+-----------+
| score | student_id | course_id |
+-------+------------+-----------+
| 98.0 | 1 | 6 |
| 72.0 | 4 | 6 |
| 43.0 | 6 | 4 |
| 79.0 | 6 | 6 |
| 92.0 | 7 | 6 |
+-------+------------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.03 sec)
还可以使用[not]exists来实现多行子查询, 这个用到的地方也不多, 就不在这里展开介绍了.
3.6 合并查询
合并查询相当于得到的是两个表中数据的并集, 使用union关键字来来实现.
语法:
-- 去重合并查询 select 字段 from 表1 where 条件 union select 字段 from 表2 where 条件; -- 不去重合并查询 select 字段 from 表1 where 条件 union all select 字段 from 表2 where 条件;
对于上面语法中的all, 带all的不会对结果去重,而不带all的会对结果去重.
示例:
查询id小于3,或者名字为“英文”的课程
mysql> select * from course where id<3 union
-> select * from course where name='英文';
+----+--------------------+
| id | name |
+----+--------------------+
| 1 | Java |
| 2 | 中国传统文化 |
| 6 | 英文 |
+----+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
-- 也可以使用or来实现
mysql> select * from course where id<3 or name='英文';
+----+--------------------+
| id | name |
+----+--------------------+
| 1 | Java |
| 2 | 中国传统文化 |
| 6 | 英文 |
+----+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
查询id小于3,或者名字为“Java”的课程(演示不去重效果)
-- 结果集中出现重复数据Java
mysql> select * from course where id<3
-> union all select * from course where name='Java';
+----+--------------------+
| id | name |
+----+--------------------+
| 1 | Java |
| 2 | 中国传统文化 |
| 1 | Java |
+----+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
这里要注意一下or和union的区别, or只能针对同一张表下得到并集, 而union能够得到不同表的并集; 也就是说合并查询不仅能够查询单表中两个结果的并集, 也能查询多表中两个结果的并集, 而or只能实现单表查询并集.
到此这篇关于MySQL约束和表的复杂查询操作的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql约束和表的复杂查询内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!




 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论